- Title
-
Crucial role of zebrafish prox1 in hypothalamic catecholaminergic neurons development
- Authors
- Pistocchi, A., Gaudenzi, G., Carra, S., Bresciani, E., Del Giacco, L., and Cotelli, F.
- Source
- Full text @ BMC Dev. Biol.
|
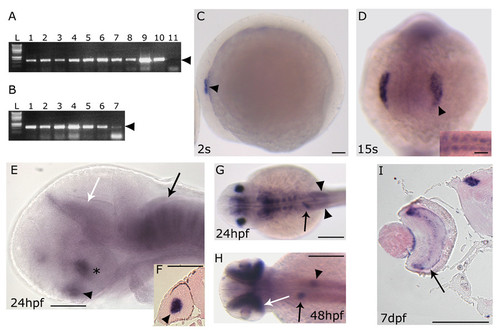
prox1 temporal and spatial expression pattern analyzed by RT-PCR and in situ hybridization. (A) RT-PCR performed on different embryonic stages: 1?2 cells stage (lane 1), 30% epiboly (lane 2), 50% epiboly (lane 3), 80% epiboly (lane 4), tail bud (lane 5), 8 somites (lane 6), 15 somites (lane 7), 24 hpf (lane 8), 72 hpf (lane 9), 5 dpf (lane 10) and negative control (lane 11) in the absence of cDNA. (B) RT-PCR performed on different adult organs: DNA ladder (L), testis (lane 1), overy (lane 2), gills (lane 3), gut (lane 4), eye (lane 5), brain (lane 6) and liver (lane 7). Arrowhead indicates the size of the prox1-specific PCR product (620 bp). (C-I) prox1 WISH (C) the first signals appeared at 2 s in the otic placode (arrowhead). (D) at 15 s the signal is detected in the lens placode (arrowhead), and somites (inset). (E) at 24 hpf prox1 is expressed the hypothalamus (asterisc), the pituitary (black arrowhead), the pretectal segment (prosomere 1) (white arrow), as well as segmentally arranged cells of the hindbrain (black arrow). (F) transverse section through the forebrain of a 24 hpf stage zebrafish embryo shows the signal in the lens (black arrowhead). (G) at 24 hpf additional prox1 signals are present in the liver primordium (arrow), and posterior lateral line primordium (arrowheads). (H) later during development, (48 hpf) prox1 expression is detected in distinct domains in the liver (arrow) and pancreas (arrowhead), while a further signal appeares in the retina (white arrow). (I) transverse section through the forebrain of a 7 dpf stage zebrafish larva shows the signals in the retina inner nuclear layer (arrow) and in the pretectal nuclei (arrowhead). (C,E) Lateral views are shown. (D) Frontal view is shown. (G,H) Dorsal views are shown. Anterior is always to the left. Scale bars indicate 100 μm (A,B,C,D,G,H,I) or 200 μm (E,F). |
|
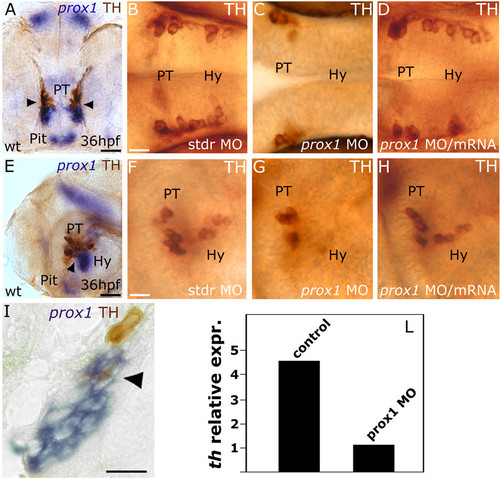
prox1 is required for the development of CA neurons in the hypothalamus. Anterior is left in all panels except (A), frontal view. Dorsal is up, except for (B,C,D), dorsal view. Eyes or lens have been removed for better lateral viewing. (A,E,I) prox1 WISH combined with TH immunohistochemistry. Anti-TH antibody labels the PT and hypothalamic CA neurons at 36 hpf. Colabelling with prox1 is evident in a fraction of TH-positive neuroblasts in the hypothalamus (arrowheads), as also confirmed by the longitudinal section of the embryo (I). (C,G) microinjection of prox1 MO lowers the number of TH-labelled CA neurons in the hypothalamus in comparison to standard control injected embryos (B,F). (D,H) coinjection of prox1 mRNA and prox1 MO rescued the morphant phenotype. (L) Quantitative real time RT-PCR. TH-specific mRNA is almost five-fold decreased following prox1 MO injection. The result represents at least three independent experiments, and 18S was used as an internal control. The following abbreviations are used: posterior tuberculum (PT), pituitary (Pit), hypothalamus (Hy), standard control morpholino oligonucleotide (stdr MO). Scale bars indicate 10 μm (B,F,I) or 20 μm (A,E). |
