- Title
-
IRES-mediated translation of the carboxy-terminal domain of the horizontal cell specific connexin Cx55.5 in vivo and in vitro
- Authors
- Ul-Hussain, M., Zoidl, G., Kloster, J., Kamermans, M., and Dermietzel, R.
- Source
- Full text @ BMC Mol. Biol.
|
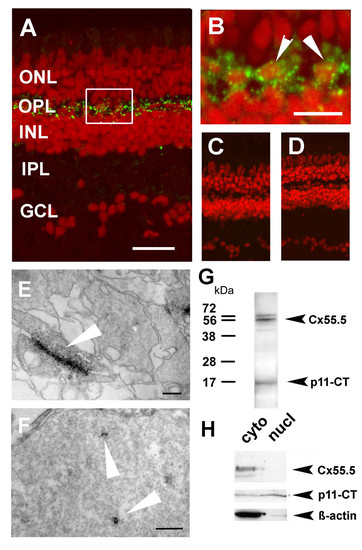
Localization of Cx55.5 immunoreactivity in the nucleus of horizontal cells. A) Confocal imaging using z-stack recordings reproducibly showed that Cx55.5 (green fluorescence) was exclusively expressed in horizontal cells of the outer retina. Scale bar: 100 μm B) The higher magnification of the region of interest (frame in A) provided evidence for small clusters of Cx55.5 immunoreactivity inside the nuclei of HCs (see arrowheads). Scale bar: 20 μm. Antibody controls, C) omitting the primary antibody and D) blocking of the primary antibody by pre-absorption with 1 μg GST-Cx55.5 fusion protein. Nuclei were stained with Sytox Orange (Invitrogen, Karlsruhe, Germany). In order to exclude the possibility that false positive fluorescent emission was recorded from out of focus planes electron microscopical immunohistochemistry of adult retina was performed. Gap junction plaques (arrow) between HCs as shown in E) resemble characteristic membrane associated structures detected with the Cx55.5 antibody, whereas the formation of small clusters (arrows) within the nucleus as shown in F) was typical for nuclear Cx55.5 immunoreactivity. The localization and number of clusters in a single section as shown in the inset was variable but did not exceed N = 3. Note that Cx55.5 immunoreactivity was never found outside the HC layer. Scale bars: 400 nm (E), 300 nm (F). (G) Western blot analysis of total protein extracts isolated from adult retina indicates a doublet of bands at the position 56 kDa and a low molecular weight band at the position 16 kDa. H) Western blot analysis of protein extracts isolated by subcellular fractionation of the adult retina (cyto = cytosolic fraction, nucl = nuclear fraction). The full length Cx55.5 protein product was enriched in the cytoplasmic fraction which is composed of soluble cytosolic proteins and membrane proteins (upper lanes). The 16 kDa protein product was found in the cytosolic and nuclear fraction (middle lanes). The lower blot depicts the β-actin control. Note the faint β-actin band in the nuclear fraction indicating minimal contamination with cytoplasmic remnants. The results shown derived from two independent western blot runs using the same samples (upper and lower lanes: 10% SDS-PAGE; middle lane; 15% SDS-PAGE). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
