Fig. 1
|
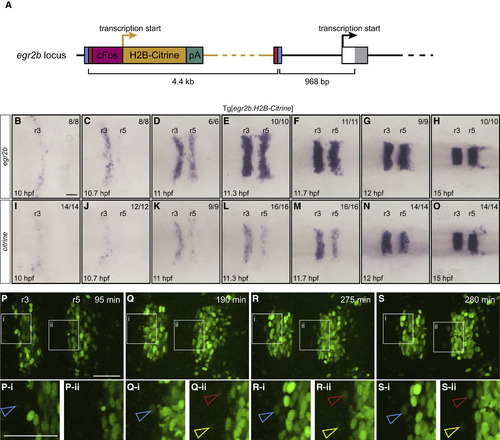
Generation of egr2b Gene Trap Expressing H2B-Citrine (A) CRISPR-mediated insertion of a donor construct with cFos minimal promoter and H2B-Citrine upstream of the transcriptional start site of egr2b to generate the Tg[egr2b:H2B-Citrine] line. (B?O) In situ hybridization to detect egr2b (B?H) and citrine (I?O) transcripts in Tg[egr2b:H2B-Citrine] embryos from 10 to 15 hpf. Embryos are flat-mounted with anterior to the left. (P?S) Selected frames from a time-lapse movie of a Tg[egr2b:H2B-Citrine] embryo acquired from 12 hpf (t = 0 min) for 280 min. A higher resolution image was captured at the final time point (S). Below each panel is a magnified view of the indicated areas (i, ii), with arrowheads pointing at three examples of H2B-Citrine-expressing cells that are ectopic at the final time point. When first detected, these cells are already surrounded by non-expressing cells. Most of the H2B-Citrine-expressing cells seen posterior to r5 are egr2-expressing neural crest cells. Scale bars: 50 ?m. |
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage Range: | 1-4 somites to 14-19 somites |
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 45, Addison, M., Xu, Q., Cayuso, J., Wilkinson, D.G., Cell Identity Switching Regulated by Retinoic Acid Signaling Maintains Homogeneous Segments in the Hindbrain, 606-620.e3, Copyright (2018) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell