- Title
-
Adult islet1 Expression Outlines Ventralized Derivatives Along Zebrafish Neuraxis
- Authors
- Baeuml, S.W., Biechl, D., Wullimann, M.F.
- Source
- Full text @ Front. Neuroanat.
|
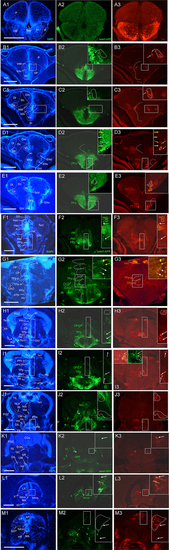
Analysis of islet1-GFP expression in the adult zebrafish brain using a rostrocaudal series of sections showing also fluorescent DAPI stain and tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) immunohistochemistry from olfactory bulb (A) to hindbrain (M). The left column (A1–M1) presents a general neuroanatomical analysis performed on the nuclear stain DAPI. In the middle column (A2–M2), only brain nuclei containing islet1-GFP cell bodies and motor cranial nerves, but not other stained fibers, are identified in green lettering. In the right column (A3–M3) only brain nuclei containing TH positive cell bodies are identified in red lettering. White arrows/fine stippled lines point to/encircle single labeled cell bodies/cell populations, whereas yellow arrows/fine stippled lines point to/encircle double-labeled cell bodies/cell populations. Occasionally, selected structures pointed out in DAPI stains with coarse stippled lines are also indicated in the islet1-GFP and TH pictures to ease identification. In (B,C), the boundary between dorsal and ventral parts of the dorsal nucleus of the subpallium is indicated with a red stippled line. In (I3), the inset in the upper left corner is taken from a different specimen. A, anterior thalamic nucleus; ac, anterior commissure; ALLN, anterior lateral line nerve; AP, area postrema; ATN, anterior tuberal nucleus; C, central canal; CC, crista cerebellaris; CCe, corpus cerebelli; cgus, commissure of secondary gustatory nuclei; cinf, commissura infima of Haller; CM, corpus mamillare; CON, caudal octavolateralis nucleus; CP, central posterior thalamic nucleus; cven, ventral rhombencephalic commissure; DAO, dorsal accessory optic nucleus; Dc, central zone of dorsal telencephalon; dIV, decussation of trochlear nerve; DIL, diffuse nucleus of inferior lobe; DiV, diencephalic ventricle; Dl, lateral zone of dorsal telencephalon; Dm, medial zone of dorsal telencephalon; DON, descending octaval nucleus; DP, dorsal posterior thalamic nucleus; Dp, posterior zone of dorsal telencephalon; DS, saccus dorsalis; DT, dorsal thalamus; DTN, dorsal tegmental nucleus; EG, eminentia granularis; End/ENv, dorsal/ventral entopeduncular nucleus; fr, fasciculus retroflexus; GC, griseum centrale; gl, glomerular layer (olfactory bulb); Had/Hav, dorsal/ventral habenular nucleus; Hc/Hd/Hv, caudal/dorsal/ventral zone of periventricular hypothalamus; iaf, internal arcuate fibers; icl, inner granular cell layer (olfactory bulb); IMRF, intermediate reticular formation; IN, intermediate hypothalamic nucleus; IO, inferior olive; IR, inferior raphe; IRF, inferior reticular formation; LIX, lobus glossopharyngeus; LVII, lobus facialis; LX, lobus vagus; LC, locus coeruleus; lfb, lateral forebrain bundle; LH, lateral hypothalamic nucleus; MA, Mauthner axon; mfb, medial forebrain bundle; MFN, medial funicular nucleus; mlf, medial longitudinal fascicle; MON, medial octavolateralis nucleus; NIII, oculomotor nerve nucleus; NIV, trochlear motor