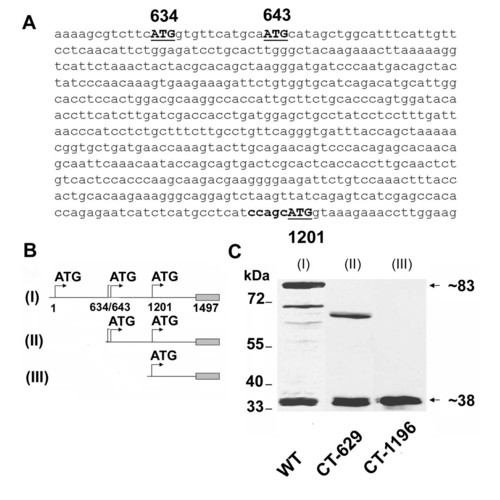
Simultaneous expression of Cx55.5 and its carboxy-terminal domain. A) Nucleotide sequence of the 5′ end of the carboxy-terminal domain, with in-frame ATG codons at nucleotide positions 634, 643 and 1201 shown in bold. B) Schematic representation of EGFP-fusion protein constructs of full length Cx55.5 (WT, I; nt1 to nt1497), carboxy terminal domain of Cx55.5 (II; CT-629; nt629 to nt1497) and 3′ half of carboxy-terminal domain (III; CT-1196; nt1196 to nt1497). C) Western blot analysis of transiently transfected N2A cells with EGFP fusion constructs: (lane I) full length Cx55.5, (lane II) full length carboxy-terminal domain (CT-629), (lane III) 3′ half of the carboxy-terminal domain (CT-1196). Note that in lane I (full length Cx55.5 construct), besides 83 kDa and 38 kDa fusion protein bands, a few putative N-terminally truncated Cx55.5 protein bands are also visible. |
|
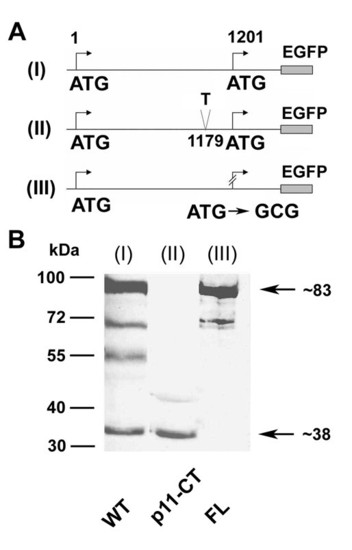
A part of the carboxy-terminal domain of Cx55.5 is translated from an internal translation site within the coding region of Cx55.5: Schematic view of wild type full length WT (I), frameshift mutated (position 1179) full length, p11-CT (II), and in-frame ATG replaced by GCG (position 1201) of full length Cx55.5 construct, FL (III). The frameshift mutation (II) leads to a premature stop codon at nucleotide position 1227. The carboxy-terminus of Cx55.5 is truncated by 90 amino acids and 15 amino acids are altered after the added "T" at nucleotide position 1179. B) Western blot of transiently transfected N2A cells: (lane I) Wild type (WT), (lane II) frameshift mutated p11-CT, and (lane III) ATG replaced by GCG of full length Cx55.5 (FL). |
|
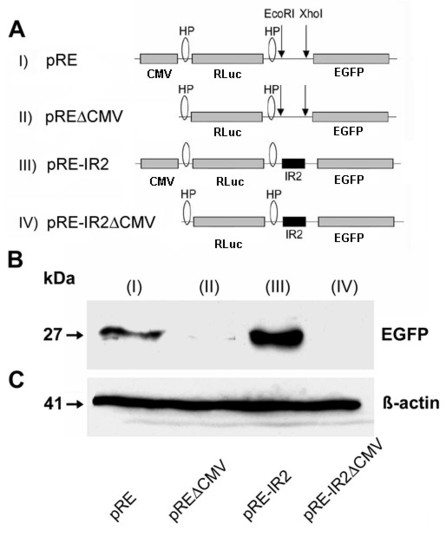
