Fig. S1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-160324-19
- Publication
- Chang et al., 2016 - CDX4 and retinoic acid interact to position the hindbrain-spinal cord transition
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
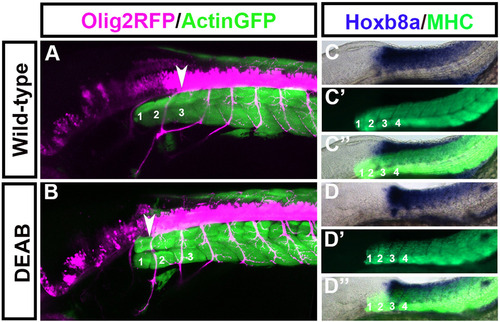
Spinal cord motor neurons shift rostrally while hox gene expression remains unchanged in embryos treated with DEAB between 50% epiboly and tailbud stage. Olig2-Rfp:Actin-Gfp double transgenic embryos were treated with DEAB between 50% Epiboly to tailbud stage. Olig2-Rfp marks spinal cord motor neurons (pink) and Actin-Gfp marks somites (green). In wildtypes the first motor neuron (A arrowhead) projects out at the level of somite 3. In DEAB treated embryos the first spinal cord motorneuron (B arrowhead) arises at the level of somite 1. At 48 hpf the anterior expression limit of hoxb8a is at the level of somite 3 in wild-types (C) and this expression limit remains unchanged in embryos treated with DEAB between 50% epiboly to tailbud stage (D). (C, D) Hoxb8a expression, (C′D′) MHC, (C′′,D′′) merge. (A-D) Embryos at 48 hpf with the anterior located to the left. (A) n=6/6, (B) n=10/10, (C, D) n=15/15. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 410(2), Chang, J., Skromne, I., Ho, R.K., CDX4 and retinoic acid interact to position the hindbrain-spinal cord transition, 178-89, Copyright (2016) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.