- Title
-
Nuclear/cytoplasmic transport defects in BBS6 underlie congenital heart disease through perturbation of a chromatin remodeling protein
- Authors
- Scott, C.A., Marsden, A.N., Rebagliati, M.R., Zhang, Q., Chamling, X., Searby, C.C., Baye, L.M., Sheffield, V.C., Slusarski, D.C.
- Source
- Full text @ PLoS Genet.
|
Generation of inducible transgenic zebrafish expressing GFP-tagged bbs6. Gateway cloning was used to generate a GFP-bbs6 construct driven by the hsp70 promoter, flanked by tol2 recombination sites (A). Expression of the transgene can be activated and observed in live fish by a single, 30-minute heat-shock; lateral view of 48 hpf embryo (top) and higher-magnification image of the 48hpf larval head (bottom), individual cells expressing GFP-bbs6 can be observed in the developing eye (B). RT-PCR of 1dpf zebrafish detecting GFP expression in Transgenic (Tg) embryos which received a single heat-shock (HS), but not in wildtype (WT) or Non-HS Tg embryos. Actin was used as cDNA library control (C). Knockdown of bbs6 results in delayed melanosome transport. Shown are dorsal views of 5dpf zebrafish with expanded and contracted melanocytes (D). Retrograde melanosome transport rate after epinephrine treatment in WT and Tg 5dpf zebrafish. The transgene rescues the bbs6 knockdown defect. Statistics performed in GraphPad Prism 6: 1-way ANOVA with Dunnet?s multiple comparisons test, p-value ** < 0.01; plot: box and whisker plot with whiskers extending from 5?95 percentiles, outliers shown as points, orange boxes are WT zebrafish, blue boxes are Tg zebrafish (E). WT = wildtype, Tg = Tg(hsp:70:GFP-bbs6), HS = heat-shock, dpf = days post-fertilization. |
|
BBS6 and SMARCC1 protein localizations overlap in subcellular compartments. A single z-slice of a confocal stack of cells in a 70% epiboly staged zebrafish embryos stained with a SMARCC1 antibody, nuclei counterstained with TO-PRO-3 (A). SMARCC1 immunostaining of 293T cells shows predominant nuclear localization, nuclei counter-stained with TO-PRO-3 (B). Cellular fractionation of 24hpf zebrafish as well as 293T cells show cytoplasmic and nuclear localization of endogenous Smarcc1a/SMARCC1, TBA1 and SP1 served as cytoplasmic and nuclear fraction controls (C). Experimental design of cellular transfection and fractionation followed by IP on individual sub-cellular fractions (D). Western blot showing myc-BBS6 can coIP with SMARCC1 in the cytoplasm and nucleus (E). Normalizing IP band intensity to input shows stronger interaction in the cytoplasm (F). Scale bars = 20?m. |
