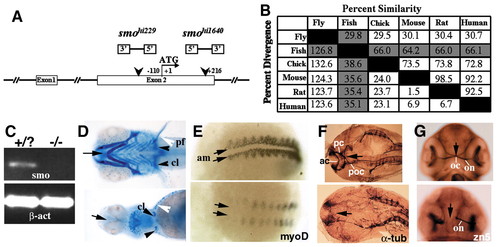
Homozygotes of two insertional mutant alleles in the zebrafish smo gene display phenotypes characteristic of a Hh signaling deficiency. Unless specified otherwise, wild type is above and anterior is on the left in each panel in all figures. (A) A schematic drawing of the two alleles indicating the locations and orientations of the proviral insertions. (B) Sequence pair distances of all known Smo proteins using the Clustal method with PAM250 residue weight table. Zebrafish column and row are highlighted. (C) RT-PCR analysis showing the lack of smo mRNA in the mutants. β-act, β-actin. (D) Ventral view of Alcian Blue-stained wild-type and mutant embryos at 120 hpf showing small head, posterior cyclopia, and absence of cartilaginous jaw and brachial arches (arrow), much reduced cleithria (black arrowhead), and absence of pectoral fins (white arrowhead) in the mutant. pf, pectoral fin; cl, cleithrium. (E) Posterior view of wild-type and mutant embryos at 14 hpf after wholemount in situ hybridization with antisense myoD probes showing the lack of adaxial mesoderm in the mutants (arrows). am, adaxial mesoderm. (F) Flattened dorsal view of head region of acetylated α-tubulin antibody stained wild-type and mutant embryos at 24 hpf, showing the absence of all three commissures in the forebrain and midbrain (arrow). ac, anterior commissure; pc, posterior commissure; poc, post-optic commissure. (G) Ventral view of Zn-5 stained wild-type and mutant embryos at 48 hpf showing failure of optic chiasm formation in the mutant embryo (arrow). Anterior points upwards. oc, optic chiasm; on, optic nerve.
|

