Fig. S1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-170208-6
- Publication
- Dona et al., 2015 - NINL and DZANK1 Co-function in Vesicle Transport and Are Essential for Photoreceptor Development in Zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
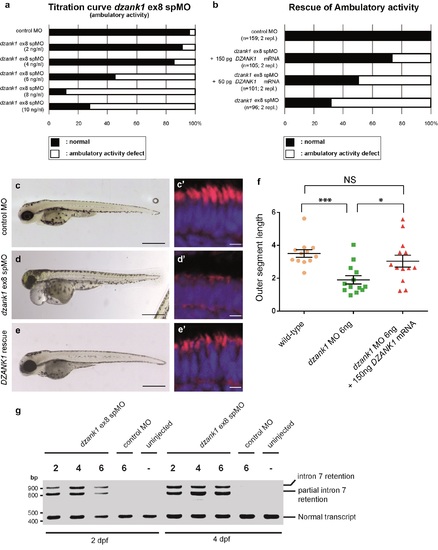
Specificity of the dzank1 ex8 spMO. Titration curve of the dzank1 ex8 spMO scored on ambulatory activity shows an increased incidence of the phenotype with an increasing dose (a). (b) Co-injection of 6 ng dzank1 ex8 spMO with 150 pg capped MO-resistant mRNA encoding human DZANK1 reduced the incidence of phenotypes including ambulatory activity, small eyes (c, d, e) (n>95/group, p<0.0001 (two-tailed Fisher's exact test) and restored photoreceptor outer segment lengths (n = 13, P<0.001 (two-tailed, unpaired Student's t-test), c', d', e', f). (f) Quantification of photoreceptor outer segment lengths revealed a significant increase in length in the DZANK1 rescue group (3.0+/-0.4 ?m) as compared to dzank1 morphants (6ng/nl; 1.9+/-0.25 ?m) (P<0.001; two-tailed, unpaired Student's t-test). Bars indicate mean OS length per group and Standard error of the mean (SEM) (g) Characterization of the effect of the dzank1 ex8 spMO at 2 and 4 dpf by RT-PCR analysis. Injection of various amounts of MO resulted in the (partial) retention of intron7, leading to a premature termination of translation. PCR fragments were analyzed by Sanger sequencing. Scale bars represent 500 ?m (c-e) and 15 ?m (c'-e'). |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagent: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Day 4 |