Fig. 2
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-150415-4
- Publication
- Ingold et al., 2015 - Proper migration and axon outgrowth of zebrafish cranial motoneuron subpopulations require the cell adhesion molecule MDGA2A
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
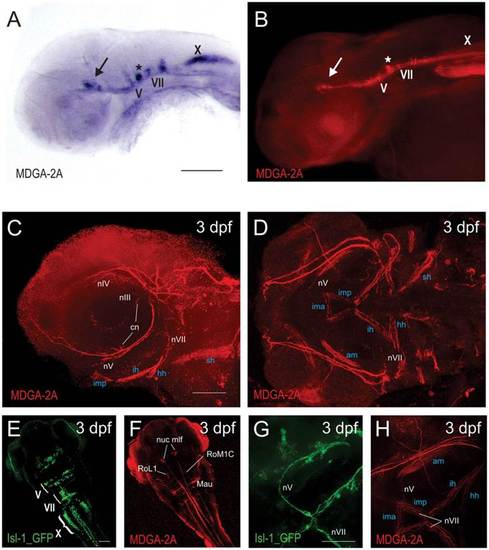
(A,B) Comparison between MDGA2A RNA and protein distribution demonstrates that the MDGA2A antibody highlights identical structures as seen with MDGA2A riboprobes. Neurons and axons of the oculomotor (arrow), the trigeminal (V) and the facial (VII) nerve are clearly MDGA2A positive (A,B). (C,D,F,H) At 3dpf MDGA2A is located on specific nerves. MDGA2A antibodies highlight branches of the ciliary nerve (cn), the oculomotor nerve (nIII), the trochlear cranial nerve (nIV), several branches of the trigeminal nerve (nV) and the facial nerve (nVII) (C,D). MDGA2A positive nV axons run ventrally along the caudal edge of the eye. The distal nV innervates the imp and merges with both the contralateral nV and the distal tip of the seventh nerve (nVII) at the midline (H). Moreover neurons and axons of medial longitudinal fascicle (mlf), the Mauthner neurons (Mau) and neurons of the reticular formation (RoM1C, RoL1) express MDGA2A (F). (E,G) Isl-1 GFP staining in cranial motoneurons. As previously reported Isl-1 GFP transgenic zebrafish display intense cranial motoneurons V, VII and X staining (E). Moreover staining in the trigeminal as well as the facial nerve can easily be seen (G). Abbreviations: am, adductor hyomandibulae; cn, ciliary nerve; hh, hyohyal muscle; ih, interhyal muscle; ima, intermandibularis anterior; imp, intermandibularis posterior; Mau, mauthner neurons; nuc, mlf nucleus of the medial longitudinal fascicle; nV, trigeminal nerve (neurons); nVII, facial nerve (neurons); nX, vagal nerve (neurons); RoL1 and RoM1C, neurons of the reticular formation; sh, sternoid muscle. Scale bars equal 100µm. |