Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-140326-15
- Publication
- Kumari et al., 2013 - An essential role for maternal control of Nodal signaling
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
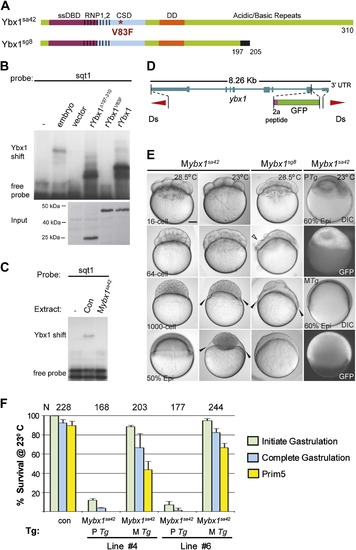
Maternal Ybx1 is essential for early development. (A) Schematic of Ybx1 showing the various domains, the V83F mutation in the CSD in ybx1sa42, and deletion of residues 197-310 in ybx1sg8 mutants. Black box in Ybx1sg8 indicates frameshift after residue 197 and premature stop after residue 205. (B) rYbx1V83F lacks detectable DLE-binding activity similar to vector control, whereas rYbx1 and rYbx1Δ197-310 peptides, and embryo lysates show binding to sqt1 probes. Western blots to detect 6xHis epitope tags show expression of recombinant Ybx1 proteins. (C) Mybx1sa42 embryo extracts show no detectable binding to sqt1 probe compared to control extracts. (D) Schematic representation of the ybx1 genomic locus (blue) with positions of viral 2a peptide (magenta bar) and gfp (green box) indicated. Red triangles indicate Ds transposon terminal repeats. (E) DIC photomicrographs showing 16-cell, 64-cell, 1000-cell and 50% epiboly stage embryos. Mybx1sa42 embryos are viable at 28.5°C. Mybx1sg8 embryos cleave aberrantly after 16-cells (open arrowhead). Mybx1sa42 embryos at 23°C, and Mybx1sg8 embryos fail to initiate gastrulation, form syncytia (black arrowheads), and arrest. Zygotic Ybx1-GFP expression from PTg does not rescue gastrula arrest in Mybx1, whereas maternal Ybx1-GFP expression from MTg leads to normal gastrulation. Scale bar, 100 µm. (F) Histogram showing rescue of gastrulation and survival till prim5 stage of Mybx1 mutants at 23°C by two independent MTg lines (MTg #4 and MTg #6). Some embryos with zygotic expression of ybx1 (PTg) from both lines can initiate gastrulation, but none survive to prim5. Error bars show standard deviation from three experiments. Number of embryos is shown on top of the histogram. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Condition: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage Range: | 1k-cell to Prim-5 |