|
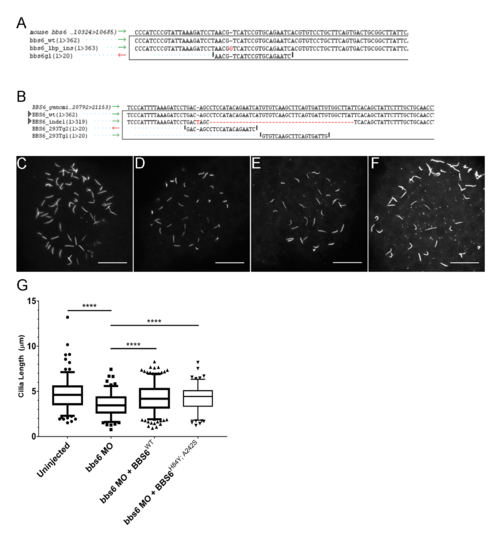
BBS6 knockout HEK 293T and IMCD3 cell lines and zebrafish bbs6 knockdown. Alignments showing the indels generated by CRISPR/Cas9 in mIMCD-3 cells (A) and HEK 293T cells. Alignment shows reference genome, wildtype control, generated mutant line, and guide(s) used for targeting (B). Cilia lengths were measured in control (C), bbs6 morphants (D), morphants with overexpression of BBS6 (E), or BBS6H84Y; A242S (F). Box and whisker plot representing the 5?95 percentiles of the collected data; n = 128?288 per group (G). PHENOTYPE:
|
|
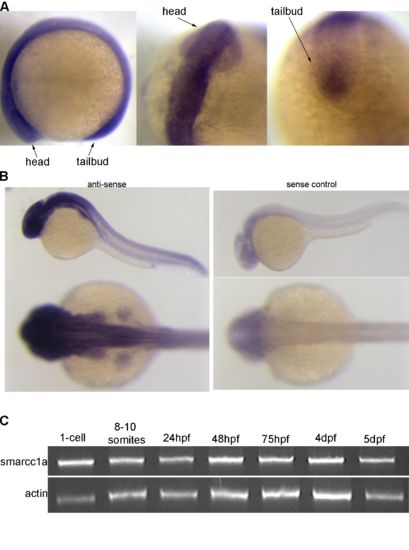
Smarcc1a expression in the zebrafish. Smarcc1a expressing in the zebrafish at the 10-somite stage of development (A) and at 1 day-post-fertilization (B), sense control on right, anti-sense probe on left. Semi-quantitative RT-PCR of smarcc1a expression over zebrafish development (C). |
|
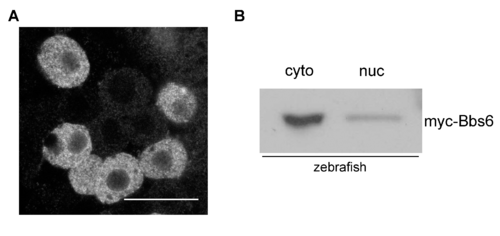
Zebrafish myc-zbbs6 expression. Single confocal slice of 70% epiboly staged zebrafish embryo expressing myc-tagged zebrafish bbs6 (A). Fractionation and western blot of 24hpf zebrafish embryo protein lysates showing bbs6 is present in the cytoplasm and nucleus (B). |
|
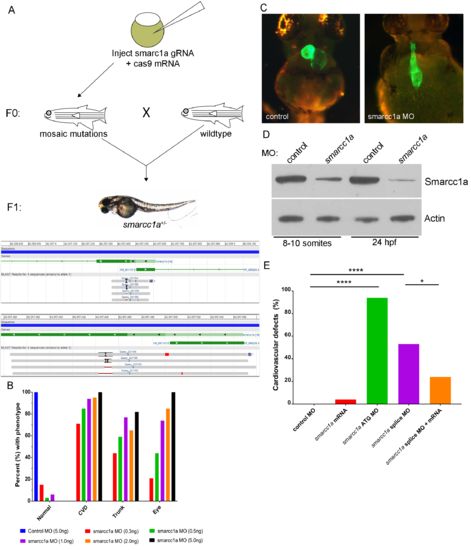
Smarcc1a knockout/knockdown causes cardiac phenotypes. Attempts to generate smarcc1a knockout zebrafish are unsuccessful because smarcc1a heterozygous fish, in the F1 generation, do not survive to breeding age (A). Smarcc1a knockdown with a translation blocking (ATG) morpholino (MO) causes multiple development phenotypes in the zebrafish in a dose dependent manner; phenotypes match smarcc1a heterozygous mutants (B). Heart labeled using transgenic line expressing GFP in differentiated cardiac tissue, Tg(myl7:EGFP) (C). Western blot for total protein validating that a human SMARCC1 antibody cross-reacts with zebrafish smarcc1a; reduced levels are observed in smarcc1a knockdown (0.5ng of MO) embryos compared to control MO injected embryos; Actin was used as a control (D). Percent of zebrafish larvae displaying cardiovascular defects from control MO, smarcc1a ATG MO, smarcc1a splice block MO, and smarcc1a splice block MO + smacc1a mRNA; fishers exact test used to compare groups, p-values: * < 0.05, **** <0.0001 (E). PHENOTYPE:
|