Fig. 8
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-121119-9
- Publication
- Rodriguez-Mari et al., 2011 - Roles of brca2 (fancd1) in Oocyte Nuclear Architecture, Gametogenesis, Gonad Tumors, and Genome Stability in Zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
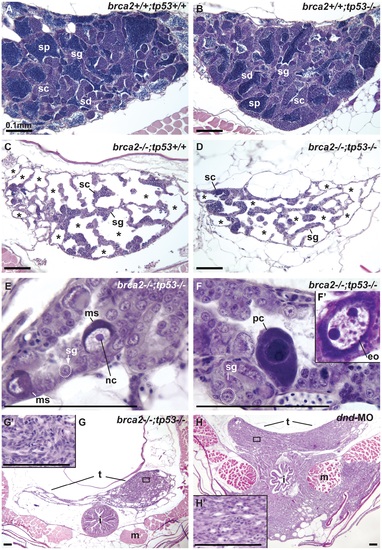
Mutation of tp53 failed to rescue infertility in brca2 mutants. (A,B) Wild-type testis and tp53 single mutant testis showed germ cells at all stages of spermatogenesis: spermatogonia, spermatocytes, spermatids and sperm. (C) brca2 single mutant testis contained spermatogonia and spermatocytes, lacked spermatids and sperm and had large regions devoid of germ cells (asterisks). (D) Testes in brca2;tp53 double mutants were similar to the brca2 single mutant, but had additional developmental problems. (E) Double mutant testis formed large cells with a single central nucleolus like spermatogonia (called here megalospermatogonia). (F) Some of these abnormally enlarged cells were pyknotic and some showed an oocyte-like morphology similar to early oocytes (inset). (G) Double mutants showed neoplastic regions of abnormal somatic cell proliferation in the posterior regions of the testes that were depleted of sperm. (G′) Enlargement of the somatic proliferation of double mutant testes. (H) Genetically wild-type testes depleted of germ cells due to dnd morpholino knockdown formed neoplasms of somatic cells of the testis similar to the ones observed in brca2;tp53 double mutants, but that invaded the intestine and muscle at older stages. (H′) Enlargement of the somatic proliferation of dnd testes. Abbreviations: asterisks (*), empty testis tubules; eo: early oocyte; i, intestine; m, muscle; ms, megalospermatogonia; nc, nucleolus; pc, pyknotic cell; sc, spermatocytes; sd, spermatids; sg, spermatogonia; sp, sperm; t, testis. |
| Fish: | |
|---|---|
| Knockdown Reagent: | |
| Observed In: | |
| Stage: | Adult |