Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-170523-34
- Publication
- Thomas-Jinu et al., 2017 - Non-nuclear Pool of Splicing Factor SFPQ Regulates Axonal Transcripts Required for Normal Motor Development
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
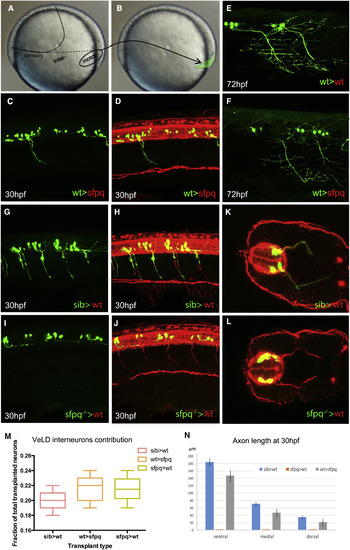
Sfpq Is Required Cell Autonomously for Motor Axon Development Homotopic transplantation at 70%?80% epiboly of sfpq?/?; Tg(mnx1:GFP) and sibling Tg(mnx1:GFP) ventral spinal cord progenitors into wild-type or sfpq?/? hosts. (A and B) Schematic of the transplants from donor (A) to host (B) embryo. (C, D, and G?L) Lateral view, anterior to the left (C, D, and G?J) or transverse (K and L) of 30 hpf zebrafish transplanted trunks, showing the transplanted mnx1+ neurons in green and all axons in red (acetylated tubulin staining). (E and F) Lateral view, anterior left of transplanted wild-type MNs (green) in early larvae (3 dpf) in wild-type (E) or sfpq?/? (F) hosts. (M) Quantification of VeLD interneurons in transplanted clones at 30 hpf (value is number of interneurons/total number of transplanted neurons, number of embryos in box). (N) Quantification of axonal lengths of transplanted neurons at 30 hpf. Scale bar, 100 ?m. |