- Title
-
A novel gene trap line for visualization and manipulation of erbb3b+ neural crest and glial cells in zebrafish
- Authors
- Brown, E.A., Kawakami, K., Kucenas, S.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Biol.
|
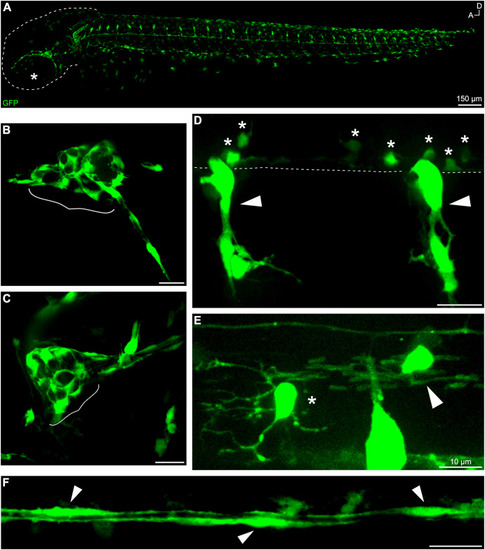
Fig. 1. gSAIzGFFD37A-driven GFP is expressed in neural crest-derived cells and glial subtypes. (A) Whole-mount, in vivo imaging of a gSAIzGFFD37A embryo at 48 hpf (dashed line outlining head; star marking eye). In vivo imaging of fluorescent structures including (B) anterior lateral line ganglion and (C) posterior lateral line ganglion (in brackets) at 48 hpf. Trunk structures include (D) neural crest-derived glia (arrows) and ventral OPCs (stars). Dashed line denotes edge of ventral spinal cord. (E) GFP+ OPC (star) and OL (arrow) at 72 hpf in the spinal cord. (F) GFP+ lateral line Schwann cells at 48 hpf. Scale bars, 20 ??m unless otherwise noted. |
|
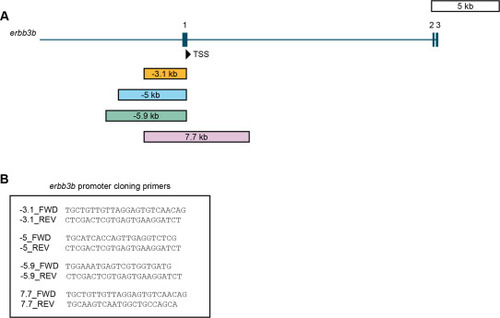
Fig. 2. gSAIzGFFD37A is located in erbb3b intron 7/8. (A) erbb3b transcript structure with exons shaded as rectangles. (B) Zoomed in view of intron 7/8 from box and arrow in panel (A). Inverse PCR sequencing (orange) revealed that the insertion site (yellow) is 61 bp downstream of erbb3b exon 7 and 2.9 ?kb upstream of exon 8 on the + strand of chromosome 23 (Tol2 ?= ?Tol2 element; FRT = FRT site; gSA ?= ?splice acceptor; IRES ?= ?internal ribosome entry sequence; zGFF2 ?= ?Gal4 transcription activator; SV40-pA ?= ?SV40 polyadenylation signal sequence; h-globin pA ?= ?globin polyadenylation signal sequence). (C) Primers used for inverse PCR and sequencing. (D) Gel electrophoresis of products from the second round of inverse PCR. (E) Chromatogram of initial sequence reads from purified 5? end bands (top) and 3? end bands (bottom) starting from the gSAIzGFFD insertion site. |
|
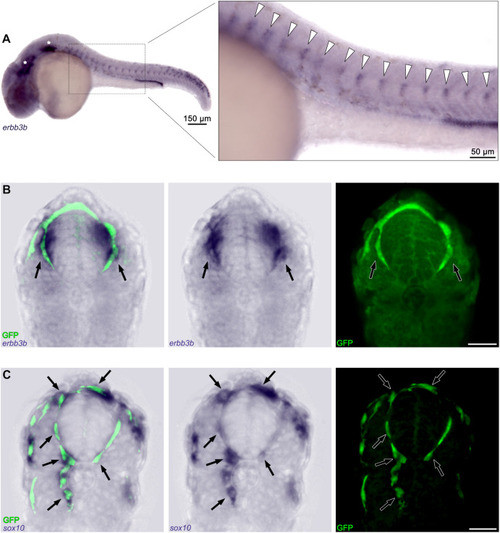
Fig. 3. In situ hybridization confirms erbb3b expression in GFP+ ?cells. (A) Whole-mount, in situ hybridization for erbb3b in gSAIzGFFD37A fish at 24 hpf. Anterior and posterior lateral line ganglia indicated by stars and trunk neural crest cells by arrowheads. Sections of (B) erbb3b and (C) sox10 in situ hybridization after antibody labeling of GFP (arrows indicate areas of colocalization between the respective mRNA transcript and erbb3b-driven fluorophore expression). Scale bars, 20 ??m unless otherwise noted. |
|
Fig. 4. erbb3b-driven transgene is co-expressed with sox10 in neural crest cells and a subset of glia (A) Images from an in vivo time-lapse movie of Tg(sox10:TagRFP);gSAIzGFFD37A embryos from 17 to 24 hpf. GFP expression is visible in trunk neural crest cells at 19.5 hpf. Neural crest delamination indicated by arrowheads. (B) Whole-mount, in vivo imaging of Tg(sox10:TagRFP);gSAIzGFFD37A larvae at 120 hpf (dashed line outlining head; star marking eye). (C) Confocal imaging of double-positive trunk neural crest-derived glia in the dorsal root ganglion such as satellite glia (white arrowheads) and peripheral glia (open arrowheads) including MEP glia and Schwann cells; TagRFP+/GFP? OL indicated by asterisk. (D) Other double-positive Schwann cells (arrowheads) along the posterior lateral line nerve. Scale bars, 20 ??m unless otherwise noted. |
|
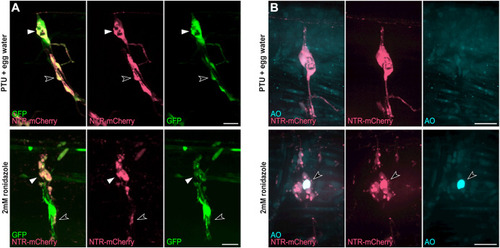
Fig. 5. Cell specific ablation using the erbb3b-driven transgene (A) Tg(UAS:NTR-mCherry);gSAIzGFFD37A larvae at 120 hpf after 24 ?h treatment of phenyl-thiourea (PTU) and egg water (Top) or 2 ?mM ronidazole (Bottom) with labeled satellite glia (white arrowheads) and Schwann cells (open arrowheads) in dorsal root ganglia (DRG). (B) Acridine orange (AO) staining of apoptotic cells (arrowhead) in Tg(UAS:NTR-mCherry);gSAIzGFFD37A (GFP-negative) larvae at 120 hpf after 24 ?h treatment of PTU and egg water (Top) or 2 ?mM ronidazole (Bottom). Scale bars, 20 ??m unless otherwise noted. |
|
figs1. |
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 482, Brown, E.A., Kawakami, K., Kucenas, S., A novel gene trap line for visualization and manipulation of erbb3b+ neural crest and glial cells in zebrafish, 114-123, Copyright (2021) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.