|
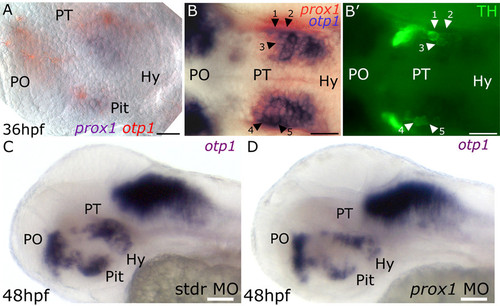
prox1 functions are required for proper otp1 and TH phenotypes in the hypothalamic area. Anterior is left, dorsal is up except for (B,B′), dorsal view. In (A) eyes have been removed. (A) prox1/otp1 double WISH. Double staining of prox1 (blue) and otp1 (red) mRNAs at 36 hpf stage reveals that otp1 and prox1 colocalize in the hypothalamus. (B,B′) 36 hpf prox1/otp1 double WISH combined with TH immunohistochemistry. (B) A group of prox1/otp1-positive cells in the hypothalamus are also positive (B′) for TH; for better orientation, some of these cells have been numbered (1?5) and indicated by black (B) and white (B′) arrowheads, respectively. otp1 hypothalamic expression in (C) standard control morpholino and (D) prox1 MO injected embryos at 48 hpf. The following abbreviations are used: posterior tuberculum (PT), preoptic area (PO), standard control morpholino oligonucleotide (stdr MO). The following abbreviations are used: posterior tuberculum (PT), preoptic area (PO), pituitary (Pit), hypothalamus (Hy). Scale bars indicate 20 μm (A,B,B′) or 30 μm (C,D). |
|
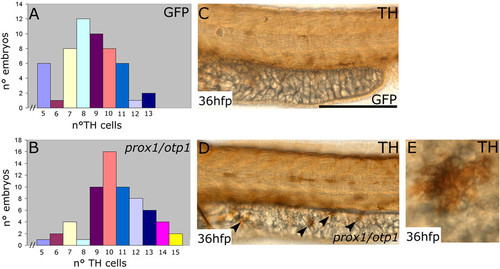
Synergistic prox1/otp1 overexpression induces the appearance of hypothalamic supernumerary TH-positive neurons and ectopic TH-positive cells on the yolk surface ectoderm. Lateral view, anterior is left and dorsal is up. (A,B) Distribution of TH positive cells in control and overexpressed prox1/otp1 embryos at 36 hpf. (A) The most numerous class in the group of GFP mRNA injected control embryos presented 8 CA hypothalamic neurons, and only 3 embryos presented more than 11 TH hypothalamic positive cells (n = 54). (B) The most numerous class in the group of the overexpressed prox1/otp1 embryos (n = 64) presented 10 CA neurons, and 20 embryos showed more than 11 TH hypothalamic positive cells. (C,D) Immunostaining with TH antibody shows ectopic TH positive cells on the yolk surface ectoderm of prox1/otp1 double injected embryos (arrowheads), while these cells are not present on the yolk of control embryos. (E) Ectopic TH positive cell on the yolk surface ectoderm. Scale bars indicate 50 μm. |
|
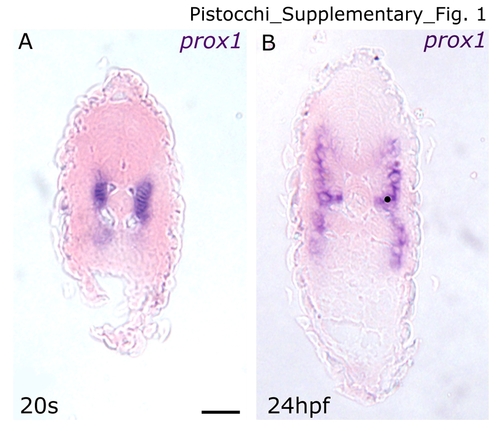
prox1 expression in the adaxial cells. Transverse section through the caudal trunk of the embryo. (A) 20 s embryo. prox1 signal is present only in the adaxial cells. This is approximately the time that these cells elongate in the anteroposterior dimension. (B) 24 hpf embryo. The adaxial cells expressing prox1 are now lateral. Dorsal is always up. Scale bar indicates 50 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
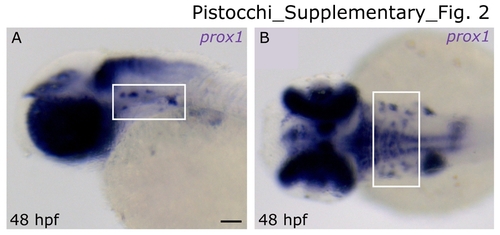
prox1 expression in cranial ganglia. 48 hpf embryo lateral (A) and dorsal (B) view, respectively. prox1 mRNA is expressed in presumptive cranial motor and sensory neurons (boxed regions). Anterior is always to the left. Scale bar indicates 50 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
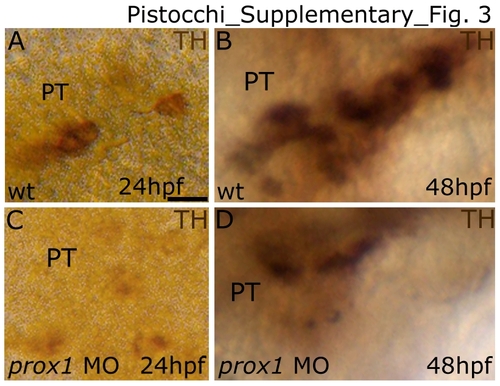