nerve nucleus; NIXm, glossopharyngeal motor nerve nucleus; NVmd, dorsal trigeminal motor nerve nucleus; NVmv, ventral trigeminal motor nerve nucleus; NVs, primary sensory trigeminal nucleus; NVIc/NVIr, caudal/rostral abducens motor nerve nucleus; NVIImc/NVIImr, caudal/rostral facial motor nerve nucleus; NXm, vagal motor nerve nucleus; pc, posterior commissure; NI, nucleus isthmi; NIn, Nucleus interpeduncularis; NLV, nucleus lateralis valvulae; OB, olfactory bulb; OENc/OENr, caudal/rostral octavolateralis efferent neurons; P, pallium; pc, posterior commissure; PG, preglomerular complex; PGm, medial preglomerular nucleus; PGZ, periventricular gray zone of optic tectum; Pit, pituitary; PLc, caudal perilemniscal nucleus; PM, magnocellular preoptic nucleus; poc, postoptic commissure; PPa/PPp, anterior/posterior parvocellular preoptic nucleus; PPr, periventricular pretectum; PR, posterior hypothalamic recess; PTN, posterior tuberal nucleus; PVO, paraventricular organ; RT, rostral tegmental nucleus (of Grover and Sharma, 1981); RV, rhombencephalic ventricle; SC, suprachiasmatic nucleus; SD, subpallial dopaminergic cells; SGN, secondary gustatory nucleus; SGT, secondary gustatory tract; SP, subpallium; SPr, superficial pretectum; SO, spino-occipital region; SR, superior raphe; SRF, superior reticular formation; SRN, superior reticular nucleus; TelV, telencephalic ventricle; TeO, optic tectum; TeV, tectal ventricle; TLa, torus lateralis; TLo, torus longitudinalis; TPp, periventricular nucleus of posterior tuberculum; TPp-p, parvocellular cell part of TPp; TPp-m, magnocellular (pear-shaped) cell part of TPp; TS, torus semicircularis; ttb, tractus tecto-bulbaris; Val, lateral part of valvula cerebelli; Vam, medial part of valvula cerebelli; Vas, vascular lacuna; Vdd/Vdv, dorsal/ventral subnucleus of dorsal nucleus of ventral telencephalon; VG, vagal group of catecholamine neurons; VH, ventral horn; VL/VM, ventrolatateral/ventromedial thalamic nucleus; vot, ventrolateral optic tract; Vp/Vs/Vv, posterior/supracommissural/ventral nucleus of ventral telencephalon; vr, ventral spinal root; Vsr, sensory trigeminal root; IV/V/VIII/IX/X, trochlear, trigeminal, octaval, glossopharyngeal, vagal nerve (motor components). |
|
Analysis of islet1-GFP expression in the adult zebrafish brain using a rostrocaudal series of sections showing also fluorescent DAPI stain and choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) immunohistochemistry from olfactory bulb (A) to spinal cord (Q). The left column (A1–Q1) presents a general neuroanatomical analysis performed on the nuclear stain DAPI. In the middle column (A2–Q2), only brain nuclei containing islet1-GFP cell bodies and motor cranial nerves, but not other stained fibers, are identified in green lettering. In the right column (A3–Q3) only brain nuclei containing ChAT positive cell bodies and some motor nerve fibers are identified in red lettering. White arrows/fine stippled lines point to/encircle single labeled cell bodies/cell populations, whereas yellow arrows/fine stippled lines point to/encircle double-labeled cell bodies/cell populations. Occasionally, selected structures pointed out in DAPI stains with coarse stippled lines