Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-171227-52
- Publication
- Vroman et al., 2014 - Extracellular ATP hydrolysis inhibits synaptic transmission by increasing ph buffering in the synaptic cleft
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
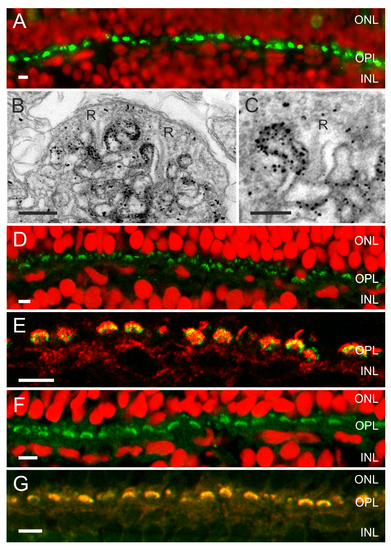
An ATP release mechanism and the enzymes needed to hydrolyze ATP and degrade adenosine are present in the synaptic complex of cones. (A) Fluorescent images of zebrafish retina showing Panx1-IR (green) and a nuclear stain (red) (from Prochnow et al. [11]). Panx1-IR is present in characteristic horseshoe-shaped structures indicative for processes invaginating the cone synaptic terminal. (B) Electronmicrograph of a cone synaptic terminal in zebrafish retina. Immunolabeling is restricted to HC dendrites flanking the synaptic ribbons (R). (C) Higher magnification of a HC dendrite lateral of the synaptic ribbon (R). Note that one HC dendrite is devoid of Panx1 labeling. (D) NTPDase1-IR (green) and a nuclear stain (red). NTPDase1-IR is also present in horseshoe-shaped structures characteristic for localization in HC dendrites. (E) Double labeling of NTPDase1 antibody with an antibody against GluR2 (green), a marker for HC dendrites [63],[64], indicated that NTPDase-1 (red) was specifically expressed on HC dendrites. (F) ADA-IR (green) was present in horseshoe-shaped structures. (G) ADA-IR colocalized with the GluR2-IR (green), indicating that ADA (red) is expressed on HC dendrites. Expression of ecto-ATPases in the photoreceptor synaptic terminal has been observed previously in rat [39], mouse, and zebrafish [61]. Scale bars in panels A, D, E, F, and G indicate 5 Ám. Scale bar in panels B and C indicate 500 nm and 250 nm, respectively. |
| Antibodies: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage: | Adult |