prox1 is required during the development of hypothalamic CA neurons. Lateral view in all panels. Anterior is to the left, and dorsal is up. Microinjection of prox1 MO lowers the number of hypothalamic CA neurons. At 24 and 48 hpf the TH-labelled cells in the hypothalamic/PT area are reduced in number in the prox1 MO injected embryos (B,D) when compared to the control embryos injected with stdr MO (A,C). The following abbreviation is used: posterior tuberculum (PT). Scale bar indicates 10 μm. |
|
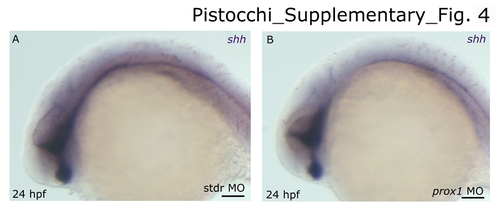
shh expression pattern in the CNS of stdr MO and prox1 MO injected embryos. Anterior is left and dorsal is up in all panels. (A) 24 hpf embryo injected with standard control morpholino oligonucleotide. (B) 24 hpf embryo injected with prox1 MO. The overall brain patterning of the ventral diencephalon is not affected in prox1 MO injected embryos, as suggested by the normal expression of shh that we used as marker of proper differentiation of the ventral diencephalon. The following abbreviations are used: standard control morpholino oligonucleotide (stdr MO). Scale bars indicate 50 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
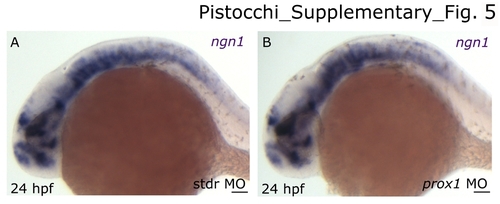
ngn1 expression pattern in the CNS of stdr MO and prox1 MO injected embryos. Anterior is left and dorsal is up in all panels. (A) 24 hpf embryo injected with standard control morpholino oligonucleotide. (B) 24 hpf embryo injected with prox1 MO. Neurogenesis is not disturbed in prox1 MO injected embryos as shown by normal ngn1 hypothalamic expression. The following abbreviation is used: standard control morpholino oligonucleotide (stdr MO). Scale bars indicate 50 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
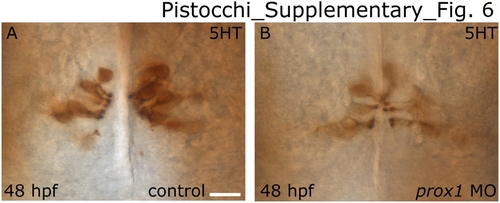
5HT expression in prox1 MO injected embryos. Ventral view in all panels. Anterior is up. Anti-5HT antibody labels the hypothalamic serotonergic neurons at 48 hpf. (B) microinjection of prox1 MO does not significantly lower the number of 5HT-labelled neurons in the hypothalamus in comparison to the 48 hpf embryos injected with the same concentration of standard control morpholino oligonucleotide (A). Scale bar indicates 10 μm. |
|
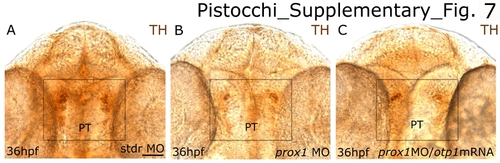
TH expression in prox1 MO/otp1 mRNA coinjected embryos. Ventral view in all panels. Anterior is up. Anti-TH antibody labels the PT and hypothalamic CA neurons at 36 hpf (boxed regions). (B) microinjection of prox1 MO lowers the number of TH-labelled CA neurons in the hypothalamus in comparison to the 36 hpf embryos injected with the same concentration of standard control morpholino oligonucleotide (A). (C) coinjection of prox1 MO and otp1 synthetic mRNA did not restore the normal TH phenotype. Scale bar indicates 20 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
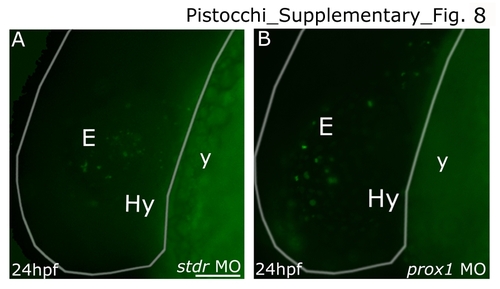
prox1 MO injected embryos do not show increased apoptosis. Lateral view in all panels. Anterior is to the left, and dorsal is up. Apoptosis in 24 hpf embryos has been evaluated by means of TUNEL assay. (B) prox1 MO injected embryos do not show increases in apoptosis when compared to the control embryos injected with stdr MO (A). The white drawing indicates the profile of the embryos. The following abbreviations are used: standard control morpholino oligonucleotide (stdr MO), eye (E), hypothalamus (Hy), yolk (y). Scale bar indicates 50 μm. |