are also indicated in the islet1-GFP and ChAT pictures to ease identification. A conspicuous islet1-GFP positive tract is present from the level of the medial preglomerular nucleus where it is encircled with a red coarse stippled line (C1,C2) and then identified with an asterisk into the isthmic level (D2–I2). #: indicates in (D3–H3) a ChAT positive fiber net (see Mueller et al., 2004). A, anterior thalamic nucleus; ac, anterior commissure; ALLN, anterior lateral line nerve; AP, area postrema; ATN, anterior tuberal nucleus; C, central canal; CC, crista cerebellaris; CCe, corpus cerebelli; cgus, commissure of secondary gustatory nuclei; cinf, commissura infima of Haller; CM, corpus mamillare; CON, caudal octavolateralis nucleus; CP, central posterior thalamic nucleus; cven, ventral rhombencephalic commissure; DAO, dorsal accessory optic nucleus; Dc, central zone of dorsal telencephalon; dIV, decussation of trochlear nerve; DIL, diffuse nucleus of inferior lobe; DiV, diencephalic ventricle; Dl, lateral zone of dorsal telencephalon; Dm, medial zone of dorsal telencephalon; DON, descending octaval nucleus; DP, dorsal posterior thalamic nucleus; Dp, posterior zone of dorsal telencephalon; DS, saccus dorsalis; DT, dorsal thalamus; DTN, dorsal tegmental nucleus; EG, eminentia granularis; End/ENv, dorsal/ventral entopeduncular nucleus; fr, fasciculus retroflexus; GC, griseum centrale; gl, glomerular layer (olfactory bulb); Had/Hav, dorsal/ventral habenular nucleus; Hc/Hd/Hv, caudal/dorsal/ventral zone of periventricular hypothalamus; iaf, internal arcuate fibers; icl, inner granular cell layer (olfactory bulb); IMRF, intermediate reticular formation; IN, intermediate hypothalamic nucleus; IO, inferior olive; IR, inferior raphe; IRF, inferior reticular formation; LIX, lobus glossopharyngeus; LVII, lobus facialis; LX, lobus vagus; LC, locus coeruleus; lfb, lateral forebrain bundle; LH, lateral hypothalamic nucleus; MA, Mauthner axon; mfb, medial forebrain bundle; MFN, medial funicular nucleus; mlf, medial longitudinal fascicle; MON, medial octavolateralis nucleus; NIII, oculomotor nerve nucleus; NIV, trochlear motor nerve nucleus; NIXm, glossopharyngeal motor nerve nucleus; NVmd, dorsal trigeminal motor nerve nucleus; NVmv, ventral trigeminal motor nerve nucleus; NVs, primary sensory trigeminal nucleus; NVIc/NVIr, caudal/rostral abducens motor nerve nucleus; NVIImc/NVIImr, caudal/rostral facial motor nerve nucleus; NXm, vagal motor nerve nucleus; pc, posterior commissure; NI, nucleus isthmi; NIn, Nucleus interpeduncularis; NLV, nucleus lateralis valvulae; OB, olfactory bulb; OENc/OENr, caudal/rostral octavolateralis efferent neurons; P, pallium; pc, posterior commissure; PG, preglomerular complex; PGm, medial preglomerular nucleus; PGZ, periventricular gray zone of optic tectum; Pit, pituitary; PLc, caudal perilemniscal nucleus; PM, magnocellular preoptic nucleus; poc, postoptic commissure; PPa/PPp, anterior/posterior parvocellular preoptic nucleus; PPr, periventricular pretectum; PR, posterior hypothalamic recess; PTN, posterior tuberal nucleus; PVO, paraventricular organ; RT, rostral tegmental nucleus (of Grover and Sharma, 1981); RV, rhombencephalic ventricle; SC, suprachiasmatic