- Title
-
The E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Mindbomb1 controls planar cell polarity-dependent convergent extension movements during zebrafish gastrulation
- Authors
- Saraswathy, V.M., Kurup, A.J., Sharma, P., Polčs, S., Poulain, M., Fürthauer, M.
- Source
- Full text @ Elife
|
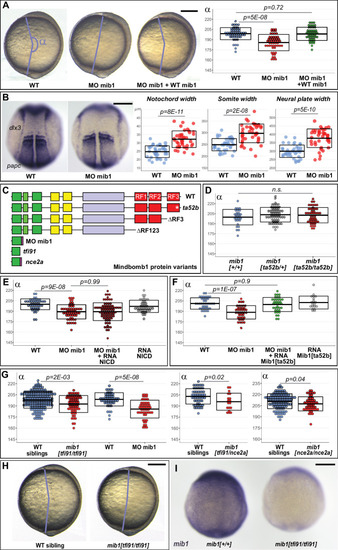
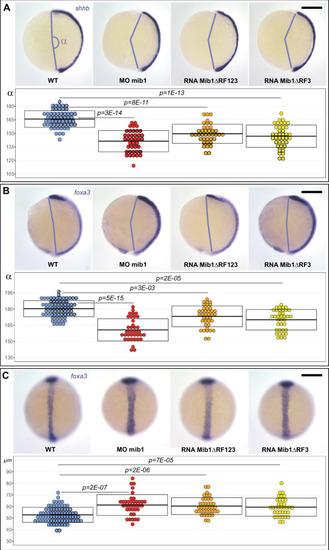
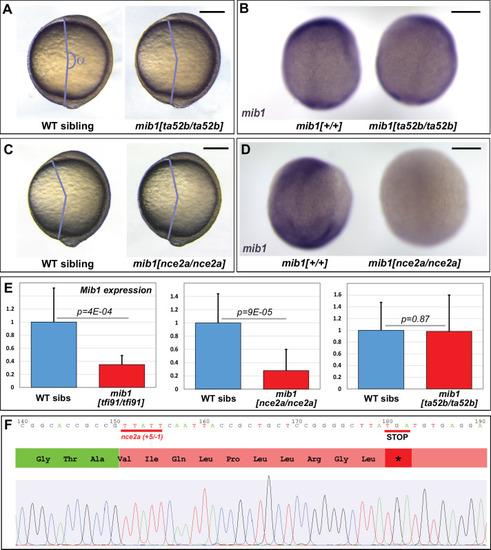
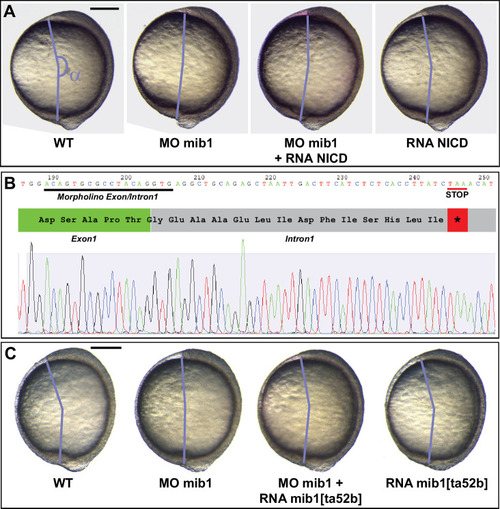
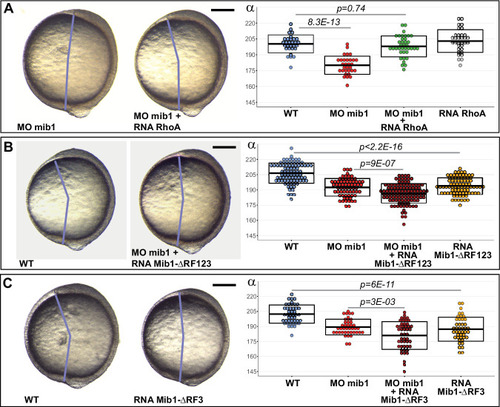
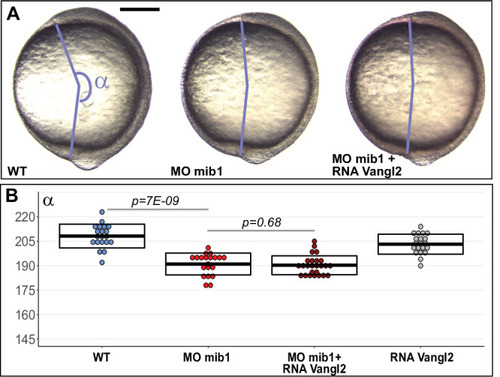
(A) Axis extension was quantified at bud stage by measuring the axis extension angle ?. Axis extension is reduced in mib1 morphants but restored upon coinjection of WT mib1 RNA. Lateral views of bud stage embryos, anterior up, dorsal to the right. (B) mib1 morphants present a widening of the notochord, somites, and neural plate. Dorsal views of 2 somite stage embryos, anterior up. dlx3 in situ hybridization outlines the neural plate, papc the somites and the adaxial cells lining the notochord. Widths indicated in microns. (C) Mib1 protein variants used in the study. (D) The mib1ta52b mutation has no effect on axis extension. (E) Constitutively activated Notch (NICD) fails to restore mib1 morphant axis extension. (F) mib1ta52b RNA injection restores mib1 morphant axis extension. (G,H) Axis extension is impaired in mib1tfi91 or mib1nce2a null mutants. On the left panel of (G) the mib1 morphant data from (A) are included for comparison. (I) In situ hybridization reveals reduced mib1 transcript levels in n = 27 mib1tfi91 mutant embryos. Dorsal views of bud stage embryos, anterior up. To warrant identical acquisition conditions, two embryos were photographed on a single picture. Scalebars: 200 µm. Boxes in (A,B, D?G) represent mean values ± SD. See Figure 1?source data 1 for complete statistical information
