|
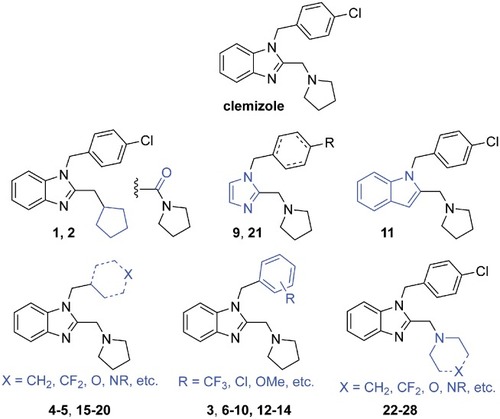
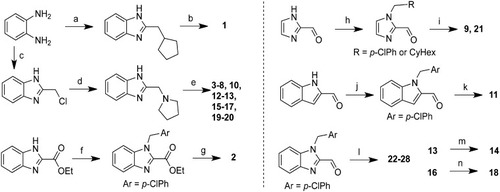
Synthesis of clemalogues. Summary of synthetic routes used to prepare clemalogues 1–28. (a) cyclopentylacetic acid, PPA, μw, 80°C, 20%; (b) ClCH2(4-ClPh), K2CO3, DMF, 60°C, 67%; (c) ethyl 4-Cl-3-oxobutanoate, SnCl2, EtOH, 80°C; (d) pyrrolidine, EtOH, 95°C; 83% for two steps (e) Br-CH2R, NaH, THF, 0°C to rt, 15–60% or Br-CH2R, NaH, TBAI, THF, 0°C to rt, 13–54% or propyl iodide, NaH, THF, 0°C to rt, 47%;(f) p-Cl-benzylchloride, NaH, DMF, rt, 54%; (g) (i) LiOH, MeOH/water, rt, (ii) pyrrolidine, HATU, DIEA, DMF, rt, 43% over 2 steps; (h) p-Cl-benzylchloride, K2CO3, CH3CN, 45°C, 85% or cyclohexylmethyl bromide, K2CO3, TBAI, CH3CN, 55°C, 30%; (i) pyrrolidine, Na(OAc)3BH, CH2Cl2; 30–46%; (j) ClCH2Ar, K2CO3, CH3CN, 45°C, 44%; (k) pyrrolidine, Na(OAc)3BH, CH2Cl2, rt, 65%; (l) HNR2, Na(OAc)3BH, CH2Cl2, rt, 47–85%; (m) H2, Pd/C, MeOH, rt, 55%; (n) 4 M HCl in dioxane, rt.
|