Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-111128-43
- Publication
- Almeida et al., 2011 - Individual axons regulate the myelinating potential of single oligodendrocytes in vivo
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
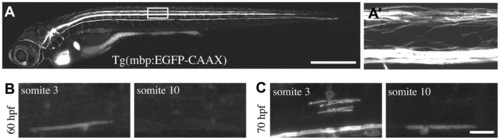
Transgenic reporters reveal first axon myelinated in vivo in zebrafish CNS. (A) Lateral view of a stable Tg(mbp:EGFP-CAAX) zebrafish at 8 dpf. Myelinating glia of the CNS and PNS are labelled, as is the heart, which serves as a marker of transgenesis. (A′) Lateral view of the spinal cord (area indicated by box in A). Prominent myelinated tracts myelinated in the dorsal spinal cord and ventral spinal cord are apparent. (B) Lateral views of a stable Tg(mbp:EGFP-CAAX) zebrafish at 60 hpf show that the very first axon to be myelinated is the large Mauthner axon in the ventral spinal cord, which is first myelinated in the anterior spinal cord. (C) Lateral views of a stable Tg(mbp:EGFP-CAAX) zebrafish at 70 hpf. Myelination of the Mauthner axon has now commenced in the more posterior part of the spinal cord. At this stage, oligodendrocytes have started to myelinate axons in the dorsal spinal cord. Dorsal is up and anterior is to the left in all images. Scale bars: 500 μm in A; 20 μm in C. |