- Title
-
Schwann cell spectrins modulate peripheral nerve myelination
- Authors
- Susuki, K., Raphael, A.R., Ogawa, Y., Stankewich, M.C., Peles, E., Talbot, W.S., and Rasband, M.N.
- Source
- Full text @ Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA
|
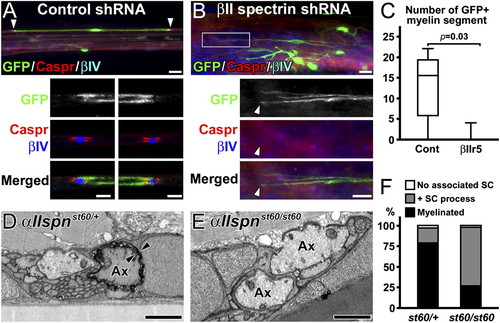
Disruption of spectrins in Schwann cells inhibits myelination in vivo. (A?C) βII spectrin silencing during sciatic nerve regeneration. The adenoviruses with shRNAs were injected 1 dpc. (A) A myelin segment produced by a Schwann cell with control shRNA at 21 dpc. The nodes (βIV spectrin in blue) and paranodes (Caspr in red) on both sides (arrowheads) are enlarged in lower panels. (B) Considerable GFP expression in cells not producing myelin in sciatic nerves injected with βIIr5 at 21 dpc. The boxed area in the upper panel is enlarged in the lower panels. The arrowhead indicates the tip of GFP+ cells with no overlapping nodes or paranodes. (C) The number of remyelinating Schwann cells with GFP signal in peroneal nerves shown in box-and-whisker plots. Remyelinating Schwann cells are significantly fewer in βIIr5 injection compared with control. A total of 76 remyelinating segments with GFP was found in five of six control animals, whereas only four were found in one of six animals with βIIr5 injection. (D?F) Control and αII spectrin mutant zebrafish. Transmission electron microscopy of transverse sections of 7-dpf larval motor nerves. Ax indicates axon, and arrowheads indicate multiple layers of myelin. One of the large primary motor axons in the heterozygous sibling has a myelin sheath (D), whereas the large axons from the mutant do not (E). (F) Quantitation of large motor nerve axons with no associated Schwann cells (SC), associated with SC process, or myelin. Data were obtained from 33 large axons from 21 nerves (four larvae) in heterozygous control or 53 large axons from 35 nerves (three larvae) in the mutant at 7 dpf. [Scale bars, 20 μm (A and B, Upper), 5 μm (A, Lower), 10 μm (B, Lower), and 1 μm (D and E).] PHENOTYPE:
|
|
Sensory nerve myelin in mutant zebrafish lacking αII spectrin. (A and B) Transmission electron microscopy images of transverse sections from 7 d postfertilization larvae posterior lateral line nerves. Compared with heterozygous control (A), no apparent myelin defects were seen in αII spectrin mutant fish (B). Ax indicates axon, and arrowheads indicate multiple layers of myelin. (Scale bars, 0.5 μm.) PHENOTYPE:
|