Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-140723-19
- Publication
- DuVal et al., 2014 - Growth differentiation factor 6 as a putative risk factor in neuromuscular degeneration
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
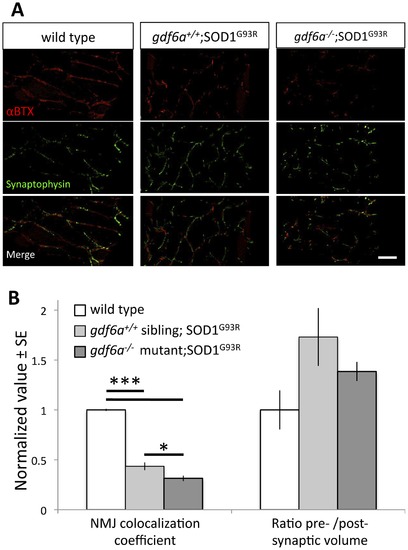
Disruption of gdf6 function exacerbates neuromuscular junction abnormalities in ALS model zebrafish. ALS model zebrafish possess disruptions to neuromuscular junctions (NMJ), and loss of gdf6 function exacerbates this by 7 months of age. A. The presynaptic junctions (labeled with synaptophysin antibody) and postsynaptic junctions (labeled with fluorescently tagged αBTX) in ALS model zebrafish expressing the mutant SOD1G93R show punctate morphology, deviations in presynaptic volume and less overall colocalization compared to WT sibling junctions. Some abnormalities are exacerbated in bigenic siblings expressing the mutant SOD1G93R that are also gdf6-/- (scale bar is 40 Ám). B. Quantification of these NMJs suggests the presynaptic/postsynaptic volume ratios of SOD1G93R and bigenic gdf6-/-;SOD1G93R zebrafish are larger than those of WT siblings at this age, though these differences do not rise to statistical significance (Kruskall-Wallis ANOVA, p = 0.134; n = 6,4,6 for WT, SOD1G93R, and bigenic fish respectively). Colocalization coefficients, that measure overall colocalization of presynaptic and postsynaptic junctions, are altered in these fish. The values for SOD1G93R zebrafish are significantly lower than wild type sibling values, indicating that presynapses and postsynapses overlap less, as characterized previously for this transgenic ALS model [28]. Bigenic SOD1G93R zebrafish that are also gdf6-/- have a dramatically lower coefficient than either sets of siblings, including being 30% lower than ALS model SOD1G93R fish with normal gdf6a (*p<0.05; ***p<0.001. Kruskall-Wallis ANOVA with pairwise comparisons). |
| Antibody: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage: | Adult |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Adult |