|
|
( |
|
( |
|
( |
|
( PHENOTYPE:
|
|
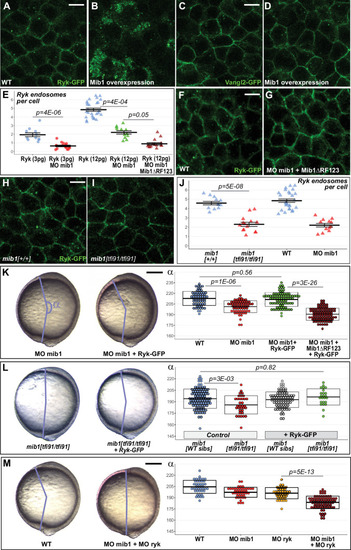
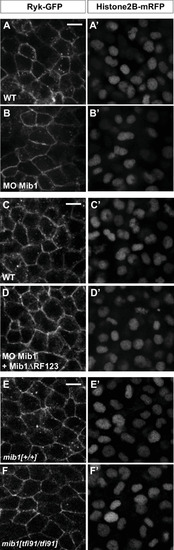
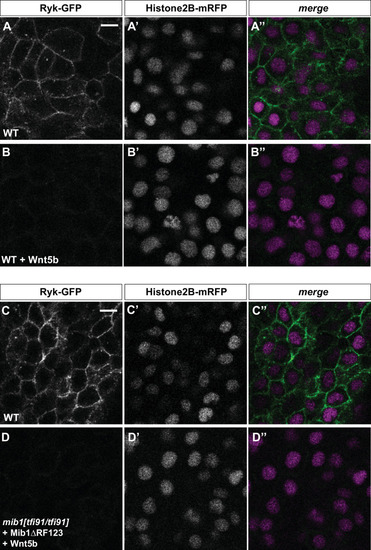
(A?D) WT mib1 RNA injection triggers Ryk internalization in 20/21 embryos (B) but has no effect on Vangl2 localization (D, n = 23). (E?G) Mib1 morpholino injection reduces the number of Ryk endosomes that are present upon injection of Ryk-GFP RNA. Increasing the dose of Ryk-GFP RNA restores endosome number in mib1 morphants but not in embryos coinjected with Mib1?RF123. (H?J) The number of Ryk endosomes that are present upon injection of Ryk-GFP RNA (12 pg) is reduced in mib1 null mutants. mib1 morphant data from panel E are shown again for comparison. (K) Ryk-GFP RNA (12 pg) rescues axis extension in mib1 morphants but not in embryos coinjected with Mib1?RF123. (L) Similarly Ryk-GFP injection rescues axis extension in mib1tf91 mutants. (M) Ryk morpholino injection aggravates mib1 morphant axis extension phenotypes. (A?D,F,G,H,I) dorsal views of 90% epiboly stage embryos, anterior up, scalebars 10 µm. (K,L,M) Lateral views of bud stage embryos, anterior up, scalebars 200 µm. In (E,J) each data point represents the mean number of endosomes for 20 cells from a single embryo. For comparison J again includes the mib1 morphant from panel E. Bars represent mean values ± SEM. In (K,L,M) boxes represent mean values ± SD. See Figure 3?source data 1 for complete statistical information.