nucleus; SD, subpallial dopaminergic cells; SGN, secondary gustatory nucleus; SGT, secondary gustatory tract; SP, subpallium; SPr, superficial pretectum; SO, spino-occipital region; SR, superior raphe; SRF, superior reticular formation; SRN, superior reticular nucleus; TelV, telencephalic ventricle; TeO, optic tectum; TeV, tectal ventricle; TLa, torus lateralis; TLo, torus longitudinalis; TPp, periventricular nucleus of posterior tuberculum; TPp-p, parvocellular cell part of TPp; TPp-m, magnocellular (pear-shaped) cell part of TPp; TS, torus semicircularis; ttb, tractus tecto-bulbaris; Val, lateral part of valvula cerebelli; Vam, medial part of valvula cerebelli; Vas, vascular lacuna; Vdd/Vdv, dorsal/ventral subnucleus of dorsal nucleus of ventral telencephalon; VG, vagal group of catecholamine neurons; VH, ventral horn; VL/VM, ventrolatateral/ventromedial thalamic nucleus; vot, ventrolateral optic tract; Vp/Vs/Vv, posterior/supracommissural/ventral nucleus of ventral telencephalon; vr, ventral spinal root; Vsr, sensory trigeminal root; IV/V/VIII/IX/X, trochlear, trigeminal, octaval, glossopharyngeal, vagal nerve (motor components). |
|
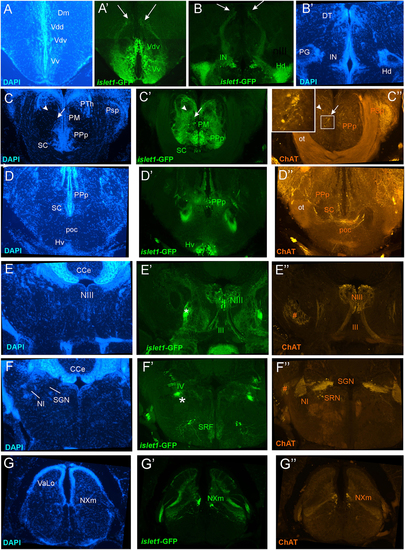
Details of islet1-GFP expression using fluorescent DAPI stain and tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) immunohistochemistry. Conventions with lettering as in Figure 1. (A,A’) islet1 expression in precommissural subpallium shows positivity in ventral, and negativity in central (Vc) and lateral nuclei (Vl). (B,B’) islet1-GFP expression in supracommissural nucleus (Vs). (C–C”’) islet1-GFP fibers in intermediate nucleus of the ventral telencephalon. Note also TH cells in the anterior parvocellular preoptic nucleus (PPa). (D–D”) Dopamine cells in magnocellular (PM), posterior parvocellular (PPp), and suprachiasmatic nuclei (SC), with only cells in PPp double-labeled for islet1-GFP. (E) Origin of the dorsal accessory optic nucleus (DAO) as suggested by a chain of islet1-GFP cells (arrowheads) that apparently migrate pially from the parvocellular periventricular posterior tubercular nucleus (TPp-p) and merge into the DAO. Straight stippled line indicates midline. (E’) Slightly more medially taken picture shows the parvocellular (TPp-p) and pear-shaped (TPp-m) parts of TPp on both brain sides in TH immunostaining. Note that some cells in TPp-p are double-labeled. (F–G) Analysis of anterior part of caudal zone of periventricular hypothalamus (Hc) and posterior tuberal nucleus (PTN) at rostral (F: DAPI, F’: islet1-GFP, F”: TH stain) and caudal levels (G: DAPI, G’: islet1-GFP, G”: TH stain). Note that there are no TH and islet1-GF double-labeled cells in PTN. ac, anterior commissure; DAO, dorsal accessory optic nucleus; DIL, diffuse nucleus of the inferior lobe; Dl, lateral zone of dorsal telencephalon; Dm, medial zone of the dorsal telencephalon; DP, dorsal posterior thalamic nucleus; E, epiphysis (pineal); ENd, dorsal entopeduncular nucleus; Hc/Hd, caudal/dorsal zone of periventricular hypothalamus; mfb, medial forebrain bundle; PG, preglomerular complex; PGZ, periventricular gray zone of optic tectum; Pit, pituitary; PM, magnocellular preoptic nucleus; PPa/PPp, anterior/posterior parvocellular preoptic nucleus; PTh, prethalamus; PTN, posterior tuberal nucleus; TLa, torus lateralis; TPp-m/TPP-p, magnocellular (pear-shaped)/parvocellular cell part of periventricular posterior tubercular nucleus; Vc/Vd/Vi/Vl/Vp/Vs/Vv, central/dorsal/intermediate/lateral/posterior/ supracommissural/ventral nucleus of ventral telencephalon; SC, suprachiasmatic nucleus; SD, subpallial dopamine cells; VI, abducens nerve. |
|
Details of islet1-GFP expression using fluorescent DAPI stain and choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) immunohistochemistry. Conventions with lettering as in Figure 2. (A,A’) Cholinergic cells in anterior parvocellular preoptic nucleus (PPa) are never double-labeled with islet1-GFP. (B,B’)Cholinergic cells in magnocellular and posterior parvocellular preoptic nuclei (PM, PPp) and suprachiasmatic nucleus (SC) are never double-labeled with islet1-GFP. (C,C’) Shows islet1-GFP positive axonal tract from the ventral nucleus of the ventral telencephalon (Vv) to the medial zone of the dorsal telencephalon (Dm). (D) Magnification shows how hypothalamic tract leads into the medial part of the secondary gustatory nucleus with some collaterals into the central gray. (E,E’) Magnification of midbrain tegmentum shows lateral to the oculomotor nerve nucleus (NIII) the additional cholinergic cells of the nucleus of Edinger–Westphal (NEW; yellow arrows) to be double-labeled for islet1-GFP. Note also the few non-cholinergic cells of the rostral perilemniscal nucleus stained for islet1-GFP. (F,F’)Highlights the few cholinergic/islet1-GFP positive cells (yellow arrows) ventrolateral to the caudal perilemniscal nucleus which itself is islet1-GFP negative, but ChAT positive. #: indicates a ChAT positive fiber net (See Mueller et al., 2004). (G,G’) islet1-GFP cells in the rostral perilemniscal nucleus (PLr). (H–H”) islet1-GFP positive cells in the nucleus of the medial longitudinal fascicle (Nmlf) and cholinergic cells in the dorsal thalamus (DT) and near the preglomerular region (PG). (I,I’) islet1-GFP cells in the Nmlf or possibly the mesencephalic sensory trigeminal nucleus at the level of an islet1-GFP axonal tract that projects from the intermediate hypothalamic nucleus (IN) to the dorsal thalamus. dIV, decussation of trochlear nerve; Dm, medial zone of dorsal telencephalon; DT, dorsal thalamus; DTN, dorsal tegmental nucleus; GC, griseum centrale; Hd, dorsal zone of periventricular hypothalamus; IN, intermediate hypothalamic nucleus; IIf, lateral forebrain bundle; NIII, oculomotor nerve nucleus; NEW, nucleus of Edinger–Westphal; NI, nucleus isthmi; NLL, nucleus of the lateral lemniscus (of Prasada Rao et al., 1987); Nmlf, nucleus of the medial longitudinal fascicle; ot, optic tract; PG, preglomerular complex; PGZ, periventricular layer of optic tectum; PLc/PLr, caudal/rostral perilemniscal nucleus; PM, magnocellular preoptic nucleus; PPa/PPp, anterior/posterior parvocellular preoptic nucleus; SC, suprachiasmatic nucleus; SGN, secondary gustatory nucleus; SRN, superior reticular nucleus; TS, torus semicircularis; Va, valvula cerebelli; Vc/Vd/Vv, central/dorsal/ventral nucleus of ventral telencephalon; IV, trochlear nerve. |
