- Title
-
A versatile transcription factor: Multiple roles of orthopedia a (otpa) beyond its restricted localization in dopaminergic systems of developing and adult zebrafish (Danio rerio) brains
- Authors
- Eugenin von Bernhardi, J., Biechl, D., Miek, L., Herget, U., Ryu, S., Wullimann, M.F.
- Source
- Full text @ J. Comp. Neurol.
|
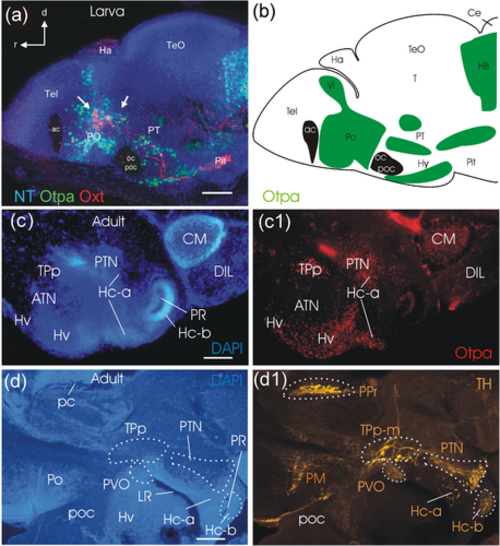
Sagittal overviews of the larval zebrafish brain (5 dpf; a,b) and the adult zebrafish basal diencephalon and hypothalamus (c-d). (a) is adapted from Herget et al. (2014) and highlights oxytocin cells (white arrows pointing to red cells) in the preoptic region among Otpa (green) immunopositive cells. (b) Drawing of this brain section shows additional Otpa domains (indicated in green, brain commissures in black), for example, in the intermediate nucleus of the ventral telencephalic area (Vi, interpreted as medial amygdala; adapted from Biechl et al., 2017), in the posterior tuberculum (PT), hypothalamus(Hy), and hindbrain (HB). (c/c1) shows a parasagittal adult section close to the midline stained for DAPI (c) and Otpa (c1) identifying some posterior tubercular and hypothalamic Otpa domains. (d/d1) shows a slightly more lateral parasagittal section (d; DAPI stained) highlighting posterior tubercular and hypothalamic catecholaminergic domains (d1; TH immunostained). Scale bars = 50 Ám (a), 250 Ám (c/d). Abbreviations: ac, anterior commissure; ATN, anterior tuberal nucleus; Ce, cerebellum; CM, corpus mamillare; d, dorsal; DIL, diffuse nucleus of hypothalamic inferior lobe; Ha, habenula; Hc-a, caudal zone of periventricular hypothalamus in front of a posterior recess; Hc-b, caudal zone of periventricular hypothalamus around posterior recess; Hv, ventral zone of periventricular hypothalamus; Hy, hypothalamus; LH, lateral hypothalamic nucleus; LR, lateral hypothalamic recess; NT, NeuroTrace; oc, optic chiasma; Oxt, oxytocin; pc, posterior commissure; Pit, pituitary; PM, magnocellular preoptic nucleus; Po (PO in panel A), preoptic region; poc, postoptic commissure; PPr, periventricular pretectum, PR, posterior hypothalamic recess; PT, posterior tuberculum; PTN, posterior tuberal nucleus; PVO, paraventricular organ; r, rostral; T, midbrain tegmentum; Tel, telencephalon; TeO, optic tectum; TPp, periventricular nucleus of posterior tuberculum; TPp-m, magnocellular cells of TPp; TPp-p, parvocellular cells of TPp; Vi, intermediate nucleus of ventral telencephalon |
|
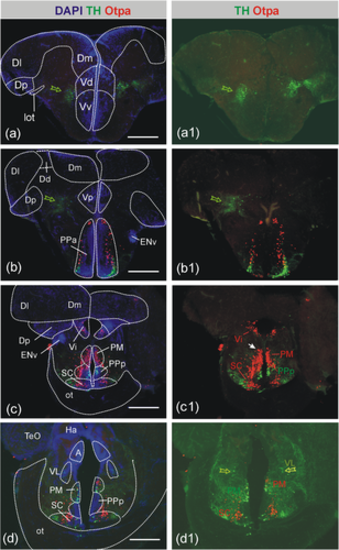
Distribution of catecholaminergic (TH) and Otpa-positive cells in the adult zebrafish forebrain I. Based on DAPI stains, epifluorescence microscopic analysis of immunostained transverse sections shows no cellular colocalization of TH and Otpa in these forebrain catecholaminergic sites, that is, in the ventral telencephalon (a/a1), in the preoptic area (b/b1-d/d1), or in the alar ventral thalamus (interpreted as zona incerta cells in the prethalamus, d/d1; Rink & Wullimann, 2002a). Open green arrows point to TH-positive cells, white arrow to gigantocellular preoptic neuron. Scale bars = 250 Ám. Abbreviations: A, anterior thalamic nucleus; Dd/Dl/Dm/Dp, dorsal/lateral/medial/posterior zone of dorsal telencephalon; ENv, ventral entopeduncular nucleus; Ha, habenula; lot, lateral olfactory tract; ot, optic tract; PM, magnocellular preoptic nucleus; PPa/PPp, anterior/posterior parvocellular preoptic nucleus; SC, suprachiasmatic nucleus; TeO, optic tectum; Vd/Vi/Vp/Vv, dorsal/intermediate/posterior/ventral nucleus of ventral telencephalon; VL, ventrolateral thalamic nucleus |
