|
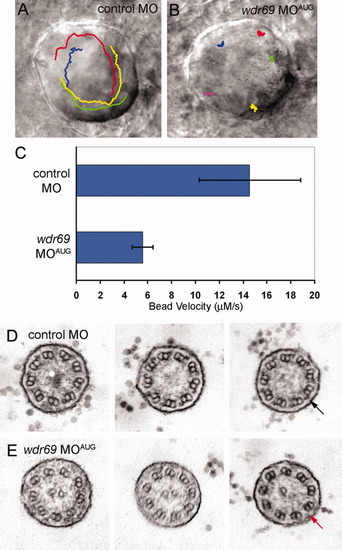
Wdr69 is needed for ciliary motility and outer arm dynein assembly. A,B: Tracking software was used to follow the flow of fluorescent beads injected into Kupffer′s vesicle (KV) of live embryos. Tracks are superimposed on images of KV. A: In control morphants, beads flowed in a circular counterclockwise direction. B: This directional flow was lost in wdr69 MOAUG morphants, where beads bounced around randomly. C: Velocity of bead movement was significantly reduced in wdr69 knockdown embryos (n = 25 beads from 5 embryos) relative to controls (n = 28 beads from 6 embryos). Error bars=one standard deviation. D,E: Electron microscopy of KV cilia. D: In control MO injected embryos, typical outer dynein arms (arrow) were present on all nine outer doublets of all cilia examined. E: In contrast, KV cilia from wdr69 MOAUG morphants displayed greatly reduced numbers of outer dynein arms. MO, morpholino oligonucleotides.
|