- Title
-
Degarelix limits the survival of mycobacteria and granuloma formation
- Authors
- Li, J., Gao, J., Gao, Y., Shi, C., Guo, X., Huang, H., Wang, J., Huang, X., Chen, H., Huang, J., Wang, W., Yang, H.
- Source
- Full text @ Microb. Pathog.
|
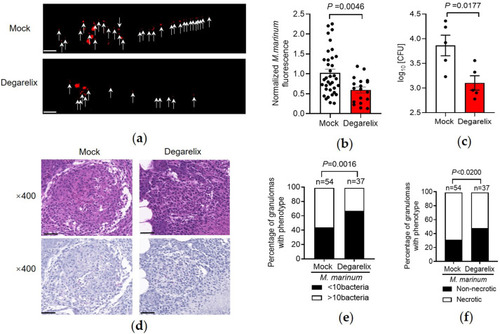
Degarelix limits mycobacterial survival and granuloma formation in zebrafish. (a) M. marinum burden distribution in wild-type zebrafish larvae treated with degarelix (1 ?M) or mock for 5 days. (b) Bacterial burden values in infected larvae treated with degarelix (1 ?M) or mock for 5 days. (c) Adult zebrafish were intraperitoneally infected with wild-type M. marinum/fish (400 CFU) for 2 weeks. Adults received oral degarelix (10 mg/kg/day) for 48 h before infection and for 14 days after. Bacterial burdens are shown (c). (d-f) Histopathology on whole fish sections using H&E or acid-fast staining at 14 dpi (scale bar = 20 ?m). Granulomas were compared between infected adult zebrafish treated with/without degarelix, and scored for <10 or >10 bacterial burden values (e) and necrotic granuloma percentages (f). PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Degarelix reduces Mtb survival in C57BL/6 mice. (a-d) Mice were aerosol-infected with 200 CFU H37Rv/mouse. Degarelix was administered just after infection via weekly intraperitoneal injection for up to 4 weeks. Lung histopathology was examined using bacterial CFUs (mean ± SEM of three mice infected for 4 weeks) (a), acid-fast (b; scale bars = 100 ?m and 20 ?m for upper and lower images, respectively; Arrows indicated the acid-fast staining positive H37Rv bacteria in lung tissue) and H&E staining (c, 1?3 = representative lung sections) in mouse lungs infected for 4 weeks. Histological scores (d). |
|
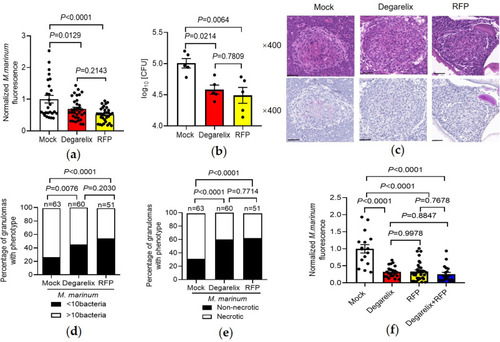
Degarelix can be used for anti-mycobacterium therapy. (a) Bacterial burden values in infected zebrafish larvae treated with mock, rifampicin (10 ?M), or degarelix (1 ?M) for 72 h. Data are represented in a scatter dot plot. (b) Adult zebrafish infected with M. marinum (400 CFU) for 1 week were orally treated (daily) with degarelix (10 mg/kg) and RFP (5 mg/kg) as a positive control up to 14 days. Bacterial burdens are shown in (b). (c-e) Histopathology assessments in whole fish sections using H&E or acid-fast staining at 14 dpi (scale bar = 20 ?m). Granulomas were compared between infected adult zebrafish treated with/without degarelix for <10 or >10 bacterial burden scores (d) and necrotic granuloma percentages (e). (f) Bacterial burden values in infected zebrafish larvae treated with mock, rifampicin (10 ?M), degarelix (1 ?M), or degarelix (1 ?M) + RFP(10 ?M) for 72h. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
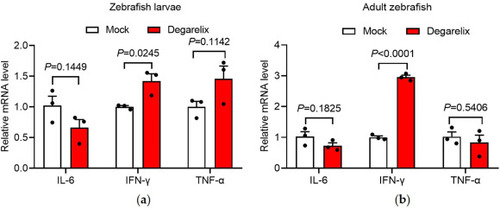
Degarelix increases IFN-? levels in M. marinum-infected zebrafish. (a) RT-qPCR analysis of IL-6, IFN-?, and TNF? mRNA expression in M. marinum-infected zebrafish larvae treated with mock or degarelix (1 ?M). (b) RT-qPCR analysis of IL-6, IFN-?, and TNF? mRNA expression in M. marinum-infected adult zebrafish treated with vehicle or degarelix (10 mg/kg). |
|
Degarelix reduces Mtb intracellular survival in BMDMs. (a, b) Intracellular CFUs and bacterial survival rates in BMDMs pretreated with degarelix (1 ?M) or mock and infected with H37RV at an MOI = 2 (data are represented by the mean ± SEM). The survival ratios were calculated by comparing the results at 24 h to those at 3 h (b). |
|
Degarelix inhibits intracellular Mtb survival via autophagy. (a, b) BMDMs pretreated with degarelix (1 ?M), AGHS (100 ?M), BafA1 (100 nM), NAC (5 mM), Z-VAD (20 ?M), or 3-MA (5 mM) were infected with H37Rv (MOI = 2) at different times after which bacterial survival was calculated by dividing 24 h data by 3 h data (b). (c) Protein levels of P62 and LC3II in H37Rv-infected BMDMs pretreated with mock or degarelix (1 ?M). |