- Title
-
Charcot-Marie-Tooth 2b associated Rab7 mutations cause axon growth and guidance defects during vertebrate sensory neuron development
- Authors
- Ponomareva, O.Y., Eliceiri, K.W., Halloran, M.C.
- Source
- Full text @ Neural Dev.
|
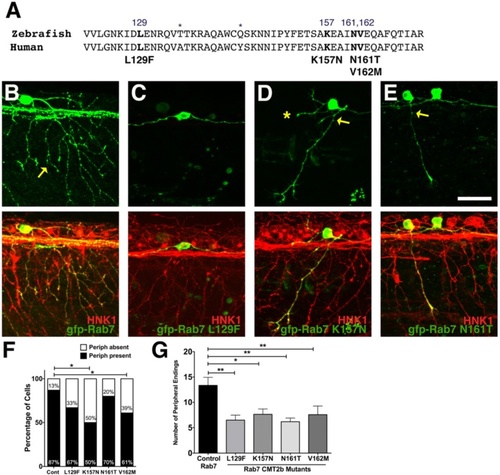
Decreased peripheral axon branching in sensory neurons expressing CMT2b Rab7 mutants. a Comparison of zebrafish and human Rab7 protein sequence in the region of CMT2b mutations. Differences in amino acid sequence indicated by asterisks. Amino acid residues associated with CMT2b are bolded. b-e Confocal images of individual RB neurons expressing wildtype GFP-Rab7 (b) or CMT2b GFP-Rab7 mutants (c) in embryos with all RB neurons labeled with HNK-1 antibody (red). Anterior to the left. b wildtype Rab7 expressing cell shows wide arborization of peripheral axons (yellow arrow). c Lack of peripheral axon outgrowth in Rab7 L129F expressing cell. d, e Reduced peripheral branching (yellow arrow) in Rab7 K157N (D) and Rab7 N161T (E) expressing cells. Asterisk = missing central axon. f Quantification of number of neurons extending peripheral axons. Cont = wildtype Rab7: n = 31 cells in 19 embryos; Rab7 L129F: n = 33 cells in 24 embryos, p = 0.08; Rab7 K157N: n = 10 cells in 10 embryos, *p = 0.03; Rab7 N161T: n = 15 cells in 14 embryos, p = 0.6; Rab7 V162M: n = 23 cells in 18 embryos, *p = 0.05. Fisher?s exact tests. g Quantification of peripheral branch endings in CMT2b-associated Rab7 mutations shows a significant decrease in branching. Wildtype Rab7: n = 20 cells in 15 embryos; Rab7 L129F: n = 21 cells in 18 embryos; Rab7 K157N: n = 11 cells in 7 embryos; Rab7 N161T: n = 12 cells in 10 embryos; Rab7 V162M: n = 16 cells in 14 embryos. *p = 0.03, **p < 0.01; Unpaired two-tailed t-test. Scale bar = 40 Ám |
|
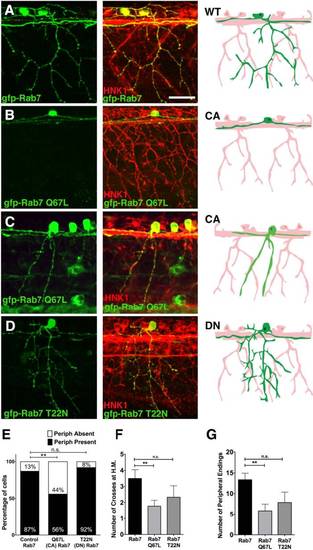
Peripheral axon outgrowth and branching defects in CA-Rab7 expressing neurons. a-c Confocal projections of embryos with all RBs labeled with HNK-1 antibody (red) and individual RBs labeled with indicated Rab7 forms (green). Drawings at right highlight morphology of one neuron in green. a Individual RB neuron labeled with GFP-Rab7 showing central axons extending anteriorly and posteriorly from the cell body, and peripheral axon branching in the skin. b Lack of peripheral axon outgrowth in GFP-Rab7 Q67L (CA) expressing cell. c Reduced peripheral branching in GFP-Rab7 Q67L (CA) expressing cell. d Normal central outgrowth and peripheral branching in GFP-Rab7 T22N (DN) mutant expressing RB cell. e