- Title
-
Characterisation of maturation of photoreceptor cell subtypes during zebrafish retinal development
- Authors
- Crespo, C., Knust, E.
- Source
- Full text @ Biol. Open
|
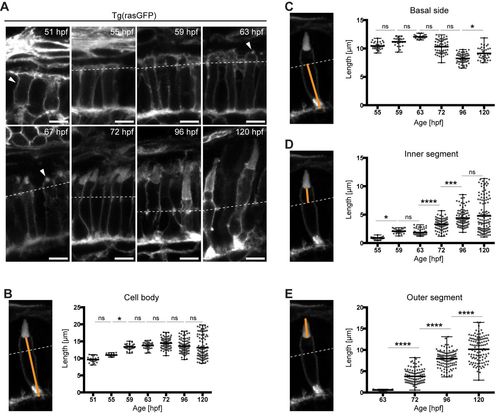
Growth of the different PRC compartments during maturation. (A) Confocal images of the PRC layer in retinal sections of Tg(rasGFP) embryos, with plasma membrane in grey at various timepoints. hpf: hours post fertilisation. Dashed lines mark the level of the outer limiting membrane, OLM. At 51?hpf, the arrowhead outlines a PRC precursor and at 63?67?hpf an emerging outer segment (OS). Scale bars: 5?Ám. (B?E) Confocal images of individual PRCs from retinal sections of Tg(rasGFP) animals at 72?hpf. The orange lines mark the compartment measured. The quantification of the length of different PRC compartments at different developmental times are shown adjacent to each image. Length of cell body (B), basal side (C), inner segment (D) and outer segment (E) are represented in dot plots with calculated minimum, mean, and maximum. On average, 70 cells from a total of 4?6 independent embryos were quantified per timepoint. Statistical significance was calculated by a one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test. The significance is as follows: ns (non-significant)=P>0.05, *=P?0.05, **=P? 0.01, ***=P?0.001, ****=P?0.0001. |
|
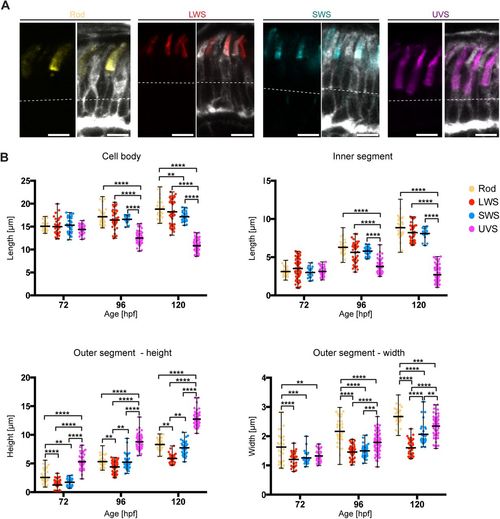
PRC subtypes show different growth of the apical domain. (A) Confocal images of the PRC layer in retinal sections of Tg(rasGFP) embryos at 120?hpf, with plasma membrane in grey and antibody staining for different opsins: rhodopsin (yellow), red opsin (red), blue opsin (blue) and UV opsin (magenta). Dashed lines mark the level of the OLM. Scale bars: 5?Ám. (B) Length of the cell body, the inner and the outer segment height and width at various stages are represented in dot plots with calculated minimum, mean, and maximum. On average, 40 cells from a total of 6?8 independent embryos were quantified per timepoint. Statistical significance was calculated by a two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test. Within the same time-point, all PRCs show no significant difference (P>0.05), with exception of samples highlighted with **(P?0.01), ***(P?0.001) and ****(P?0.0001). |
|
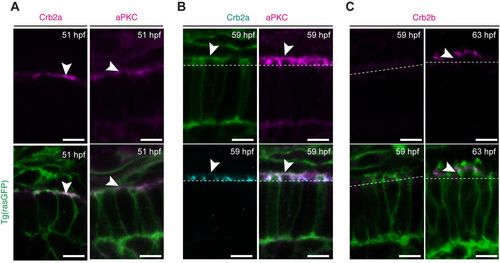