|
Distribution of catecholaminergic (TH) and Otpa-positive cells in the adult zebrafish forebrain II. Based on DAPI stains, epifluorescence microscopic analysis of immunostained transverse sections shows no cellular colocalization of TH and Otpa in most of these catecholaminergic forebrain sites, that is, neither in the periventricular pretectum (PPr; a/a1-b/b1), the paraventricular organ (PVO; c,c1), the small-celled (parvocellular) part of the periventricular posterior tuberculum (TPp-p; c/c1), nor in the caudal zone of the periventricular hypothalamus (Hc-a/b; d/d1?e/e1). Furthermore, the ventral zone of the periventricular hypothalamus (Hv), and the anterior tuberal and lateral hypothalamic nuclei (ATN, LH) as well as the intermediate hypothalamic nucleus only contain Otpa-positive cells. However, cellular colocalization of Otpa and TH is seen in the pear-shaped magnocellular part of the posterior tuberculum (TPp-m; b/b1) and the posterior tuberal nucleus (PTN; see also Figures 7; 8). Scale bars = 250 Ám. Abbreviations: A, anterior thalamic nucleus; ATN, anterior tuberal nucleus; CM, corpus mamillare; CP, central posterior thalamic nucleus; DP, dorsal posterior thalamic nucleus; Hc-a, caudal zone of periventricular hypothalamus in front of posterior recess, Hc-b, caudal zone of periventricular hypothalamus around posterior recess; Hd/Hv, dorsal/ventral zone of periventricular hypothalamus; IN, intermediate hypothalamic nucleus; LH, lateral hypothalamic nucleus; LR, lateral hypothalamic recess; PGl/PGm, lateral/medial preglomerular nucleus; PPp, posterior parvocellular preoptic nucleus; PPr, periventricular pretectum; PR, posterior hypothalamic recess; PTN, posterior tuberal nucleus; PVO, paraventricular organ; TPp, periventricular nucleus of posterior tuberculum; SCO, subcommissural organ; VL/VM, ventrolateral/ventromedial thalamic nucleus |
|
Distribution of Otpa-positive cells in the adult zebrafish midbrain and anterior hindbrain. Epifluorescent microscopic analysis shows Otpa domains in anterior midbrain and hindbrain regions. (a?f) A series of sequential transverse sections shows DAPI stain-based analysis of brain nuclei and tracts with red outlines indicating major Otpa-positive cell populations. Immunohistochemical detection of Otpa-positive cells is shown in the same sections in panels (a1) through (f1). Otpa-positive cells are seen in the perilemniscal (a-d) and the dorsal tegmental nucleus (a, b), in the nucleus lateralis valvulae (c-e), in the interpeduncular nucleus (d), as well as in the superior reticular formation (c-f) and the central gray (d-f; see text for details). Note that the Otpa immunostain does not adhere strictly to boundaries of brain nuclei as defined by the DAPI stain. Note complete absence of Otpa-positive cells in optic tectum (a), cerebellum (a-f), and dorsal/caudal zone of periventricular hypothalamus around lateral/posterior recess ventricle, respectively (a-c) and all nuclei of the inferior lobe (e.g., diffuse and central nuclei, corpus mamillare; a1-e1). Slide and section numbers are indicated in upper right corner for giving an estimate of relative anteroposterior distance between levels shown. Scale bar in B = 250 Ám (applies to all panels). Abbreviations: act, anterior cerebellar tract; CCe, corpus cerebelli; ccer, cerebellar commissure; CIL, central nucleus of the hypothalamic inferior lobe; CM, corpus mamillare; DIL, diffuse nucleus of the hypothalamic inferior lobe; DTN, dorsal tegmental nucleus; EG, eminentia granularis; Hc, caudal zone of periventricular hypothalamus; Hd, dorsal zone of periventricular hypothalamus; llf, lateral longitudinal fascicle; LR, lateral hypothalamic recess; mlf, medial longitudinal fascicle; NIII, oculomotor nucleus; NIV, trochlear motor nucleus; NIn, interpeduncular nucleus; NLV, nucleus lateralis valvulae; Nmlf, nucleus of mlf; NVs, primary sensory trigeminal nucleus; pct, posterior cerebellar tract; PGZ, periventricular gray zone of optic tectum; PL, perilemniscal nucleus; RV, rhombencephalic ventricle; TeV, tectal ventricle; TLo, torus longitudinalis; tmca/p, tractus mesencephalocerebellaris anterior/posterior; TSc, central nucleus of torus semicircularis; TSvl, ventrolateral nucleus of torus semicircularis; ttb, tractus tectobulbaris; Val, lateral division of valvula cerebelli; Vam, medial division of valvula cerebelli; Vas. vascular lacuna of area postrema, III oculomotor nerve |
|
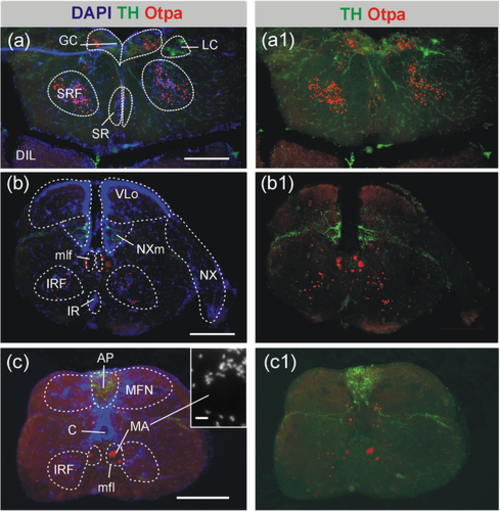
Distribution of catecholaminergic (TH) and Otpa-positive cells in the adult zebrafish posterior hindbrain. Based on DAPI stains, epifluorescence microscopic analysis of transverse sections shows no cellular colocalization in the locus coeruleus (a/a1) and in the vagal catecholamine group (b/b1). In the area postrema, catecholaminergic (TH-positive) and Otpa-positive cells intermingle, but with no apparent double-labeled cells (c/c1). Otpa-positive cells are furthermore seen in the central gray, superior reticular formation, and superior raphe (very few, a/a1), as well as in the inferior reticular formation (b/b1-c/c1). Scale bars = 250 Ám (a-c), 10 Ám, inset in (c). Abbreviations: AP, area postrema; C, central canal; DIL, diffuse nucleus of hypothalamic inferior lobe; GC, central gray; IRF, inferior reticular formation; LC, locus coeruleus; MA, Mauthner axon; MFN, medial funicular nucleus; mlf, medial longitudinal fascicle; NX, vagal nerve; NXm, vagal motor nucleus; SR, superior raphe; SRF, superior reticular formation; VLo, vagal lobe |
|
Confocal microscopic analysis of catecholaminergic (TH) and Otpa-positive cells in the adult zebrafish diencephalon at the level of the paraventricular organ. An ideal transverse section for displaying the periventricular pretectum (PPr), dorsal thalamus (DT), periventricular nucleus of the posterior tuberculum (TPp), ventral periventricular hypothalamic zone (Hv), as well as anterior tuberal and lateral hypothalamic nuclei (ATN/LH) is shown for DAPI stain (a), and Otpa (a1), TH (a2) and merged Otpa/TH immunostains (a3). Separate enlarged microphotographs show Otpa (a4), TH (a5) and merged Otpa/TH (a6) immunostained cells and demonstrate that no cellular colocalization occurs in the paraventricular organ (PVO; white arrows), as is obviously also the case for the periventricular nucleus of the posterior tuberculum (TPp), the periventricular pretectum (PPr), the ventral zone of the periventricular hypothalamus (Hv), and the anterior tuberal and lateral hypothalamic nuclei (ATN/LH). Scale bars = 250 Ám (a), 125 Ám (a4), applies also to (a5/a6). Abbreviations: ATN, anterior tuberal nucleus; DT ,dorsal thalamus; Ha, habenula; Hv, ventral zone of periventricular hypothalamus; LH, lateral hypothalamic nucleus; PG, preglomerular complex; PPr, periventricular pretectum; PVO, paraventricular organ; TeO, optic tectum; TPp, periventricular nucleus of posterior tuberculum |
