- Title
-
Zebrafish cardiac enhancer trap lines: New tools for in vivo studies of cardiovascular development and disease
- Authors
- Poon, K.L., Liebling, M., Kondrychyn, I., Garcia-Lecea, M., and Korzh, V.
- Source
- Full text @ Dev. Dyn.
|
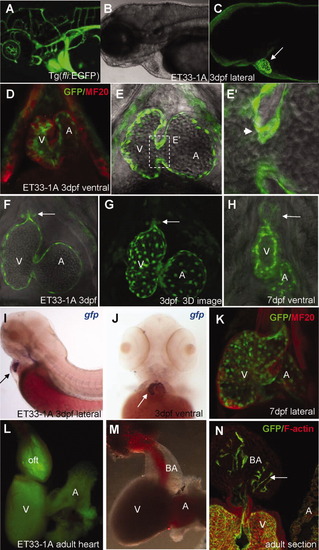
CETs that define development of the endocardium in vivo. A: Anterior vasculature in Tg(fli-GFP). B: Bright-field view of anterior body. C: Endocardium-specific EGFP expression in ET33-1A at low magnification. Arrow indicates fluorescence only in the heart. D, K: Confirmation of EGFP-positive cells in the endocardial layer as evidenced by double immunohistochemistry with MF20 (red), which marks the myocardium. EGFP-positive cells are in the inner layer: (D) 3 dpf, (K) 7 dpf. E-H: In vivo imaging of the endocardium at high magnification. G: High-resolution 3D reconstruction of the endocardium in vivo revealing the intricate network of endocardial cells. Arrowhead (E′) and arrows (F-H) point to endocardial leaflets at A-V junction and BA, which in the latter thickens from 3 dpf (F) to 7 dpf (H), respectively. I, J: Lateral (I) and ventral (J) views of the heart after WISH using anti-gfp probe. Arrows indicate the heart. L, M: Low-resolution fluorescent (L) and bright-field images (M) of adult heart. N: Adult heart sections immunostained with anti-EGFP and F-actin. All images (except A) are of ET33-1A. C, G: Fluorescent images. E, E′, F, H: Composite fluorescent/DIC images. A, atrium; BA, bulbus arteriosus; V, ventricle. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
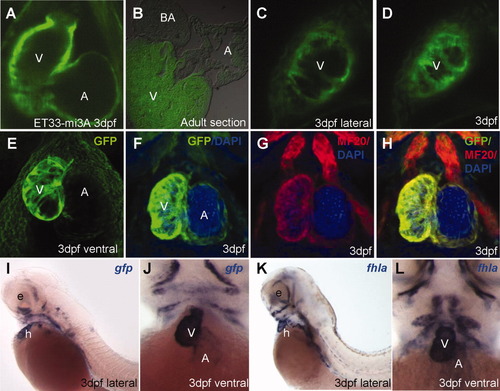
CETs that define development of the myocardium in vivo. A: EGFP-positive embryonic myocardium in the ventricle is thicker compared to that in the atrium. B: EGFP expression in adult heart sections of myocardium-specific ET33-mi3A. C, D: Single optical sections of ventricular myocardium in the live embryo at high magnification (lateral view). E: High-resolution 3D-reconstruction of myocardium live. F-H: Myocardium immunolabelled with EGFP/MF20(red)/DAPI(blue). A, C, D, E: In vivo imaging of live embryos at 3 dpf. I,J: Lateral and ventral view of larva after WISH with anti-gfp probe. K, L: Lateral and frontal view of larva after WISH with anti-fhla probe. All images are ET33-mi3A. A, atrium; BA, bulbus arteriosus; V, ventricle. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
CETs that define the epicardium in vivo. A, B: ET27 with EGFP-positive cells covering the ventricle; note that EGFP expression in the BA precedes that in the epicardium; C, D: The EGFP-positive epicardial cells (arrow) enveloping the internal cmlc2 highlighted myocardium at high magnification. E: Cross-section of the adult ET27 heart at low magnification, with GFP-labelled epicardium on the external surface of the BA, atrium and ventricle (arrow). B-D: Double transgenic embryos of ET27 and Tg(cmlc2:dsRed). All except D are fluorescent images. D: Composite fluorescent/DIC images. A, atrium; BA, bulbus arteriosus; V, ventricle. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
The CET line, ET31, marks a unique subset of myocardium at the early A-V valve. A: ET31 crossed with Tg(cmlc2:dsRed) showing a subset of myocardium positive for EGFP at the A-V junction and chambers (arrowhead). Note the EGFP expression at the BA. B, C: High magnification of A-V junction reveals differential GFP intensity between a different subset of myocardial cells. Arrows point to non-overlapped ET31 EGFP expression. D, E: High magnification of A-V junction lined with endocardial cells adjacent to cmlc2 marked myocardium (shown for comparison). Arrows point to A-V junction that ET31 marks. F-H: anti-gfp WISH demonstrates that the expression domain at the A-V node represents a ring. A-C: Double transgenic embryos of ET31 and Tg(cmlc2:dsRed). D, E, Double transgenic embryos of ET33-1A and Tg(cmlc2:dsRed). B, D: Fluorescent images. C, E: Composite fluorescent/DIC images to reveal cellular morphology. A, atrium; BA, bulbus arteriosus; A-V, atrio-ventricular valve; V, ventricle. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
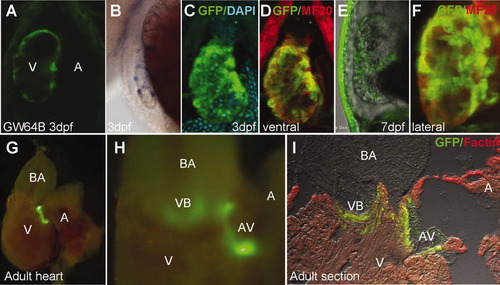
Developmental changes in a CET line with early ventricle-specific expression (GW64B). A: EGFP expression at 3 dpf was found in the ventricle (ventral view). B: Same stage larvae stained by WISH using anti-gfp probe (lateral view). C, D, F, I: Double immunolabelling with MF20(red) performed on 3-dpf (C, D), 7-dpf (F), and adult heart section (I). C-F: The ventricular expression revealing trabeculated myocardium was maintained until 7 dpf. In the adult heart, EGFP expression was found at the A-V junction (G), and at the VB junction, where it defines valves (H, I). All images are GW64B. A, atrium; A-V, atrio-ventricular valve; BA, bulbus arteriosus; V, ventricle; VB, ventriculo-bulbar valve. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
Developmental changes in CET lines with early BA-specific expression. A: EGFP expression in the BA and ventral aorta (VA) in wildtype 3-dpf ET27. B: smo mutation affects the ventral aorta, but not the domain of EGFP expression corresponding to BA. C, C′: ET27 adult heart sections shown at low (C) and high (C′) magnification. D: ET31 embryonic expression in BA. E, E′, E″: Cardiac valves; VB (E′) and AV (E″) marked in adult heart of ET31 shown on F-actin-stained sections. F: BA restricted embryonic expression of GW2C. G: GW2C adult heart sections at low magnification. G′, H: Serial sections of VB valve showing its different morphology at high magnification. I, I′: ET33-1A adult heart sections shown at low (I) and high (I″) magnification, for comparison of endocardal cell morphology in BA with ET27 (C′). A, B, D, F: Ventral view at 3dpf; C, C′: Sections of the adult heart immunostained for EGFP and MF20. E′, E″, H, I: Sections counterstained with F-actin. A-V, atrio-ventricular valve; BA, bulbus arteriosus; VB, ventriculo-bulbar valve; V, ventricle. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|