Polarity proteins show differential expression at the initial stages of PRC maturation. Confocal images of the PRC layer in retinal sections of Tg(rasGFP) embryos showing the plasma membrane in green and the respective polarity protein. (A) Crb2a and PrkC antibody staining of embryos at 51?hpf in magenta. (B) PrkC (magenta) and Crb2a (cyan) antibody staining of embryos at 59?hpf. (C) Crb2b antibody staining of embryos at 59?hpf and 63?hpf in magenta. Dashed lines mark the level of the OLM and arrowheads highlight antibody staining. Scale bars: 5?Ám. |
|
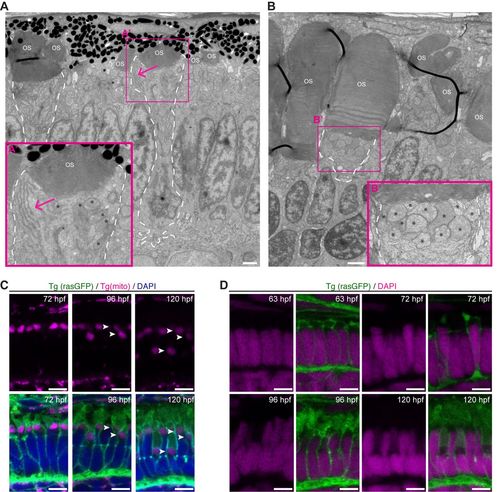
Organelles show different positioning during PRC maturation. (A) Electron micrograph of a section through the PRC layer of a wild-type zebrafish embryo at 72?hpf. (A?) Blow-up of the box indicated in A, showing Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) clusters (arrow) in the ellipsoid region of rod-like PRCs. (B) Electron micrograph of a section through the PRC layer in the ventral patch, a rod enriched region, of a wild-type zebrafish embryo at 120?hpf. (B?) Blow-up of the box indicated in B, showing mitochondria accumulate in the inner segment (arrow). ER clusters are no longer visible. For both A and B, asterisks mark the mitochondria, ?OS? the OSs, and PRCs with large OS are outlined with a dashed line. (C) Confocal images of retinal sections of zebrafish embryos at 72?hpf, 96?hpf and 120?hpf. Endogenous fluorescence of Tg(mito:GFP) (magenta) and Tg(rasGFP) (green). DAPI staining (nuclei) in blue. Arrowheads point to mitochondria. Note that mitochondria can be found in three distinct layers by 120?hpf. (D) Confocal images of retinal sections of zebrafish embryos at 63?hpf, 72?hpf, 96?hpf and 120?hpf. Endogenous fluorescence of Tg(rasGFP) (green) DAPI staining in magenta. Scale bars: A?B: 1?Ám, C?D: 5?Ám. |
|
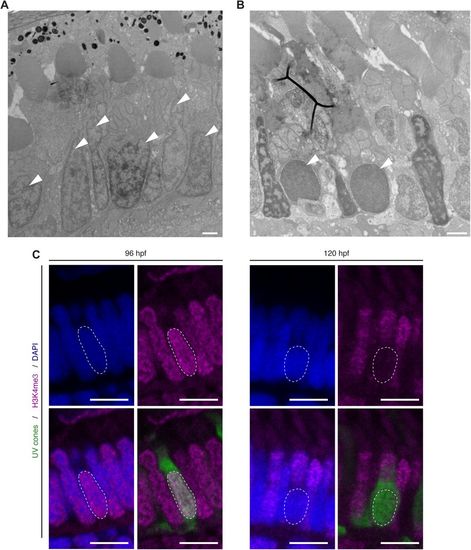
UV sensitive cones show changes in chromatic organisation. (A,B) Electron micrographs of sections through the PRC layer in the central retina of a wild-type zebrafish embryos at 96?hpf (A) and 120?hpf (B). Nuclei of some PRCs show alteration in chromatin at 120?hpf (arrowheads). (C) Confocal images of the PRC layer in retinal sections of Tg(-5.5opn1sw1:EGFP) embryos at 96?hpf and 120?hpf, with DAPI in blue, antibody staining for H3K4me3 in magenta and endogenous GFP fluorescence in green. UVS positive cells (green) show no staining for H3K4me3, a marker for euchromatin. Dashed lines mark the nucleus outline of a UVS cone. Scale bars: A?B: 1?Ám, C: 5?Ám. |
|
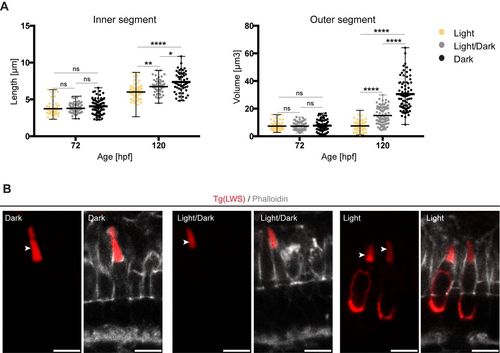
