Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-101122-14
- Publication
- Appelbaum et al., 2009 - Sleep-wake regulation and hypocretin-melatonin interaction in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
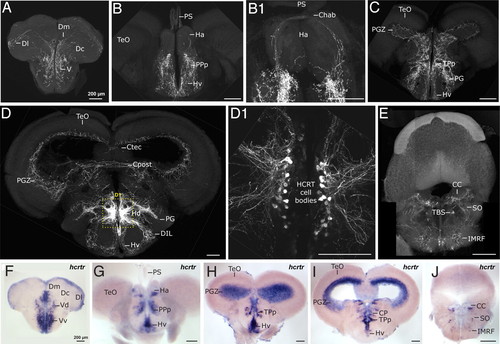
Adult zebrafish HCRT circuit. (A?E) Confocal imaging of 100 μm transversal brain sections from a stable hcrt:EGFP transgenic adult fish (reconstructed stacks of 0.5- or 1-μm sections). Note the compact organization of the HCRT cell bodies in the periventricular hypothalamus (D and dashed-box close up in D1). (F?J) hcrtr mRNA ISH pattern in equivalent brain sections to A?E. Note the similar distribution of HCRT fibers and hcrtr mRNA. Compare sections of telencephalon (A vs. F), telencephalon-midbrain boundary (B and B1 vs. G), anterior diencephalon and mesencephalon (C vs. H), mid diencephalon and mesencephalon (D vs. I), rhombencephalon (E vs. J). Chab, commissura habenularum; Ctec, commissura tecti; Cpost, commissura posterior; CC, crista cerebellaris; CP, central posterior thalamic nucleus; D, dorsal telencephalic area; Dm, medial zone of D; Dc, central zone of D; Dl, lateral zone of D; DIL, diffuse nucleus of the inferior lobe; Ha, habenula; Hv, ventral zone of the periventricular hypothalamus; Hd, dorsal zone of the periventricular hypothalamus; IMRF, intermediate reticular formation; PG, preglomerular nucleus; PGZ, periventricular gray zone of the optic tectum; PPp, parvocellular preoptic nycleus, posterior part; PS, pineal stalk; SO, secondary octaval population; TBS, tractus bulbospinalis; TeO, optic tectum; TPp, periventricular nucleus of posterior tuberculum; V, ventral telencephalic area; Vv, ventral nucleus of V; Vd, dorsal nucleus of V. |