- Title
-
A novel keratin18 promoter that drives reporter gene expression in the intrahepatic and extrahepatic biliary system allows isolation of cell-type specific transcripts from zebrafish liver
- Authors
- Wilkins, B.J., Gong, W., and Pack, M.
- Source
- Full text @ Gene Expr. Patterns
|
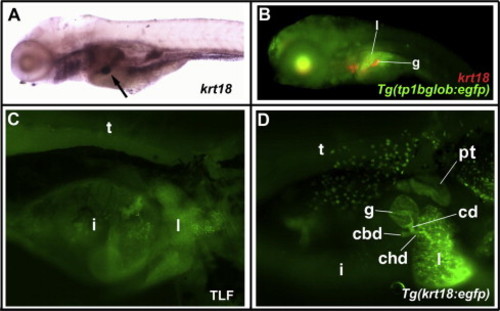
krt18 and Tg(krt18:egfp) are expressed in the developing biliary system. (A) Whole-mount in situ hybridization of 5 dpf wild-type larva (left lateral view), showing gallbladder expression of krt18 (arrow). (B) Combined immunostaining and fluorescent in situ hybridization of 5 dpf Tg(tp1bglob:egfp) larva (left lateral view), showing Notch-responsive GFP protein in intrahepatic bile ducts within the liver (l), but not the krt18-expressing gallbladder (g). Red signal anterior to the liver is background staining. (C) Whole-mount right lateral-inferior fluorescent image of 5 dpf wild-type control larva, stained with anti-GFP, showing background autofluorescence in larval tissues. (D) Whole-mount right lateral-inferior fluorescent image of 5 dpf Tg(krt18:egfp) larva stained with anti-GFP, showing EGFP expression in the developing biliary system, skin, and proximal tubule. Abbreviations: l = liver, g = gallbladder, i = intestine, t = trunk, cd = cystic duct, chd = common hepatic duct, cbd = common bile duct, pt = proximal tubule. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
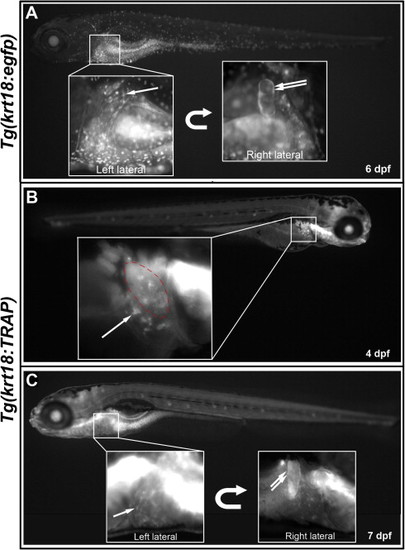
krt18-driven reporters allow live detection of the developing biliary system. (A) Fluorescent micrograph of live 6 dpf Tg(krt18:egfp) larva, showing EGFP expression in intrahepatic biliary cells (single arrow) and gallbladder epithelium (double arrow), partly obscured by skin expression. (B) and (C) Fluorescent micrographs of live 4 dpf (B) and 7 dpf (C) Tg(krt18:TRAP) larvae, showing visualization of EGFP-Rpl10a fusion protein in developing intrahepatic biliary cells (single arrows) and gallbladder epithelium (double arrow). Red dashed line in (B) indicates gallbladder overlying the liver, out of the focal plane. |
|
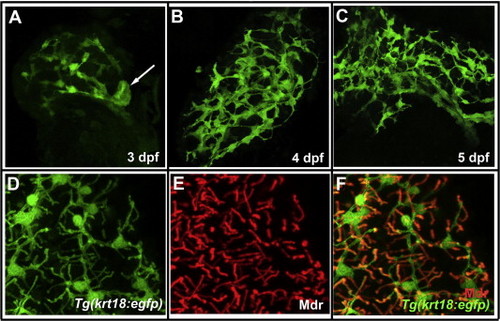
Tg(krt18:egfp) is expressed at all levels of the developing intrahepatic and extrahepatic biliary system. (A?C) Confocal projections of dissected livers from 3, 4, and 5 dpf Tg(krt18:egfp) fish, indicating biliary proliferation and remodeling (400× magnification). Arrow in panel A indicates rudimentary gallbladder. (D?E) Confocal projections from dissected liver of 5 dpf Tg(krt18:egfp) larva stained with (D) anti-GFP and (E) anti-Mdr to mark biliary cells and hepatocyte canaliculi, respectively. (F) Merged projection from panels D and E, demonstrating colocalization of canaliculi with GFP-positive terminal ductules (D?F: 630× magnification). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
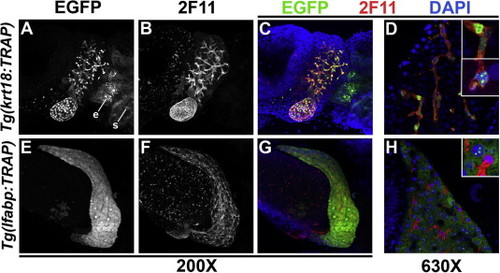
Generation of transgenic zebrafish for liver translating ribosome affinity purification (TRAP). (A?C) Confocal projection of dissected liver and gallbladder from a 5 dpf Tg(krt18:TRAP) larva, showing EGFP-Rpl10a fusion protein (A) and biliary marker 2F11 (B), which co-localize (C; EGFP ? green; 2F11 ? red). EGFP is also visualized in krt18-expressing cells of the esophagus (e) and skin (s). (D) High-magnification confocal scan of liver from the same larva shows localization of TRAP fusion protein to biliary cell cytoplasm and nucleus, with a subset showing nucleolar enrichment (insets). (E?G) Confocal projection of dissected liver and gallbladder from 5 dpf Tg(lfabp:TRAP) larva, showing hepatocyte expression of TRAP fusion protein (E) that is non-overlapping with biliary 2F11 staining (F). (H) High-magnification confocal scan of liver from same larva, showing localization of TRAP fusion protein to the hepatocyte cytoplasm and nucleolus (inset), exclusive of biliary cells stained red with the 2F11 antibody. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
Reprinted from Gene expression patterns : GEP, 14(2), Wilkins, B.J., Gong, W., and Pack, M., A novel keratin18 promoter that drives reporter gene expression in the intrahepatic and extrahepatic biliary system allows isolation of cell-type specific transcripts from zebrafish liver, 62-68, Copyright (2014) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Gene Expr. Patterns