Confirmation of the activity of the IRES element by western blot analysis. A) Schematic representation of the Di-cis vectors with EGFP as second cistron. (I) indicates pRE as control vector, (II) pREΔCMV with the corresponding promoterless control vector, (III) shows the pRE-IR2 with IRES element IR2 (nt631 to nt990) in the inter-cistronic region, and (IV) the corresponding promoterless construct (pRE-IR2ΔCMV). B) Western blot of the expression product of the Di-cis constructs transiently transfected in N2A cells: The blots show the increased expression of the downstream EGFP cistron mediated by the IR2 element (III). C) Western blot of β-actin as loading control. |
|
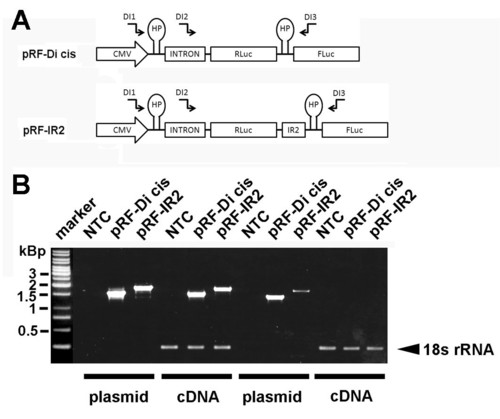
RT-PCR analysis of Di-cis constructs. (A) Schematic view of the Di-cis constructs used for the RT-PCR analysis including the relative position of the haipin structure (HP), the chimeric human globin intron (137 nt), and the primers used for RT-PCR analysis indicated as arrows (see Additional file 5). B) RT-PCR from N2A cells transiently transfected with the control vector pRF-Di cis and the pRF-IR2 construct. A 1 kbp DNA ladder is shown on the left side of the gel. NTC, denotes no template control, PCR products generated from plasmid DNA are denoted as plasmid. RT-PCR products are indicated as cDNA. The 18s rRNA control PCR served as internal standard as described previously (49) |
|
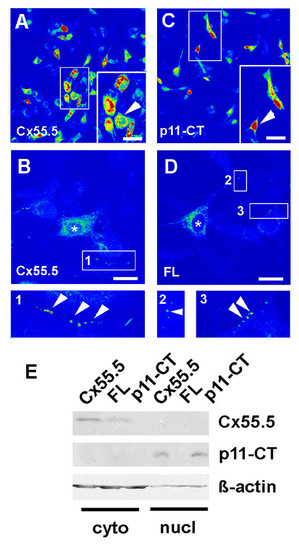
Subcellular localization of the Cx55.5 protein isoforms in vitro. The subcellular distribution of FLAG tagged Cx55.5, FL and p11-CT proteins was determined by immunocytochemistry. All constructs were transiently expressed in NIH3T3 cells. Confocal images were collected using the LSM510 Meta system and software. Pictures shown represent single optical planes which are presented in pseudocolours for better representation of the staining intensity. Red label indicates maximal concentration. A, B) Wild-type Cx55.5 construct (WT) co-expressing the full length Cx55.5-FLAG and p11-CT-FLAG fusion proteins. (magnification in A: 40x, Scale bar = 30 μm; in B: 63x magnification, Scale bar = 15 μm). Highest concentrations occur in perinuclear regions and the nucleus. B) Higher magnification of the WT construct with a ROI (1) showing punctuate membrane label. C) FLAG-tagged p11-CT with maximal concentration in the nuclei. The arrowheads in the inset indicates the characteristic nuclear localization of p11-CT. (magnification: 40x; Scale bar 30 μm). D) FLAG-tagged FL protein encoding for the full length Cx55.5 protein only (magnification 63x, Scale bar: 15 μm). Besides lack of nuclear staining plaque-like protein assemblies occur at sites of cell contacts (indicated by arrowheads in inset 2 and 3). Such membrane bound fluorescence was not observed with the p11-CT construct. (E) Western blot analysis of cytosolic and nuclear fractions of Cx55.5-FLAG, FL-FLAG and p11-CT-FLAG transfected N2A cells. 