Exposure to constant light prevents leads to small apical domains in maturing PRCs. (A) IS length and OS volume of LWS cones of fish kept at different light conditions are shown: constant light (yellow), light/dark cycle (grey) and constant dark (black). All measurements are represented in dot plots with calculate minimum, mean, and maximum. On average, 65 cells from 4?6 independent embryos were quantified per timepoint. Statistical significance was calculated by a one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test. The significance is as follows: ns (non-significant) =P>0.05, *=P?0.05, **=P? 0.01, ****=P?0.0001. (B) Confocal images of retinal sections of Tg(LWS) zebrafish embryos at 120?hpf. Embryos were exposed to different light conditions, constant dark, light/dark cycle (14?h/10?h) and constant light. mKate2-tagged opsin is shown in red and phalloidin staining in grey. Outer segments are highlighted by arrowheads. Scale bars: 5?Ám. |
|
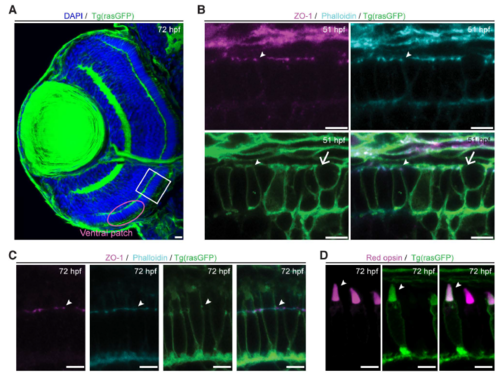
Tg(rasGFP) line as a tool to identify PRC compartments. A-D: Retinal section of zebrafish Tg(rasGFP) embryos at 72 hpf, with endogenous fluorescence of membranes marked in green. A: Confocal image of the full zebrafish eye section with DAPI in blue. The white box ventral to the optic nerve demarcates the region from which the images shown in Fig. 1 were taken, and the magenta circle demarcates the ventral patch. B: Confocal image of PRCs stained with ZO-1 (magenta) and phalloidin (cyan). Arrowheads highlight junctions and arrows point to dividing cell. C: Fluorescent structures marked by Tg(rasGFP) (green) co-localise with ZO-1 (magenta) and phalloidin (cyan) (arrowheads), thus highlighting the junction. D: Endogenous fluorescence of TgBac(opn1lw1:opn1lw1-mNeonGreen/opn1lw2:opn1lw2-mKate) (magenta) highlights the OS, which overlaps with the cone-shaped structure marked by Tg(rasGFP). Arrowhead highlights OSs. Scale bars: A: 10 Ám, B-D: 5 Ám. |
|
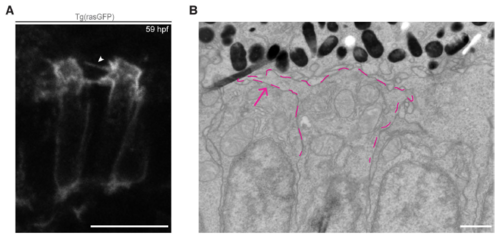
Formation of processes in the growing IS of maturing PRCs. A: Visualisation, by confocal imaging, of retinal sections of embryos at 59 hpf expressing the Tg(rasGFP) construct (plasma membrane marker). Processes (arrowhead) appear at the same time as the IS becomes visible and are still visible when OSs form. B: Electron micrograph of a section through the PRC layer in zebrafish embryo aged 55 hpf. The magenta dashed line highlights a process extending from the growing IS (magenta arrow). Scale bars: A: 10 Ám, B:1 Ám. |