Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-140327-1
- Publication
- Kumari et al., 2013 - An essential role for maternal control of Nodal signaling
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
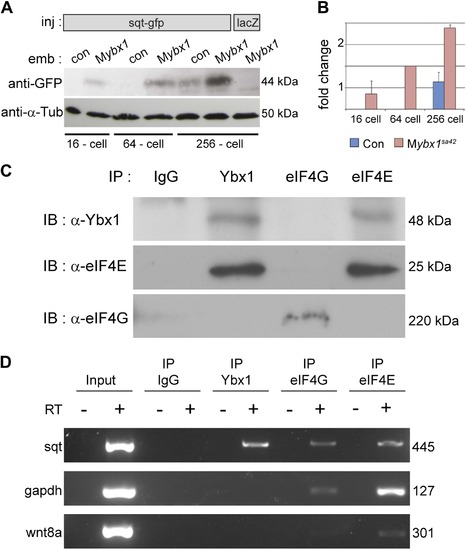
Ybx1 interacts with the translation initiation machinery and represses translation of sqt RNA. (A) Western blot to detect GFP shows injected sqt-gfp is translated by 16-cells in Mybx1, whereas in controls, Sqt-GFP is detected at blastula stages, and lacZ control injection shows no Sqt-GFP. (B) Sqt-GFP protein expression is precocious and elevated in Mybx1 embryos. Error bars in B show standard deviation from three experiments. (C) Co-immunoprecipitation in embryo lysates followed by western blot analysis shows that Ybx1 interacts with eIF4E. eIF4G binds poorly with Ybx1. Faint smear in control IgG lane for eIF4G is spillover from input lane (see Figure 5-figure supplement 1C for complete blot for eIF4G). (D) Antibodies towards Ybx1, eIF4G and eIF4E pull down sqt RNA in embryos lysates. RT-PCR on the embryos lysates in panel C shows sqt RNA but not control gapdh or wnt8a RNA in RNA-IP with αYbx1 antibodies. Control IgG antibodies do not show any RT-PCR product, whereas antibodies to the translation initiation factor eIF4E can pull down sqt RNA, wnt8a and gapdh RNA, and antibodies to eIF4G detects weak bands for sqt and gapdh in the RNA-IPs. RT-PCR from whole embryo lysates is the positive control. PCR product sizes are indicated on the right. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Observed In: | |
| Stage Range: | 16-cell to 256-cell |