FIGURE
Fig. S1
Fig. S1
|
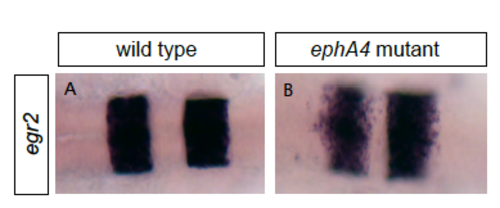
Analysis of ephA4 mutant embryos (A, B): An ephA4 mutant has disrupted sharpening of the r2/r3, r3/r4 and r5/r6 borders. MO-mediated knockdown disrupts ephA4 function since the same phenotype occurs in ephA4 morphant embryos (Cooke et al., 2005; Terriente et al., 2012). |
Expression Data
Expression Detail
Antibody Labeling
Phenotype Data
Phenotype Detail
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 45, Addison, M., Xu, Q., Cayuso, J., Wilkinson, D.G., Cell Identity Switching Regulated by Retinoic Acid Signaling Maintains Homogeneous Segments in the Hindbrain, 606-620.e3, Copyright (2018) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell