Fig. S1
|
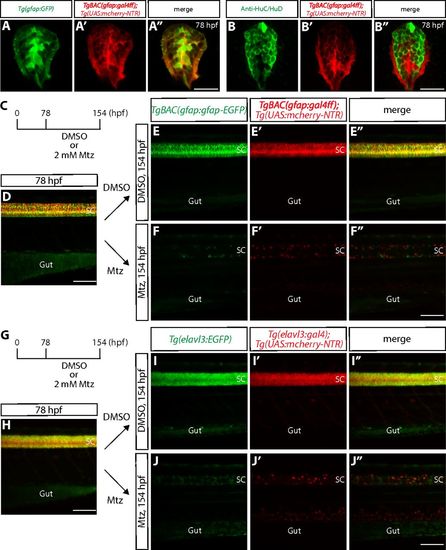
Radial glia and neuronal ablation by the NTR/Mtz-mediated cell ablation method. (A?A?) 78 hpf Tg(gfap:GFP);TgBAC(gfap:gal4ff);Tg(UAS:mcherry-NTR) trunk spinal cord section. GFP+ radial glia and mCherry+ cells are largely colocalized. (B?B?) 78 hpf TgBAC(gfap:gal4ff);Tg(UAS:mcherry-NTR) trunk spinal cord section immunostained for HuC/HuD (green). EGFP+ neurons and mCherry+ cells are mostly distinct. (C) Time course of NTR/Mtz-mediated cell ablation of radial glia for D?F?. (D) 78 hpf TgBAC(gfap:gfap-EGFP);TgBAC(gfap:gal4ff);Tg(UAS:mcherry-NTR) trunk. TgBAC(gfap:Gfap-EGFP) expression and TgBAC(gfap:gal4ff);Tg(UAS:mCherry-NTR) expression are observed in the spinal cord in an overlapping manner. SC, spinal cord. (E?E? and F?F?) 154 hpf TgBAC(gfap:gfap-EGFP);TgBAC(gfap:gal4ff);Tg(UAS:mcherry-NTR) trunk after treatment with DMSO (E?E?) or Mtz (F?F?) starting at 78 hpf. Unlike DMSO-treated fish that show strong coexpression of TgBAC(gfap:Gfap-EGFP) and TgBAC(gfap:gal4ff);Tg(UAS:mCherry-NTR) in their spinal cord, Mtz-treated fish show a dramatic reduction of this coexpression. (G) Time course of NTR/Mtz-mediated cell ablation of neurons for H?J?. (H) 78 hpf Tg(elavl3:EGFP);Tg(elavl3:gal4);Tg(UAS:mcherry-NTR) trunk. Tg(elavl3:EGFP) expression and Tg(elavl3:gal4);Tg(UAS:mCherry-NTR) expression are observed in the spinal cord in an overlapping manner. (I?I? and J?J?) 154 hpf Tg(elavl3:EGFP);Tg(elavl3:gal4);Tg(UAS:mcherry-NTR) trunk after treatment with DMSO (I?I?) or Mtz (J?J?) starting at 78 hpf. Unlike DMSO-treated fish that show strong coexpression of Tg(elavl3:EGFP) and Tg(elavl3:gal4);Tg(UAS:mCherry-NTR) in their spinal cord, Mtz-treated fish show a dramatic reduction of this coexpression. (Scale bars, 100 Ám in D, F?, H, and J? and 20 Ám in A? and B?.) |