Fig. 3
- ID
- ZDB-FIG-050817-3
- Publication
- Sonawane et al., 2005 - Zebrafish penner/lethal giant larvae 2 functions in hemidesmosome formation, maintenance of cellular morphology and growth regulation in the developing basal epidermis
- Other Figures
- All Figure Page
- Back to All Figure Page
|
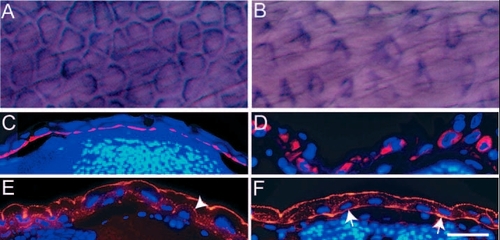
pen function is essential for the maintenance of the organisation of cytoskeletal elements in basal epidermal cells. (A-D) Immunohistological staining in 5-day-old wild-type (A,C) and pen mutant larvae (B,D) using anti keratin (Ks pan-8) antibody. In whole mounts, basal epidermal cells appear polygonal in wild type (A) and spindle shaped in mutants (B). Histological sections of 5-day-old wild-type and pen mutants stained for keratin counterstained by DAPI (C,D), show that in contrast to wild type (C), keratin (red) does not remain localised to the basal cortex in mutant larvae (D). (E,F) Immunohistological staining with anti-actin antibody followed by counterstaining with DAPI indicates punctate localisation of actin (red) at apical and lateral borders of basal epidermal cells in wild type (arrowhead in E). By contrast, actin is also localised basally in mutants (arrows in F). Scale bar: 40 µm in A,B; 60 µm in C-F. |