- Title
-
Vesicular stomatitis virus enables gene transfer and transsynaptic tracing in a wide range of organisms
- Authors
- Mundell, N.A., Beier, K.T., Pan, Y.A., Lapan, S.W., Göz Aytürk, D., Berezovskii, V.K., Wark, A.R., Drokhlyansky, E., Bielecki, J., Born, R.T., Schier, A.F., Cepko, C.L.
- Source
- Full text @ J. Comp. Neurol.
|
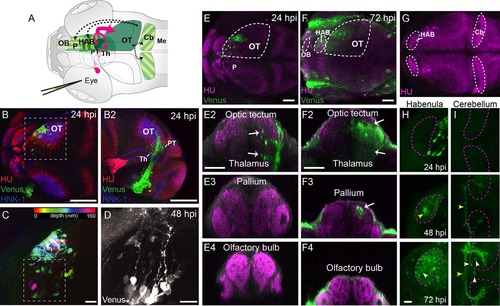
Transsynaptic labeling of the visual pathway in larval zebrafish infected with rVSV(VSV-G). (A) Diagram of unilateral eye injection. RGC axons (red arrows) project contralaterally to the optic tectum, pretectum, and thalamus. The locations of rVSV(RABV-G)-infected cells are indicated by green shaded areas. Putative axonal projections from the OT to the pallium, habenula, and cerebellum are labeled as dashed arrows. (B?D) rVSV(VSV-G) infection of the OT. Dorsal (B) and lateral (B2) views of a 24 hpi zebrafish stained for Venus (green), HuC/D (red, pan-neuronal marker), and HNK1 (blue, neuropil). Labeled RGC termini and tectal cell bodies can be seen in the right (contralateral) tectum. Boxed area in B is shown at higher magnification in C. Spectrum of colors represents depth from the dorsal surface of the tectum (red-yellow) to the ventral surface (blue-pink) for Venus-labeled cells. (D) High magnification of contralateral Venus-labeled tectal cells at 48 hpi, in location similar to C (boxed area). The majority of the labeled tectal neurons had a single process extending medially, consistent with the previously described morphology of retinorecipient neurons (Robles et al., 2011). (E,F) Dorsal views of confocal maximal projections show rVSV(VSV-G) labeling at 24 hpi (E) and 72 hpi (F). Areas delineated by dashed lines are the OT, habenula, and olfactory bulb. Transverse optical sections from each stage are shown in panels below (E2?E4 for 24 hpi and F2?F4 for 72 hpi). (G?I) Dorsal view of the zebrafish brain (3 dpf), stained with HuC (G). Areas delineated by dashed lines are the habenula and cerebellum, which are shown at higher magnification in H and I, respectively. 24 hpi labeling was restricted to the optic tectum, pretectum, and thalamus. At 72 hpi, labeling broadened and included cells in the pallium (F3), habenula (H), and the cerebellum (I). Labeled cells are indicated by white arrows or arrowheads and axons are labeled with yellow arrowheads). Venus-expressing cells were not present in the olfactory bulb (E4, F4). CB: cerebellum, HAB = habenula, Me = medulla, OB = olfactory bulb, OT = optic tectum, P = pallium, PT = pretectum, Th = thalamus. Scale bars = 100 µm in B?B2; 20 µm in C,D; 50 µm E?F4; 20 µm in H,I. |
|
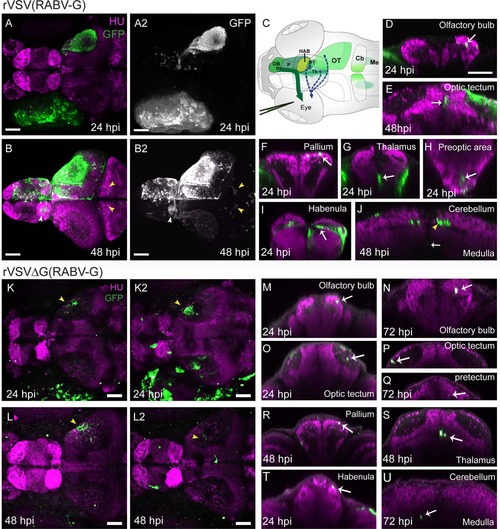
Labeling of centrifugal circuits in zebrafish with rVSV(RABV-G). (A,B) Dorsal view of confocal maximal projections showing rVSV(RABV-G) labeling (green, GFP) and HU (magenta, pan-neuronal marker) at 24 hpi (A) and 48 hpi (B). GFP channel from (A,B), with signal enhanced to show cells in the brain, is shown in (A2,B2). Images in (B-B2) were captured after dissection of the brain from surrounding tissues. GFP-labeled axonal projections from the contralateral to the ipsilateral habenula (white arrowhead) and projections from the OT to the cerebellum (yellow arrowheads) are indicated in (B-B2). (C) Illustration showing injection of rVSV(RABV-G) into the eye of 3 dpf larval zebrafish. Centrifugal axons in the terminal nerve (tn) originate from the contralateral olfactory bulb (OB) and ventral pallium (P), and project to target cells in the retina (dark green arrow). The locations of rVSV(RABV-G)-infected cells after unilateral eye injection is indicated by green shaded areas. Projections from other centrifugal neurons previously reported among teleost fish are indicated by dashed arrows from the thalamus (Th), OT, and pretectum (PT). (D-J) Transverse optical sections from 24 hpi or 48 hpi are shown. At 24 hpi, labeling is restricted to the RGC axons in the neuropil of OT, and cell bodies in the OB (D), OT (E, 48 hpi shown), pallium (F), thalamus (G), preoptic area (H), habenula (I), medulla (J, 48 hpi shown), and pretectum (not shown). At 48 hpi, additional labeling was seen, including GFP-positive efferent axons (yellow arrowhead) projecting into the contralateral and ipsilateral cerebellum (J). (K-L2) Confocal maximal projections of GFP expression and HU after injection of 1 × 108 ffu/mL (K,L), or 1 × 109 ffu/mL (K2,L2) rVSVΔG(RABV-G), at 24-48 hpi. Yellow arrowheads in (K-L2) indicate RGC axons in the neuropil of the OT. In zebrafish injected with the higher dose of rVSV?G(RABV-G), labeling revealed primary infection in centrifugal neurons. (M-U) Representative transverse optical sections from 24-72 hpi show the results of centrifugal labeling, as sparse GFP-expressing cells in the OB (M,N), OT (O,P), pretectum (Q), pallium (R), thalamus (S), habenula (T), and medulla (U). GFP-labeled cells were not detected in the preoptic area (not shown) and labeled axons were not present in the cerebellum (U) following infections with rVSV?G (RABV-G). CB = cerebellum, HAB = habenula, Me = medulla, OB = olfactory bulb, OT = optic tectum, P= pallium, PT = pretectum, PO = preoptic area, tn = terminal nerve, Scale bars: = 50 µm. |