|
Details of islet1-GFP expression using fluorescent DAPI stain and choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) immunohistochemistry at 6 months of age. Conventions with lettering as in Figure 2. (A,A’) shows islet1-GFP positive axonal tract from the ventral nucleus of the ventral telencephalon (Vv) to the medial zone of the dorsal telencephalon (Dm). (B,B’) islet1-GFP axonal tract that projects from the intermediate hypothalamic nucleus (IN) to the dorsal thalamus. (C,D)Analysis of preoptic region at (C: DAPI, C’: islet1-GFP, C”: ChAT) level of magnocellular preoptic nucleus (PM) and (D: DAPI, D’: islet1-GFP, D”: ChAT) postoptic commissure (poc). Note that preoptic cholinergic cells are never double-labeled for islet1-GFP and strong cholinergic terminal field in the parvocellular superficial pretectal nucleus (PSp) originating in nucleus isthmi. Arrowhead in (C) indicates artifact (no DAPI cell nucleus seen). (E–E”) Magnification of midbrain tegmentum shows oculomotor nerve nucleus (NIII) and nerve exiting the brain (III). Asterisk points out hypothalamo-secondary gustatory nuclear tract. # indicates a ChAT positive fiber net (see Mueller et al., 2004). (F–F”)Region of secondary gustatory nucleus (SGN) shows ChAT cells in SGN and nucleus isthmi (NI) and superior reticular nucleus (SRN). Asterisk points out hypothalamo-secondary gustatory nuclear tract. # indicates a ChAT positive fiber net (see Mueller et al., 2004). (G–G”) Region of vagal sensory lobe (VaLo) and vagal motor nerve nucleus (NXm) shows some cholinergic vagal motor cells double-labeled for islet1-GFP. CCe, corpus cerebelli; Dm, medial zone of dorsal telencephalon; Hd/Hv, dorsal/ventral zone of periventricular hypothalamus; IN, intermediate hypothalamic nucleus; NI, nucleus isthmi; NIII, oculomotor nerve nucleus; NXm, vagal motor nerve nucleus; ot, optic tract; PM, magnocellular preoptic nucleus; poc, postoptic commissure; PPp, posterior parvocellular preoptic nucleus; PSp, parvocellular superficial pretectal nucleus; PTh, prethalamus; SC, suprachiasmatic nucleus; SGN, secondary gustatory nucleus; SRF, superior reticular formation; SRN, superior reticular nucleus; VaLo, vagal (sensory) lobe; Vdd/Vdv, dorsal/ventral subnucleus of dorsal nucleus of ventral telencephalon; Vv, ventral nucleus of the ventral telencephalon; III, oculomotor nerve; IV, trochlear nerve. |
|
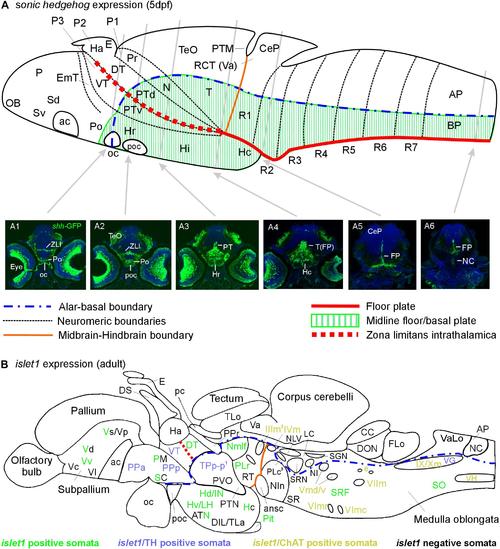
Schematic sagittal sections of a larval (A) and an adult (B) zebrafish brain. (A) summarizes sonic hedgehog-GFP expression at the larval stage (4–5 days) in floor plate of midbrain/hindbrain and forebrain basal/alar plate as described previously (Biechl et al., 2016). (A1–A6) Transverse sections illustrate shh-GFP expression at levels indicated. Note that at larval stages, the most anterior sonic hedgehog-GFP expression site is in the alar plate preoptic region and that there is no additional basal telencephalic expression. (B) shows adult islet1-GFP expression (color letters) versus structures negative for this gene expression (black letters) as established in the present study. See figure for color code of islet1-GFP structures either singly labeled or double-labeled for tyrosine hydroxylase or choline acetyltransferase in addition. Structures with islet1-GFP cells in a restricted subarea are shown using black and colored letters. Overall, islet1-GFP expressing structures are in the basal plate, except for the preoptic region, the thalamus and the subpallial telencephalon (see text for more information). (1) Note that the large posterior tubercular pear-shaped dopaminergic neurons (TPp-m) projecting to basal ganglia (Vd) are islet1-GFP negative. Note furthermore that islet1-GFP cells of the dorsal accessory optic nucleus appear to originate in TPp-p. (2) Note that also the visceromotor Edinger–Westphal nucleus is double-labeled. (3) Note that cholinergic cells ventrolateral to the also cholinergic caudal perilemniscal nucleus (PLc) express islet1-GFP. ac, anterior commissure; ansc, ansular commissure; AP, alar plate in (A) and area postrema in (B); ATN, anterior tuberal nucleus; BP, basal plate; CC, crista cerebellaris; CCe, corpus cerebelli; CeP, cerebellar plate; DIL, diffuse nucleus of inferior lobe; DON, descending octaval nucleus; DS, saccus dorsalis; DT, dorsal thalamus; e, octavolateralis efferent neurons; EmT, eminentia thalami; FLo, facial (sensory) lobe; FP, floor plate; Ha, habenula; Hc/Hd/Hv, caudal/dorsal/ventral zone of periventricular hypothalamus; Hi/Hr (larval), intermediate/rostral hypothalamus; IN, intermediate hypothalamic nucleus; LC, locus coeruleus; LH, lateral hypothalamic nucleus; N, area of nucleus of medial longitudinal fascicle; NC, notochord in A6, commissural nucleus of Cajal in (B); NI, nucleus isthmi; NIn, nucleus interpeduncularis; NLV, nucleus lateralis valvulae; OB, olfactory bulb; oc, optic chiasma; P, pallium; pc, posterior commissure; Pit, pituitary; PLc/PLr, caudal/rostral perilemniscal nucleus; PM, magnocellular preoptic nucleus; Po, preoptic region; poc, postoptic commissure; PPa/PPp, anterior/posterior parvocellular preoptic nucleus; Pr, pretectum; PTd/PTv, dorsal/ventral posterior tuberculum; PTM, posterior tectal membrane; PTN, posterior tuberal nucleus; PVO, paraventricular organ; R1–R7, rhombomeres 1–7; RCT, rostral cerebellar thickening; SC, suprachiasmatic nucleus; SCm, spinal cord motor cells; Sd/Sv (larval), dorsal/ventral subpallium; SGN, secondary gustatory nucleus; SO, spino-occipital region; SR, superior raphe; SRF, superior reticular formation; SRN, superior reticular nucleus; T, midbrain tegmentum; TeO, optic tectum; TLa, torus lateralis; TLo, torus longitudinalis; TPp-p, parvocellular cell part of periventricular posterior tubercular nucleus; Va, valvula cerebelli; VaLo, vagal (sensory) lobe; Vc/Vd/Vp/Vs/Vv, central/dorsal/posterior/supracommissural/ventral nucleus of ventral telencephalon; VG, vagal group of catecholamine neurons; VH, spinal ventral horn motor cells; VT, ventral thalamus; ZLI, zona limitans intrathalamica; IIIm, oculomotor nerve nucleus; IVm, trochlear motor nerve nucleus; IXm, glossopharyngeal motor nerve nucleus; Vmd, dorsal trigeminal motor nerve nucleus; Vmv, ventral trigeminal motor nerve nucleus; VImc/VImr, caudal/rostral abducens motor nerve nucleus; VIImc/NVIImr, caudal/rostral facial motor nerve nucleus; IX/NXm, glossopharyngeal/vagal motor nerve nucleus. |