|
Confocal microscopic analysis of catecholaminergic (TH) and Otpa-positive cells in the adult zebrafish diencephalon at levels of the posterior tuberal nucleus, intermediate hypothalamic nucleus, as well as dorsal and prerecess caudal periventricular hypothalamic zones. Four transverse levels (a-d/a2-1 to d2-1): DAPI stain; (a1-d1/a2-2 to d2-2): merged TH/Otpa immunostain) cover the rostrocaudal extent of the posterior tuberal nucleus (PTN). Note that (a2-1/a2-2) to (d2-1/d2-2) are separate enlarged microphotographs. The PTN shows rostrally TH cells (two lower white arrows in a2-2) and few Otpa-positive cells. Increasingly more Otpa-positive cells in PTN occur caudally (b2-1/b2-2 to d2-1/d2-2) where also the majority of TH/Otpa double-labeled cells in PTN sit (respective yellow arrows in b2-2 to d2-2). These three levels also show presence of TH/Otpa colabeled magnocellular cells of the periventricular posterior tuberculum (TPp-m; a2-2 to c2-2; respective yellow arrows, white arrow in [d2-2] shows a TH-only positive TPp-m cell). The parvocellular TPp-p is not double-labeled (two upper white arrows in a2-2/c2-2). The intermediate hypothalamic nucleus (IN) is characterized by a distinct Otpa-positive cell cluster, two white arrowheads in (a2-2); white arrowhead in (b2-2). Some TH-positive cells of PTN sit at the medial edge of IN, one of them double-labeled with Otpa. The caudal periventricular hypothalamic zone in front of the posterior recess (Hc-a) contains many Otpa-positive cells basal to its TH-positive cells (b1-d1). TH-positive cells in Hc-a are indicated by a white arrow in the right lower corner of (b2-2 to d2-2), note their bipolar liquor-contacting nature in (b2-2). Scale bars = 250 Ám (a) applies also to (b-d) and (a1-d1), 125 Ám (a2-1) applies also to (b2-1 to d2-1) and (a2-2 to d2-2). Abbreviations: ATN, anterior tuberal nucleus; DIL, diffuse nucleus of hypothalamic inferior lobe; DT, dorsal thalamus; Hc-a, caudal zone of periventricular hypothalamus in front of posterior recess; Hd/Hv, dorsal/ventral zone of periventricular hypothalamus; IN, intermediate hypothalamic nucleus; LH, lateral hypothalamic nucleus; pc, posterior commissure; PG, preglomerular complex; PTN, posterior tuberal nucleus; TLa, torus lateralis; TPp, periventricular nucleus of posterior tuberculum; TPp-m, magnocellular cells of TPp; TPp-p, parvocellular cells of TPp |
|
Confocal microscopic analysis of TH- and Otpa-positive cells in the adult zebrafish preoptic region and diencephalon at levels of the periventricular posterior tuberculum, posterior tuberal nucleus, and caudal periventricular hypothalamic zone. Note that a1/a2-e1/e2 are separate enlarged microphotographs of these transverse sections. The entire preoptic complex shows no cellular co-localization of TH and Otpa (a-b) as demonstrated for the posterior parvocellular preoptic (PPp) and suprachiasmatic nucleus (SC; a-a2; white arrows). Only the pear-shaped magnocellular part of the periventricular posterior tuberculum (TPp-m; b-b2/c-c2) shows cellular colocalization of TH and Otpa, but not the parvocellular