Fig. 1
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-090320-36
- Publication
- Sims Jr et al., 2009 - Connexin43 regulates joint location in zebrafish fins
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
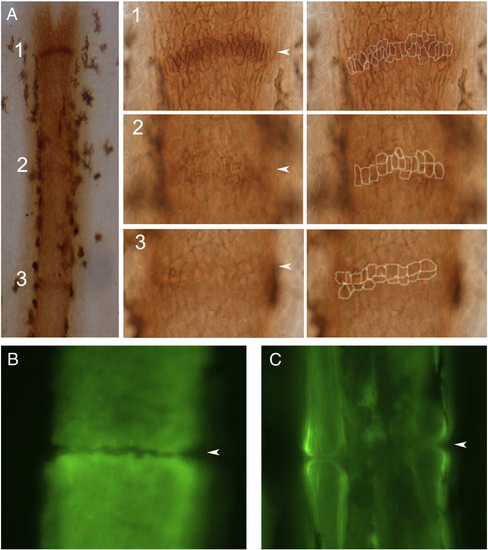
Joint formation in zebrafish fin rays. (A) Fins were stained with the osteoblast marker ZNS5, and detected using HRP (brown). At this level joints are detected as condensations of ZNS5-positive cells, which appear with differing maturities along the proximal?distal axis. Joint 1 is the most-distal joint and the least mature. At higher magnification distinct morphologies of ZNS5-positive cells can be observed (and outlines of the ZNS5-positive cells are shown to the right). (B) The morphology of the bone matrix in the newest joint is observed using calcein. (C) The morphology of the bone matrix in a fully mature joint is observed using calcein. Arrowheads point to joints. |
| Antibody: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Term: | |
| Stage: | Adult |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 327(2), Sims Jr, K., Eble, D.M., and Iovine, M.K., Connexin43 regulates joint location in zebrafish fins, 410-418, Copyright (2009) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.