Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-100616-46
- Publication
- Pang et al., 2010 - Role of G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1, GPER, in inhibition of oocyte maturation by endogenous estrogens in zebrafish
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
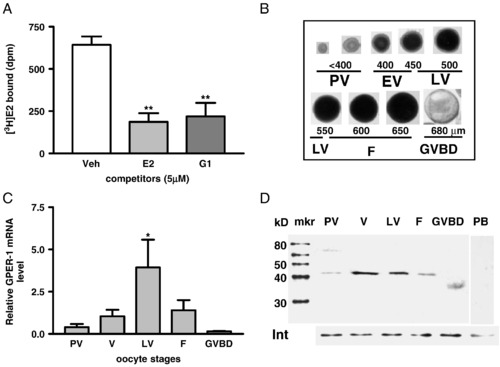
Estrogen binding to ovarian membranes and pattern of GPER mRNA and protein expression in zebrafish oocytes at different developmental stages. (A) Single-point competitive binding of [3H]-E2 to ovarian plasma membranes in the presence of 500-fold excess E2 and G-1 competitors. ∗∗, P < 0.01 vs. vehicle (Veh). (B) Appearance and diameters of zebrafish oocytes at different developmental stages. PV, pre-vitellogenic oocytes. EV, early-vitellogenic oocytes. LV, late-vitellogenic oocytes. F, full-grown oocytes. GVBD, oocytes undergoing germinal vesicle breakdown. (C) Quantitative RT-PCR measurement of GPER mRNA levels in the oocytes at different developmental stages. (D) Western blot analysis of GPER protein expression on the plasma membranes of oocytes at different development stages using a specific GPER antibody. mkr, protein size marker. Int, integrin loading control. PB, peptide block. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 342(2), Pang, Y., and Thomas, P., Role of G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1, GPER, in inhibition of oocyte maturation by endogenous estrogens in zebrafish, 194-206, Copyright (2010) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.