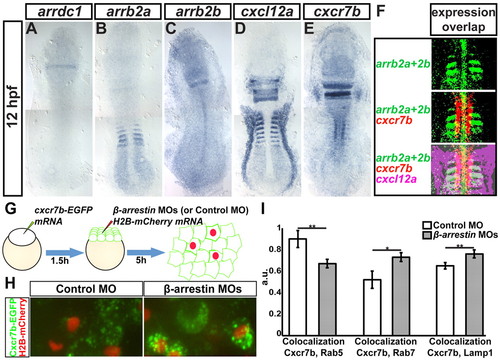
Expression patterns of β-arrestin genes, cxcl12a and cxcr7b and control of Cxcr7b localization by β-arrestins. (A-E) Expression pattern of arrdc1 (A), arrb2a (B), arrb2b (C), cxcl12a (D) and cxcr7b (E) in 12-hpf zebrafish embryos. (F) Partial overlap of arrb1a, arrb2b, cxcr7b and cxcl12a expression patterns in the anterior somites, freeing lateral Cxcl12a expression domains (magenta) from Cxcr7 and β-arrestin effects. (G) The procedure for generating uniform Cxcr7b-EGFP expression (green) and cell clones knocked down for β-arrestins by injection with MOs targeting all β-arrestins (or control MO) and Histone H2B-mCherry for clone labeling (red). (H) In control 7-hpf mosaic embryo (left), Cxcr7b is found in small vesicles. In cells compromised for β-arrestin function (red nuclei, right), Cxcr7b vesicles are often enlarged. (I) Average colocalization coefficient (see supplementary material Fig. S12) among Cxcr7b-ECFP and Rab7-mCherry (at 5 hpf), Lamp1-DsRedmonomer and Rab5-mCherry (at 8 hpf) in control and β-arrestin knockdown cells. Data were averaged among six measurements (one image per embryo, <80 cells in the field of view). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, Student’s t-test. Error bars indicate s.e.m.
|