Expression of CA-Rab7, but not DN-Rab7, mutant construct increases percentage of RB neurons that do not extend a peripheral axon. n = 31 cells in Rab7 control, 30 cells in CA-Rab7, and 14 cells in DN-Rab7, **p = 0.006, Chi-Square test. f Number of peripheral axons that cross horizontal myoseptum (H.M.) is reduced in CA-Rab7 expressing cells. CA-Rab7: n = 9 cells; wildtype Rab7 control: n = 12 cells. **p = 0.009, paired t-test. g Number of peripheral axon endings in individually labeled neurons **p = 0.005, Unpaired two tailed t-test. Wildtype Rab7: 31 cells in 19 embryos; Rab7 Q67L: 30 cells in 15 embryos; Rab7 T22N: 14 cells in 9 embryos. All views anterior to the left. Scale bar = 40 Ám |
|
Central axon guidance errors in sensory axons expressing CMT2b Rab7 mutants. a-c Confocal projections (lateral views, anterior to the left) of embryos labeled with HNK-1 antibody (red) and individual RBs expressing GFP-Rab7 forms (green). Drawings at right highlight morphology of one neuron in green. a Wildtype GFP-Rab7 expressing neuron with two central axons traveling in the dorsal longitudinal fascicle (DLF), and with one peripheral axon branching in the skin. b, c RB neurons expressing GFP-Rab7 L129F show lack of outgrowth of ascending central axon (b) or central axon guidance errors (c). Central axon leaving DLF indicated by an arrow in (c). d Quantification of percentage of neurons lacking a central axon. Cont = wildtype Rab7: n = 30 cells in 15 embryos; Rab7 L129F: n = 22 cells in 20 embryos, *p = 0.03; Rab7 K157N: n = 12 cells in 8 embryos, *p = 0.02; Rab7 N161T: n = 16 cells in 11 embryos, p = 0.3; Rab7 V162M: n = 14 cells in 12 embryos, p = 0.3; Fisher?s exact tests. e Quantification of percentage of cells with central axon guidance errors. Cont = wildtype Rab7: n = 30 cells in 15 embryos; Rab7 L129F: n = 24 cells in 19 embryos, *p = 0.03; Rab7 K157N: n = 13 cells in 9 embryos, p = 0.3; Rab7 N161T: n = 13 cells in 11 embryos, p = 0.09; Rab7 V162M: n = 14 cells in 12 embryos, p = 0.3. Scale bar = 40 Ám |
|
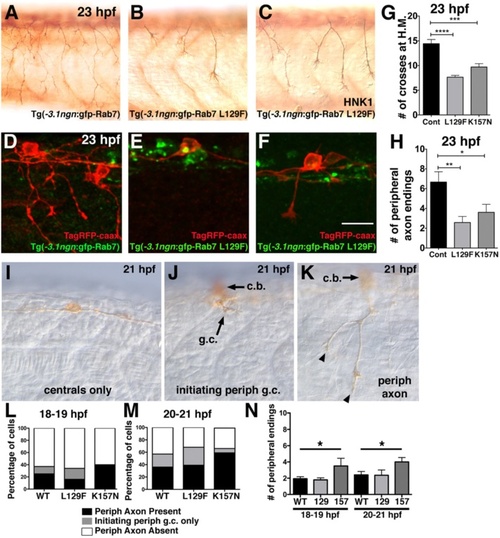
Decreased peripheral axon branching in transgenics expressing CMT2b Rab7 mutants. a-c Lateral views (anterior to the left) of RB neurons labeled with HNK-1 antibody (brown) in 23 hpf transgenic embryos expressing wildtype GFP-Rab7 (a) or GFP-Rab7 L129F (b-c) in all RB neurons, showing decreased branching in Tg(GFP-Rab7L129F) embryos. d-f Mosaic labeling of single RB cells with TagRFP-caax membrane label (red) in 23 hpf transgenic embryos expressing wildtype