nucleus of the periventricular posterior tuberculum (TPp-p), as demonstrated in magnifications (b1-c1/b2-c2, white and yellow arrows, respectively). Similarly, in the posterior tuberal nucleus (PTN) many cells show co-localization of TH and Otpa (d1-d2/e1-e2, white versus yellow arrows). Note complete absence of such overlap in the paraventricular organ (PVO; c1-c2) and the entire caudal hypothalamus (Hc; d1/e1), but TH immunostain in liquor-contacting cells of the ventral posterior recess lining of the Hc-b (e1). In both, TPp-m and PTN many?but not all?cells show colocalization of TH and Otpa. Scale bars = 250 Ám (a-e), 100 Ám (a1-e1), 50 Ám (a2-e2). Abbreviations: ATN, anterior tuberal nucleus; Ha, habenula; Hc-a, caudal zone of periventricular hypothalamus in front of posterior recess; Hc-b, caudal zone of periventricular hypothalamus around posterior recess; Hd/Hv, dorsal/ventral zone of periventricular hypothalamus; LH, lateral hypothalamic nucleus; ot, optic tract; PGa/PGm, anterior/medial preglomerular nucleus; PPp, posterior parvocellular preoptic nucleus; PTN, posterior tuberal nucleus; PVO, paraventricular organ; SC, suprachiasmatic nucleus; TeO, optic tectum; TLo, torus longitudinalis; TPp, periventricular nucleus of posterior tuberculum; TPp-m, magnocellular cells of TPp; TPp-p, parvocellular cells of TPp; VM, ventromedial thalamic nucleus |
|
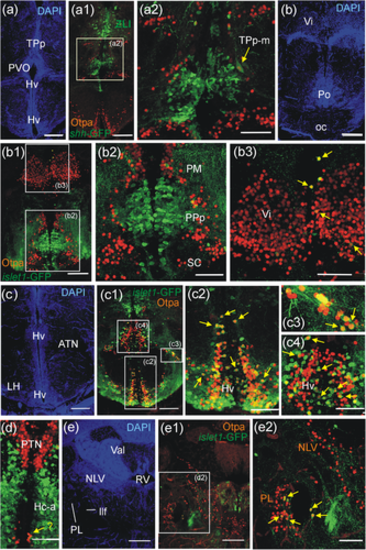
Distribution of Otpa-positive cells compared to shh-GFP cells in the adult zebrafish brain. Four transverse section levels in DAPI stain (a-d), Otpa immunostain (a1-d1), GFP immunostain (a2-d2) and merged pictures (a3-d3). (a-a3): telencephalon and preoptic region. (b-b3 to d-d3): three levels of posterior tuberculum and hypothalamus. White arrows in (b1-b2) point to the only shh-GFP cells double-labeled with Otpa. See text for more details. Scale bar = 250 Ám. Abbreviations: Dm, medial zone of dorsal telencephalon; Hc-a, caudal zone of periventricular hypothalamus in front of posterior recess; Hd/Hv, dorsal/ventral zone of periventricular hypothalamus; IN, intermediate hypothalamic nucleus; LH, lateral hypothalamic nucleus; Nmlf, nucleus of medial longitudinal fascicle; PG, preglomerular complex; PM, magnocellular preoptic nucleus; PTN, posterior tuberal nucleus; PVO, paraventricular organ; TPp, periventricular nucleus of posterior tuberculum; Vi, intermediate nucleus of ventral telencephalon; ZLI, zona limitans intrathalamica |
|
Distribution of Otpa-positive cells compared to islet1-GFP cells in the adult zebrafish brain. Five transverse sections levels in DAPI stain (a-e), Otpa immunostain (a1-e1), GFP immunostain (a2-e2) and merged pictures (a3-e3). (a/b-a3/b3): telencephalon and preoptic region. Note one double-labeled cell in the supraoptic ventral telencephalic nucleus (Vs), yellow arrow in (a3) and two further ventricularly located double-labeled cells in (b3) (yellow arrows; see text). (c/d/e) to (c3/d3/e3): three levels of posterior tuberculum and hypothalamus. Several double-labeled cells sit in the ventral periventricular hypothalamic zone (Hv), yellow arrows in (c3). Note single labeled Otpa and islet1-GFP cells in the intermediate hypothalamic nucleus (IN), white arrows pointing dorsally in (d1-d3), and single labeled islet1-GFP cells in the ventral periventricular hypothalamic zone (ventrally pointing white arrows in d3). See text for