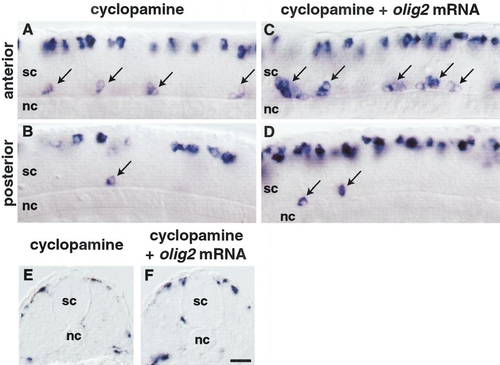
olig2 requires Hedgehog signaling to promote primary motor neuron and oligodendrocyte development. (A-D) Side views of 22-hpf embryos hybridized with isl2 probe. (A) Anterior and (B) posterior trunk spinal cord (sc) of embryo treated with cyclopamine. Slightly fewer isl2-positive primary motor neurons developed in anterior trunk relative to wild type (compare Fig. 8A with Fig. 5A), whereas few primary motor neurons developed in posterior trunk (B). (C) Anterior and (D) posterior trunk spinal cord of embryo injected with olig2 mRNA and treated with cyclopamine. Slightly more primary motor neurons developed in anterior trunk (C) compared with noninjected embryos (A), whereas primary motor neurons rarely developed in posterior trunk and tail (D), similar to noninjected embryos (B). (E, F) Transverse sections of 48-hpf embryos hybridized with sox10 probe. Spinal cord cells did not express sox10 in cyclopamine-treated embryos (E) or in olig2-injected embryos treated with cyclopamine (F). Scale bar, 20 μm.
|

