Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-130907-30
- Publication
- McCarthy et al., 2013 - Pdgfra protects against ethanol-induced craniofacial defects in a zebrafish model of FASD
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
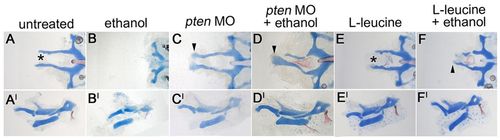
Elevating PI3K/mTOR signaling rescues the craniofacial defects in ethanol-treated pdgfra mutants. (A-F2) 5 dpf pdgfra mutant neurocrania (A-F) and the corresponding pharyngeal skeletal elements (A2-F2). (A,A2) Untreated mutants have clefting of the ethmoid plate (asterisk, n=10/10). (B,B2) Treatment with 1.0% ethanol at 10-24 hpf causes loss of the palatal skeleton and hypoplasia of the pharyngeal skeleton (n=12/12). (C-D2) pten morpholino (MO) injection rescues the craniofacial phenotypes of both (C,C2, n=4/4) untreated and (D,D2, n=8/20) ethanol exposed pdgfra mutants. (E,E2) Most L-leucine-treated mutants have trabeculae (n=12/17; five embryos lacked trabeculae). (F,F2) Supplementing ethanol-treated mutants with L-leucine causes rescue of the trabeculae (n=10/32). Arrowheads mark the partially rescued ethmoid plates. Asterisk in E indicates clefting of the ethmoid plate. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Condition: | |
| Knockdown Reagents: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Day 5 |