20 μg of total nuclear and 10 μg of cytosolic protein was separated by SDS-PAGE on a 12% gel. Immunoblot detection was done using anti-Cx55.5 as primary antibody (1 μg/ml). The upper lanes represent the full length Cx55.5 protein products expressed by the Cx55.5 wildtype protein and the FL mutant. The middle lane refers to the p11-CT protein expressed by the Cx55.5 wildtype and p11-CT proteins, but not by the FL mutation. The lower blot depicts the β-actin control. Note that the β-actin signal in the nuclear fraction is significantly reduced despite the fact that more protein was loaded on the gel. This indicates a minimal contamination with cytoplasmic remnants. |
|
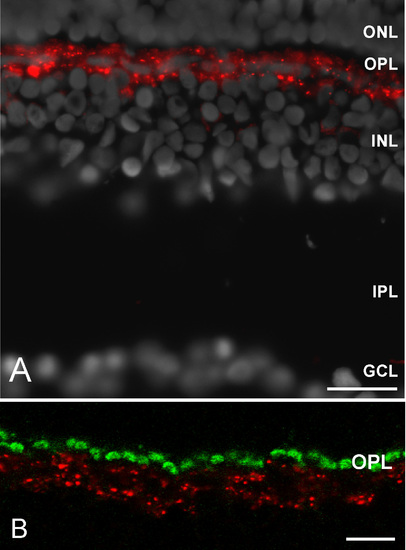
Cx55.5 protein localization in the outer retina of the zebrafish. (A) Overview of the retina demonstrating the highly restricted expression of Cx55.5 in a single band like cell layer. (B) The higher magnification demonstrates the co-localization of Cx55.5 and GluR2 proteins in horizontal cells. (Abbreviations: ganglion cell layer, GCL; inner plexiform layer, IPL; inner nuclear layer, INL; outer plexiform layer, OPL; outer nuclear layer, ONL; pigment epithelium, PE). Scale bar in Fig A = 20 μm. Scale bar in B = 10 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
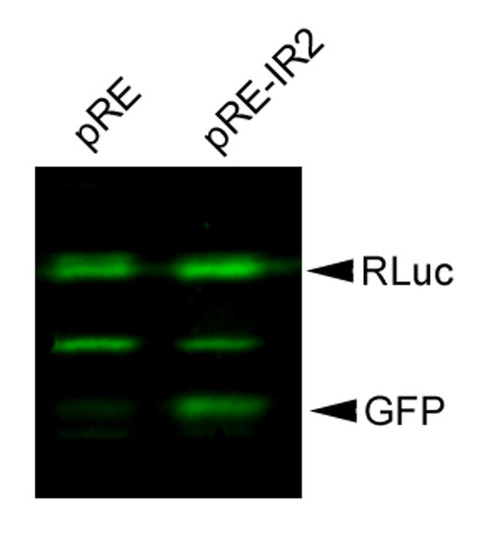
IR2 mediated upregulation of GFP expression in the bi-cistronic vector assay. Western blot of pRE and pRE-IR2 transfected N2A cells. This experiment demonstrates that the IRES element substantially promoted expression of the EGFP protein. |
|
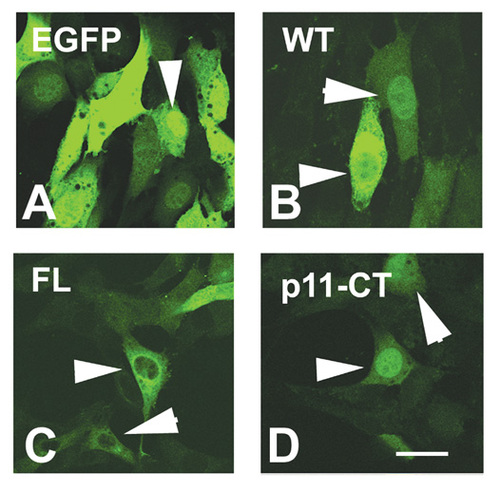
Subcellular localization of Cx55.5 protein variants in transfected NIH3T3 cells: Confocal laser scanning imaging of the subcellular distribution of EGFP and the Cx55.5-EGFP fusion protein constructs in NIH3T3 cells. This experiment confirmed the distinct distribution of FL and p11-CT isoforms. Note that p11-CT showed a pronounced nuclear accumulation with some staining in the cytoplasm. Scale bar: 25 μm. |