more details. Scale bar = 250 Ám. Abbreviations: Ac, anterior commissure; ATN, anterior tuberal nucleus; Dm, medial zone of dorsal telencephalon; ENv, ventral entopeduncular nucleus; Ha, habenula; Hc-a, caudal zone of periventricular hypothalamus in front of posterior recess; Hd/Hv, dorsal/ventral zone of periventricular hypothalamus; IN, intermediate hypothalamic nucleus; PM, magnocellular preoptic nucleus; PPa/PPp, anterior/posterior parvocellular preoptic nucleus; PTN, posterior tuberal nucleus; PVO, paraventricular organ; SC, suprachiasmatic nucleus; TeO, optic tectum; TPp, periventricular nucleus of posterior tuberculum; Vi/Vs, intermediate/supracommissural nucleus of ventral telencephalon |
|
Confocal microscopic analysis of Otpa-positive cells in adult zebrafish brains of shh-GFP or islet1-GFP transgenic zebrafish line brains shows cellular co-localization of Otpa and shh-GFP in TPp-m cells (a?a2) and of Otpa and islet1-GFP in few midline pallial cells and within Vi (b-b3), massive such co-localization in Hv and some in ATN (c-c4) and Hc-a (d), as well as in PL (e-e2). Abbreviations. ATN, anterior tuberal nucleus; Hc-a, caudal zone of periventricular hypothalamus in front of posterior recess; Hv, ventral zone of periventricular hypothalamus; LH, lateral hypothalamic nucleus; llf, lateral longitudinal fascicle; NLV, nucleus lateralis valvulae; oc, optic chiasma; PL, perilemniscal nucleus; PM, magnocellular preoptic nucleus; Po, preoptic region; PPa/PPp, anterior/posterior parvocellular preoptic nucleus; PTN, posterior tuberal nucleus; PVO, paraventricular organ; RV, rhombencephalic ventricle; SC, suprachiasmatic nucleus; TPp, periventricular nucleus of posterior tuberculum; TPp-m, magnocellular cells of the periventricular posterior tubercular nucleus; Val, valvula cerebelli; Vi, intermediate nucleus of ventral telencephalon |
|
Schematic lateral view of adult zebrafish brain shows summary of (a) TH-positive brain nuclei (modified from Rink & Wullimann, 2002a; Wullimann & Rink, 2002), and (b) Otpa domains. (c) Schematic lateral view of adult zebrafish brain shows telencephalic and spinal connections of posterior tubercular nuclei. In (a), Arabic numbers, which were initially introduced in our developmental studies (Rink & Wullimann, 2002a; Wullimann & Rink, 2002), are also indicated for diencephalic and hypothalamic dopaminergic cell groups. Note that descending spinal projections of dopaminergic parvocellular periventricular posterior tubercular cells (TPp-p; Becker et al., 1997), and ascending projections of dopaminergic positive TPp-p and magnocellular pear-shaped periventricular posterior tubercular cells (TPp-m; Rink and Wullimann, 2001) have been previously established in the adult zebrafish brain (in larvae: Tay et al., 2011). Furthermore, TH-negative posterior tuberal (PTN) cells project to the zebrafish pallium (Rink & Wullimann, 2001, 2004; confirmed in goldfish by Northcutt, 2006). We propose the hypothesis that there are two populations of TPp-m cells, one with exclusive ascending projections to the striatum, and one with additional spinal projections, plus additional TPp-p projections to the striatum as well as ascending projections to the pallium from the posterior tuberal nucleus. (c) is modified from Rink and Wullimann (2002b). Abbreviations: A, ansulate commissure, ac anterior commissure; AP, area postrema; ATN, anterior