Fig. S1
|
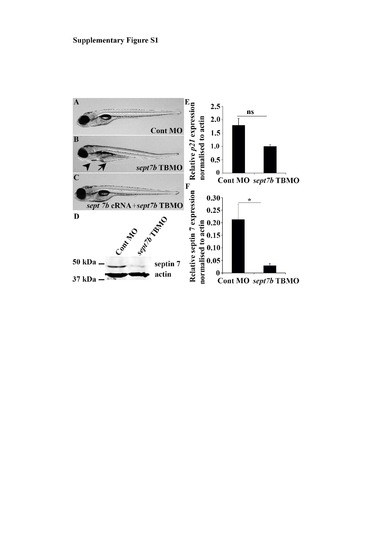
sept7b TBMO specifically knocks down sept7b in zebrafish larvae. (A-C) Images of zebrafish larvae injected with control MO (A), sept7b TBMO (B) and sept7b TBMO together with sept7b cRNA (C) at 5 dpf. Knockdown of sept7b leads to pericardial (arrowhead) and yolk sac (arrow) edema, and co-injection of sept7b cRNA with sept7b TBMO rescues the phenotype. (D) The expression of septin 7 protein is reduced in sept7b TBMO-injected zebrafish larvae compared to control MO-injected larvae at 5 dpf. Larvae were lysed in RIPA buffer as previously described1 and proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE. Western blotting was performed with a rabbit polyclonal antibody against septin 7 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA) and a mouse monoclonal antibody against actin (Sigma-Aldrich, St Louis, MO) followed by Alexa-Fluor-680-conjugated donkey anti-rabbit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) and IR-Dye-800-conjugated donkey anti-mouse IgGs (LI-COR, Lincoln, NE). (E) qPCR reveals that the expression of p21 mRNA shows a trend of downregulation in sept7b TBMO-injected larvae compared to control MO-injected larvae at 5 dpf. (F) Quantification of four replicate blots similar to the blot in (A) reveals significant downregulation of septin 7 protein in sept7b TBMO-injected larvae compared to control MO-injected larvae. Error bars represent mean ± SEM. ns, non-significant; * p? 0.05. |