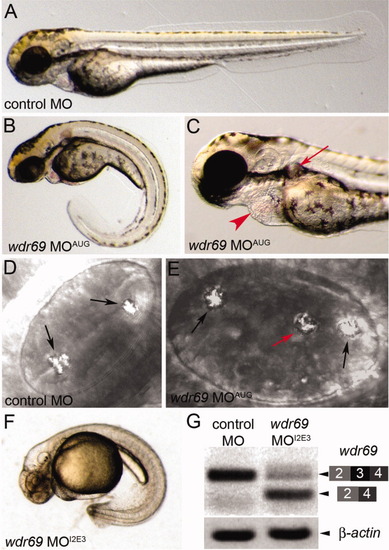
wdr69 morpholino oligonucleotides (MO) knockdown embryos develop phenotypes associated with defects in ciliary motility. A-C: Live embryos at 2 days postfertilization (dpf). Control MO injected embryos exhibited normal morphology (A), whereas wdr69 MOAUG morphant embryos developed phenotypes associated with cilia defects, including a curled tail (B), kidney cysts (arrow in C) and pericardial edema (arrowhead in C). D,E: Otoliths in otic vesicles at 2 dpf. Control MO injected embryos developed two correctly positioned otoliths (arrows in D). wdr69 MOAUG morphants often developed a third ectopically positioned otolith (red arrow in E). F:wdr69 MOI2E3 morphants developed the same phenotypes as wdr69 MOAUG morphants (this embryo was treated with PTU to inhibit melanin biosythesis for RNA in situ analysis). G: RT-PCR analysis shows wdr69 MOI2E3 causes mis-splicing of wdr69 transcripts. A normally spliced cDNA containing exons 2-4 was detected in control MO injected embryos. The level of this cDNA was reduced in wdr69 MOI2E3 morphants and a smaller fragment lacking exon 3 was observed in wdr69 MOI2E3 morphants. β-actin was amplified as a loading control.
|

