Fig. 10
|
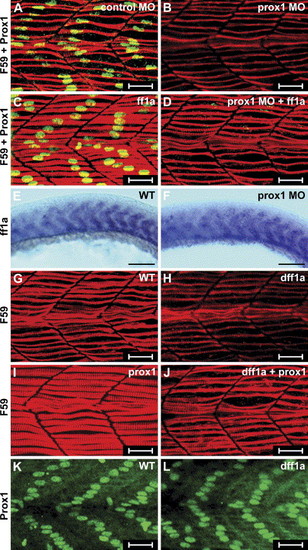
Epistatic relationship of ff1a and prox1. Wild-type (WT) embryos were injected with control MO (A, E), prox1 MO (B, D, F), β-gal RNA (G, K), dff1a RNA (H, J, L), full-length ff1a RNA (C, D), or prox1 RNA (I, J). Gene expression was detected by in situ hybridization with ff1a probe (A, B), F59 antibody (red, A?D, G?J), or Prox1 antibody (green, A?D, K, L). (B) In Prox1 morphant, slow twitch myofibril is thinner. (C) Ectopic expression of ff1a did not perturb Prox1 expression, but the myofibrils as stained by F59 were expanded. (D) Co-injection of ff1a mRNA with prox1 MO restored the striation in myofibrils, although Prox1 staining is absent. Expression of ff1a in the slow muscle in the control (E) and the prox1 morphant (F) is not perturbed. (H) Knockdown of ff1a by dff1a RNA resulted in thinner myofibril. (K) Ectopic expression of prox1 mRNA in wild type embryos expanded the width of the myofibril. (J) When prox1 RNA was co-injected with dff1a RNA, slow myofibrils were thicker than those in panel (H) but thinner than those in panel (I). Expression of Prox1 is detected in (K) β-gal or (L) dff1a RNA-injected embryos. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 286(2), Sheela, S.G., Lee, W.C., Lin, W.W., and Chung, B.C., Zebrafish ftz-f1a (nuclear receptor 5a2) functions in skeletal muscle organization, 377-390, Copyright (2005) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.