GFP-Rab7 (d) or GFP-Rab7 L129F (e, f) in all RB neurons. d Red-labeled RB in wildtype GFP-Rab7 transgenic embryo with widely branched peripheral axon. e Red-labeled RB in GFP-Rab7 L129F transgenic embryo does not extend a peripheral axon. c Red-labeled RB in GFP-Rab7 L129F transgenic embryo extends a short peripheral axon that does not branch. Scale bar = 20 Ám. g Quantification of peripheral branches crossing horizontal myoseptum in 23 hpf Tg(-3.1ngn:gfp-Rab7) control (Cont) embryos (n = 14 embryos), Tg(-3.1ngn:gfp-Rab7 L129F) embryos (L129F, n = 63 embryos), and Tg(-3.1ngn:gfp-Rab7 K157N) embryos (K157N, n = 20 embryos). ****p < 0.0001, ***p = 0.0001. Unpaired, two-tailed t-test. h Number of peripheral branch tip endings in 23 hpf Tg(-3.1ngn:gfp-Rab7) control (n = 9 cells in 6 embryos), Tg(-3.1ngn:gfp-Rab7 L129F) (n = 24 cells in 24 embryos), or Tg(-3.1ngn:gfp-Rab7 K157N) (n = 21 cells in 15 embryos) embryos is significantly reduced in embryos expressing CMT2b-associated Rab7 mutants. **p = 0.002, *p = 0.04. Unpaired, two-tailed t-test. i-k Lateral views of 21 hpf embryos injected with ngn:TagRFP-caax and labeled with anti-TagRFP antibody. I, Example of RB with central axons only and no peripheral axon. j Example of RB with a peripheral growth cone (g.c.) just initiating (arrow). Cell body (c.b.) is out of focus. k, Example of RB with short peripheral (with 2 endings, arrowheads) extended out of the spinal cord. Cell body (c.b.) is out of focus. l-m Quantification of percentage neurons with peripheral axons at 18?19 hpf (l) and 20?21 hpf (m). There are no significant differences between wildtype and CMT2b Rab7 mutants. At 18?19 hpf: wildtype n = 65 neurons, CMT2b L129F n = 61 neurons, CMT2b K157N n = 10 neurons, p = 0.30 Chi-Square test. At 20?21 hpf: wildtype n = 75 neurons, CMT2b L129F n = 28 neurons, CMT2b K157N n = 27 neurons, p = 0.15 Chi-Square test. n, Analysis of peripheral axon branch endings. At 18?19 hpf and 20?21 hpf, wildtype vs. CMT2b K157N, *p = 0.03 unpaired student?s t-test EXPRESSION / LABELING:
PHENOTYPE:
|
|
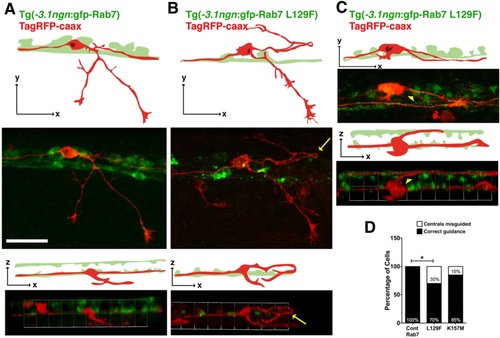
Central axon guidance defects in transgenics expressing CMT2b Rab7 mutants. a Lateral (top two panels) and 3D rotation dorsal (bottom two panels) views of TagRFP-caax labeled RB neuron in Tg(-3.1ngn:gfp-Rab7) embryo at 23 hpf showing ascending and descending ipsilateral projections of central axons. Two bilateral rows of RB cells (green) are best seen in dorsal views. b-c Lateral (top two panels) and 3D rotation dorsal (bottom two