- Title
-
Pleiotropic effects in Eya3 knockout mice
- Authors
- Soker, T., Dalke, C., Puk, O., Floss, T., Becker, L., Bolle, I., Favor, J., Hans, W., Hoelter, S.M., Horsch, M., Kallnik, M., Kling, E., Morth, C., Schrewe, A., Stigloher, C., Topp, S., Gailus-Durner, V., Naton, B., Beckers, J., Fuchs, H., Ivandic, B., Klopstock, T., Schulz, H., Wolf, E., Wurst, W., Bally-Cuif, L., Hrabe de Angelis, M., and Graw, J.
- Source
- Full text @ BMC Dev. Biol.
|
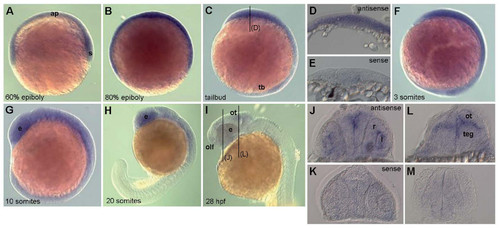
Whole-mount in-situ hybridization for eya3 expression in zebrafish embryos. Whole-mount in-situ hybridization for eya3 expression in zebrafish embryos reveals a ubiquitous expression of eya3 throughout gastrulation and early somitogenesis (A-F). Cross sections at the tailbud stage (level indicated in C) confirm expression in all cell layers (D), compared to a hybridization using the sense probe (E). The expression is more restricted to the anterior part of the embryo at 14 hpf (G). From 19 hpf the expression is most prominent in the developing brain and eye (H). By the beginning of the second day (28 hpf) (I) eya3 expression strongly decreases and is only weakly detectable in the eye, optic tectum, tegmentum and olfactory placode. This is confirmed on cross sections (J, L, at the levels indicated in I) compared to hybridization with the sense probe (K, M). Abbreviations: ap, animal pole; e, eye; l, lens; ot, optic tectum; olf, olfactory placode; r, retina; s, shield; tb, tailbud; teg, tegmentum. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|