tuberal nucleus; CC, crista cerebellaris; DON, descending octaval nucleus; DS, saccus dorsalis; DT, dorsal thalamus; DTN, dorsal tegmental nucleus; E, epiphysis; Flo, facial (sensory) lobe, GC, central gray; Ha, habenula; Hc/Hd/Hv, caudal/dorsal/ventral zone of periventricular hypothalamus; IN, intermediate hypothalamic nucleus; LC, locus coeruleus; LH, lateral hypothalamic nucleus; LR lateral hypothalamic recess; NC, commissural nucleus of Cajal; NLV, nucleus lateralis valvulae; Nmlf, nucleus of medial longitudinal fascicle; NIn, interpeduncular nucleus; OB, olfactory bulb; oc, optic chiasma; pc, posterior commissure; PL, perilemniscal nucleus; PM, magnocellular parvocellular preoptic nucleus; PMg, gigantocellular part of PM; Po, preoptic region; PPa/PPp, anterior/posterior parvocellular preoptic nucleus; PM, magnocellular preoptic nucleus; PPr, periventricular pretectum; PTN, posterior tuberal nucleus; PVO, paraventricular organ; SR, superior raphe; SRF, superior reticular formation; T, midbrain tegmentum; TLo, torus longitudinalis; TPp-m, magnocellular cells of the periventricular posterior tubercular nucleus; TPp-p, parvocellular cells of periventricular posterior tubercular nucleus; Va, valvula cerebelli; VLo, vagal (sensory) lobe; Vd/Vi//Vs/Vv, dorsal/intermediate/supracommissural/ventral nucleus of ventral telencephalon; VT, ventral thalamus |
|
The embryonic mouse basal diencephalon. (a) Schematic sagittal view of the embryonic mouse brain (modified from Vernier & Wullimann, 2009, based on data by Smeets & Gonzßlez 2000; MarÝn et al., 2005; Bj÷rklund & Dunnett, 2007; Vitalis et al., 2000) shows embryonic mammalian dopamine systems. Note position of A11 in the alar plate of prosomere 1 (P1). (b) Embryonic mouse brain sagittal section shows all major otp expression domains (taken from Developmental Mouse Brain Atlas, Allen Institute) except for that in the medial amygdala which is out of section plane. Note strong expression in the alar plate of P1 and sparse expression in the basal plate of P1 through P3. (c) Embryonic mouse brain sagittal section shows expression of bHLH gene ngn2 (modified from Osˇrio et al., 2010). Note the large domain selectively demarcating the region of interest, that is, the basal plate portions of midbrain and P1 through P3 (incl. spear-shaped expression domains flanking in addition the zona limitans intrathalamica between dorsal and ventral thalamus). (d) Embryonic mouse brain sagittal section shows expression domains of the geneTle4 (transducin-like enhancer of split 4; taken from Developmental Mouse Brain Atlas, Allen Institute) which has a potential role in basal diencephalic regions (P1?P3). Scale bar: 500 Ám (applies to all panels). Abbreviations: A8-A14, mammalian dopaminergic cell groups (see text). aP1/2, alar plates of prosomeres 1/2; bP1-3, basal plates of prosomeres 1?3; Ce, cerebellum; DT, dorsal thalamus; EmT, eminentia thalami; InCo, inferior colliculus; M, midbrain tegmentum; MA, mammillary hypothalamus; MO, medulla oblongata; OB, olfactory bulb; P, pallium; P1-P3, prosomeres 1?3; POA, anterior preoptic area; Pr, pretectum; PreM, premammillary region; PVN, paraventricular nucleus; RCH, retrochiasmatic area; RL, rhombic lip; S, subpallium; SC, spinal cord; SuCo, superior colliculus; Tub, tuberal hypothalamus; Ve (telencephalic), ventricle; VT, ventral thalamus; ZLI, zona limitans intrathalamica |