|
|
( |
|
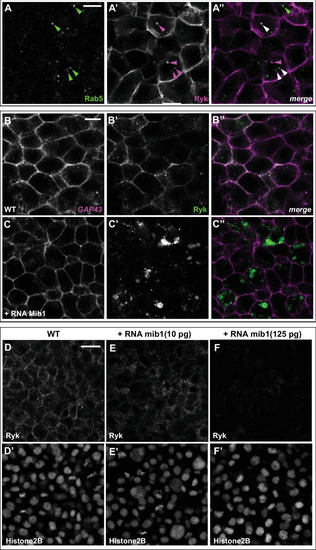
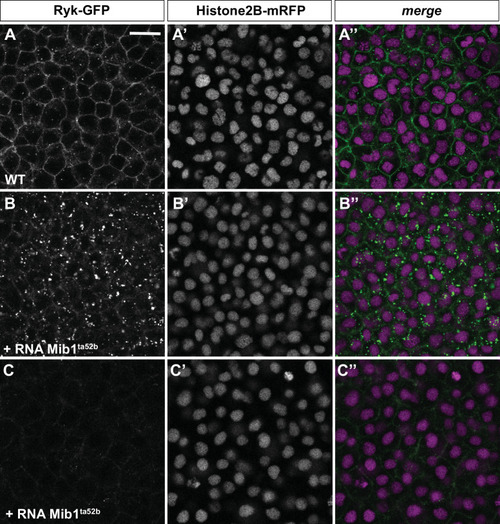
(A?C) Microinjection of RNA encoding the Mib1ta52b mutant protein induces Ryk internalisation (B, n = 16/23 embryos) or degradation (C, n = 7/23 embryos) as compared to WT controls (A, n = 21). Dorsal views of 90% epiboly stage embryos, anterior up. The Histone2B-mRFP signal (A?-C?) was used to ascertain that control and Mib1ta52b-expressing embryos had received comparable amounts of injected material. Scalebar: 20 µm.
|
|
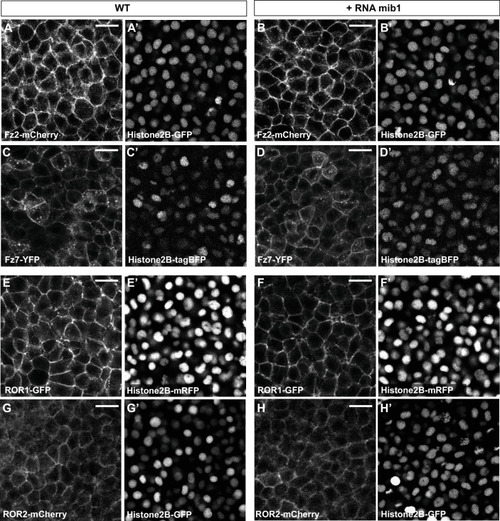
(A?D) Mib1 overexpression has no effect on the localization of the Wnt receptors Frizzled2 (Fz2, n = 6) or Frizzled7 (Fz7, n = 8). (E?H) Mib1 overexpression has no effect on the localization of the Wnt-binding receptor tyrosine kinases ROR1 (n = 7) or ROR2 (n = 10). All pictures depict dorsal views of 90% epiboly stage embryos, anterior up. (G,H) are sum projections of three consecutive confocal slices. A?-H? Display the signal for fluorescently tagged Histone2B constructs that were coinjected to ascertain that control and mib1-expressing embryos had received a comparable amounts of injected material. Scalebars: 20 µm.<
|
|
( |
|
( |
|
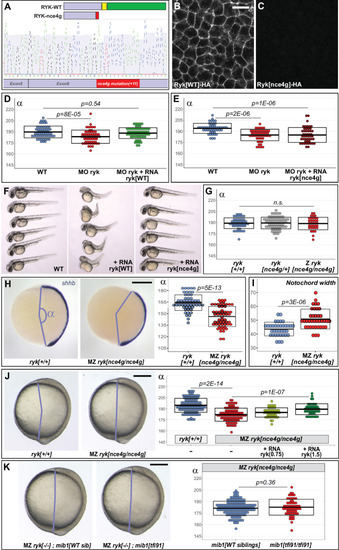
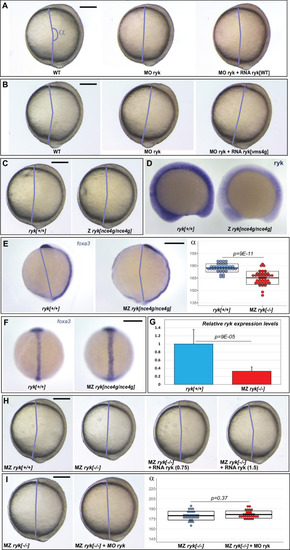
(A) ryknce4g mutants present an 11 base pair insertion in exon 6. The RYK-nce4g mutant protein comprises only part of the extracellular (blue) and lacks the entire transmembrane (yellow) and intracellular (green) domains. (B,C) Accordingly, a C-terminal HA tag that allows to localize WT Ryk (B, n = 12) becomes undetectable upon introduction of the ryknce4g mutation (C, n = 14). Dorsal views of 90% epiboly stage embryos, anterior up. Scalebar 20 