Fig. 5
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-080506-27
- Publication
- Chuang et al., 2001 - Zebrafish genes rx1 and rx2 help define the region of forebrain that gives rise to retina
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
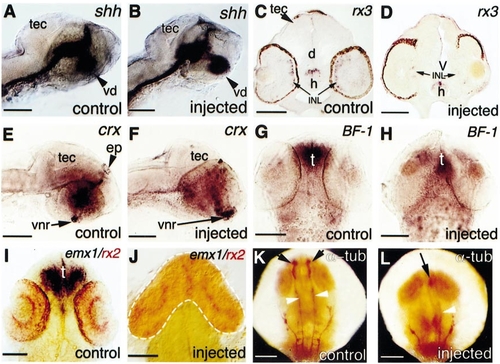
Selective loss of forebrain structures in embryos following rx2 overexpression. (A-D) Comparison of shh and rx3 expression in control and injected embryos at 24 hpf (A, B; lateral view) or 60 hpf (C, D; transverse section). (C) rx3 is expressed in the inner nuclear layer of the neural retina and in the hypothalamus. (E-J) Comparison of crx, BF-1, and emx1 expression in control and injected embryos at 36 hpf (E-H) or 24 hpf (I, J). (E) and (F) are lateral views; (G-J) are dorsal views. Note the absence of crx expression in the epiphysis in (F), the strong suppression of BF-1 in the telencephalon in (H), and the absence of emx1 expression in (J). Arrows in (E) and (F) indicate strong expression of crx in the earliest differentiating retina, located at the ventronasal edge. (K, L) Anti-acetylated α-tubulin (α-tub) staining (dorsal view, 24 hpf). Black arrows show the major axonal tracts in the forebrain and white arrowheads show the axonal tracts in the midbrain region. Embryos were injected with 1 ng rx2ΔC′ (B, D, J, L), or 300 pg rx2ΔRx (F, H) RNA. d, diencephalon; ep, epiphysis; h, hypothalamus; INL, inner nuclear layer; t, telencephalon; tec, optic tectum; V, ventricle; vd, ventral diencephalon; vnr, ventral neural retina. Scale bars: 100 μm. |
| Genes: | |
|---|---|
| Fish: | |
| Anatomical Terms: | |
| Stage Range: | Prim-5 to Pec-fin |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 231, Chuang, J.-C. and Raymond, P.A., Zebrafish genes rx1 and rx2 help define the region of forebrain that gives rise to retina, 13-30, Copyright (2001) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.