- Title
-
Tcap Deficiency in Zebrafish Leads to ROS Production and Mitophagy, and Idebenone Improves its Phenotypes
- Authors
- Lv, X., Zhang, R., Xu, L., Wang, G., Yan, C., Lin, P.
- Source
- Full text @ Front Cell Dev Biol
|
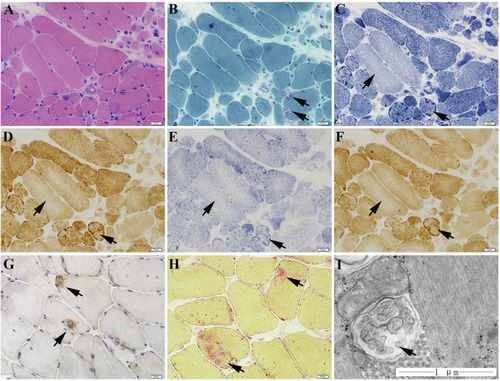
The muscle biopsy specimen from LGMD2G patient. |
|
|
|
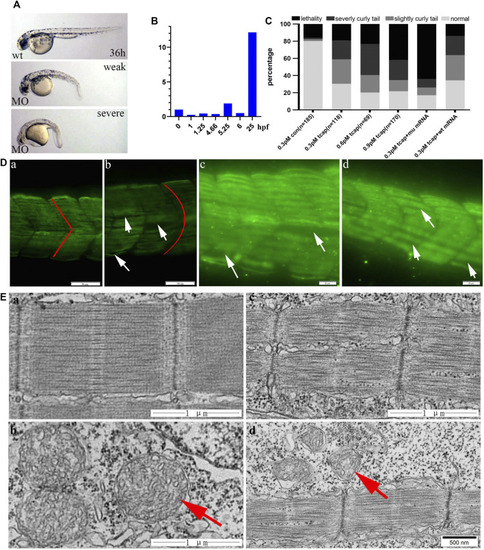
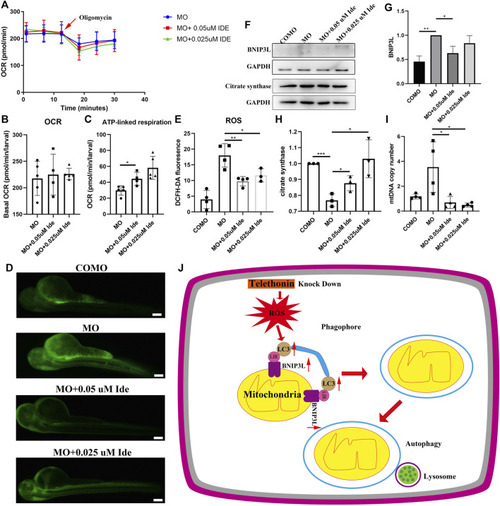
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|