µm. (D,E) The Convergent Extension (CE) phenotypes of ryk morphant animals can be rescued using 1.5 pg WT ryk (D) but not ryknce4g mutant (E) RNA. (F) Overexpressing high levels (25 pg) WT ryk RNA causes severe embryonic malformations while no effect is observed using ryknce4g mutant RNA. 32 hpf embryos, anterior to the left, dorsal up (n = 24 embryos/condition). (G) Zygotic (Z) ryk loss of function does not impair CE. (H?J) In contrast, Maternal Zygotic (MZ) ryk mutants present characteristic CE phenotypes such as a reduced axial elongation (H, shhb in situ hybridization) and an increased width of the notochord (I, foxa3 in situ hybridization, see also Figure 4?figure supplement 1F). (J) ryk WT RNA injection allows a significant rescue of MZ ryk mutant CE defects. (K) Similar CE defects are observed in MZ ryk single mutants and MZ ryk; mib1 double mutants. (H,J,K) Lateral views of bud stage embryos, anterior up, dorsal to the right. Scalebars 200 µm. In (D,E,G?K) boxes represent mean values ± SD. See Figure 4?source data 1 for complete statistical information.
|
|
( |
|
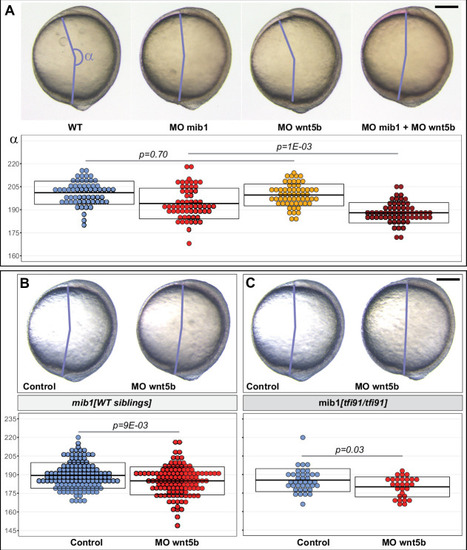
(A) Analysis of the axis extension angle ? in bud stage embryos reveals that a subliminal dose of wnt5b morpholino (MO wnt5b) that has no effect on Convergent Extension (CE) in WT significantly enhances the defects observed in animals injected with mib1 morpholino (MO mib1). (B,C) wnt5b morpholino injection impairs CE in mib1tfi91 WT siblings (B) and enhances CE defects in mib1tfi91 homozygous mutants (C). (A?C) Lateral views of bud stage embryos, anterior up, dorsal to the right. Scalebars 200 µm. Boxes represent mean values ± SD. See Figure 5?source data 1 for complete statistical information.
|
|
( |