panels) views of TagRFP-caax labeled RB neurons in Tg(-3.1ngn:gfp-Rab7 L129F) embryos at 23 hpf. b Misguided descending central axon (yellow arrow) turns around to travel anteriorly and dorsally from its normal pathway. c Misguided central axon (yellow arrowhead) crosses dorsal midline to join the contralateral central fascicle. All views anterior to the left. Scale bar = 40 Ám. d Quantification of number of neurons with central axon guidance errors. Cont Rab7 = Tg(-3.1ngn:gfp-Rab7): 10 neurons in 7 embryos; Tg(-3.1ngn:gfp-Rab7 L129F): 43 cells in 43 embryos, *p = 0.05; Tg(-3.1ngn:gfp-Rab7K157M): 48 cells in 27 embryos, p = 0.2; Chi Square test PHENOTYPE:
|
|
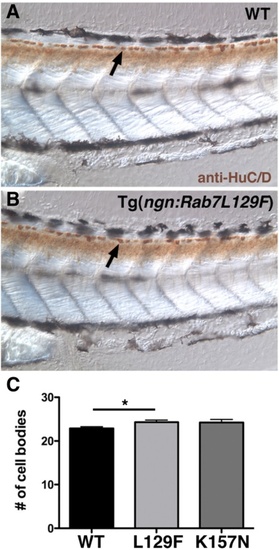
CMT2b Rab7 mutants do not cause increased cell death at 3 dpf. a-b Lateral views of 3 dpf wildtype (a) and CMT2b L129F (b) larvae labeled with anti-HuC/D in brown. Arrows indicate RB cell bodies. c Quantification of cell body number in five segments beginning at end of the yolk extension. CMT2b L129F is significantly greater than wildtype, *p = 0.02, student?s t-test. N = 20 embryos for each group PHENOTYPE:
|
|
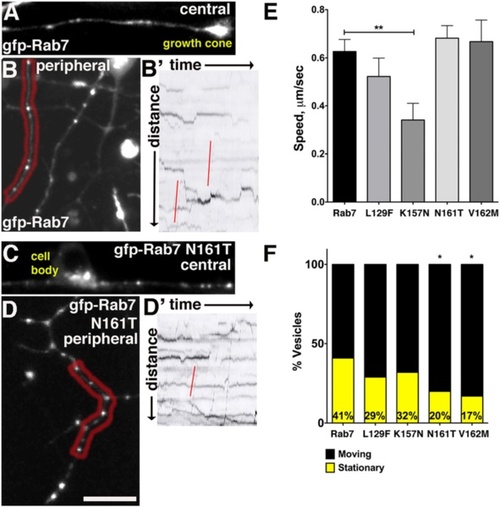
In vivo imaging of CMT2b Rab7 mutant containing vesicles reveals changes in endosome dynamics. a-b Confocal images of neurons with GFP-Rab7 labeled endosomes in central (a) and peripheral (b) axons. b′ Kymograph of peripheral RB axon in red region in (b). Red lines indicate rapid retrograde vesicle runs. c-d Confocal images of neurons with GFP-Rab7 N161T expressing endosomes in central (c) and peripheral (d) axons. d′ Kymograph of peripheral axon in red region in (d). Red line indicates rapid retrograde vesicle runs. e Speeds of vesicles containing Rab7 K157 mutants were significantly reduced in central and peripheral axons. **p = 0.009, Unpaired, two-tailed t-test. Wildtype Rab7 control: n = 97 vesicles in 8 cells in 6 embryos; Rab7 L129F: n = 37 vesicles in 6 cells in 4 embryos; Rab7 K157N: n = 24 vesicles in 3 cells in 2 embryos; Rab7 N161T n = 73 vesicles in 8 cells in 6 embryos; Rab7 V162M n = 33 vesicles in 5 cells in 3 embryos. f Decreased percentage of stationary vesicles in central and peripheral axons expressing Rab7 N161T and V162M mutants. *p = 0.01, Fisher?s exact test. Wildtype Rab7 control: n = 39 vesicles in 8 cells in 6 embryos; Rab7 L129F: n = 86 vesicles in 6 cells in 4 embryos; Rab7 K157N: n = 37 vesicles in 3 cells in 2 embryos; Rab7 N161T n = 137 vesicles in 8 cells in 6 embryos; Rab7 V162M n = 60 vesicles in 5 cells in 3 embryos |