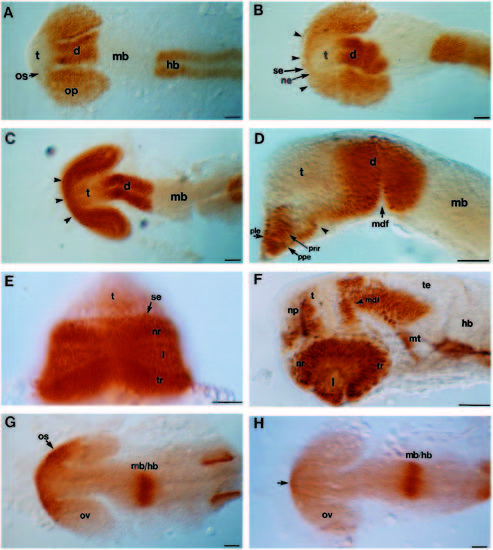
Pax protein distribution in wild-type and cyclops mutant embryos. Whole-mounted embryos labelled with anti-Pax6 antibody (A-F), or labelled with anti-Pax2 antibody (G,H). (A,B) Dorsal views of 15-16s wild-type and cyclops embryos respectively. The arrowheads in B indicate the bridge of rostral retinal fusion. (C,D) Dorsal and lateral (focused on the midline) views respectively of 20s cyclops embryos. The arrowheads indicate the area of retinal fusion in C. In D the lateral portions of the cyclopic eye have been removed. The arrowhead indicates the caudal limit of eye fusion. (E) Frontal view of 28s cyclops mutant embryo. (F) Lateral view of 28 hour cyclops mutant embryo also labelled with anti-tubulin antibody (black labelling of axons). This embryo was also examined in a different study (Macdonald et al., 1994). (G,H) 18- 20s dorsal views of wild-type (G) and cyclops (H) embryos labelled with anti-Pax2 antibody. The arrow in H indicates a few cells near the midline weakly labelled with anti-Pax2 antibody. Abbreviations: d, diencephalon; hb, hindbrain; mb, midbrain; mdf, mid-diencephalic furrow; l, lens; mt, midbrain tegmentum; ne, neural ectoderm; nr, nasal retina; os, optic stalks; np, nasal placode; op, optic primordia; ov, optic veiscle; ple, presumptive lens ectoderm; pnr, presumptive neural retina; ppe, presumptive pigment epithelium; se, surface ectoderm; t, telencephalon; te, tectum; tr, temporal retina; vd, ventral diencephalon. Scale bars, 50 μm.
|

