- Title
-
Generation of FGF reporter transgenic zebrafish and their utility in chemical screens
- Authors
- Molina, G.A., Watkins, S.C., and Tsang, M.
- Source
- Full text @ BMC Dev. Biol.
|
Generation of Dusp6 DNA construct and expression of d2EGFP in transgenic embryos. (A) Diagram showing the Dusp6 gene locus and the DNA construct used in generating transgenic zebrafish. (B, E, & H) dusp6 expression at oblong (B), dome (E), and shield stage. (C) d2EGFP mRNA expression at sphere stage. (D, F, G, I, & J) Tg(Dusp6:d2EGFP)pt6 embryos at dome (D), 30% epiboly (F & G), and shield (I & J) stage. (B-F & I) are lateral views and (H & J) are animal views. Red arrowheads mark dorsal region of the embryo. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
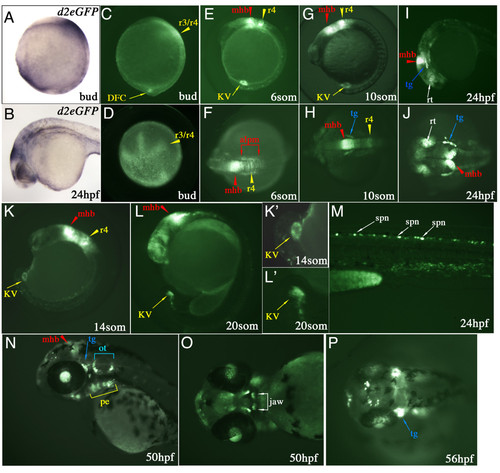
Spatial and temporal d2EGFP expression in Tg(Dusp6:d2EGFP)pt6 embryos. (A & B) Lateral views of d2EGFP mRNA expression at Bud stage and 24 hpf. (C-P) d2EGFP expression in Tg(Dusp6:d2EGFP)pt6 embryos, stages are indicated in each panel. At bud stage (C & D), d2EGFP is detected in the hindbrain (r3/r4, yellow arrowhead) and within the caudal region in the DFCs. (E, G & K) From 8- to 14-somite stages, lateral views show expression of d2EGFP in cells lining Kupffer's vesicle, within r4 (r4, yellow arrowhead) and the mid-hindbrain boundary (mhb, red arrowhead). (F & H) Dorsal views show high d2EGFP expression within the MHB, r4 and the anterior lateral plate mesoderm (alpm, red brackets). (H) At 10-somite stage initial d2EGFP expression is detected within the trigeminal ganglia (tg, blue arrow). (I & J) 24 hpf embryo showing d2EGFP expression in the MHB, trigeminal ganglia, dorsal retina (rt, white arrow) and pharyngeal endoderm (pe, yellow bracket). (K & L) 14 and 20-somite stage embryo highlighting the expression of d2EGFP in Kupffer's vesicle. Higher magnifications are show in (K' & L'). (M) Trunk region shows d2EGFP expression within the dorsal spinal cord neurons (spn, white arrow) at 24 hpf. (N) At 50 hpf expression is noted in the MHB, trigeminal ganglia, pharyngeal endoderm and otic vesicle (ot, blue bracket). (O) Ventral view of 50 hpf, showing d2EGFP expression in the jaw (white bracket). (P) At 56 hpf, strong expression in noted in the trigeminal ganglia, the jaw and also in neurons within the dorsal diencephalon. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
D2EGFP expression is dependant on FGF signaling. (A & B) Lateral views of gastrula staged Tg(Dusp6:d2EGFP)pt6 embryos. Control uninjected is shown in (A), while in (B) fgf8 mRNA injected at the 2-cell stage. Expression of d2EGFP is greatly expanded in fgf8-injected embryos. (C & D) Lateral views of 28 hpf transgenic embryos. (C) Control MO injected (D) fgf8-MO injected embryo shows loss of d2EGFP expression within the MHB, dorsal retina and smaller otic vesicles. Red arrowhead: MHB; yellow arrow: dorsal retinal; blue arrowhead: optic stalk; red bracket: otic vesicle. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
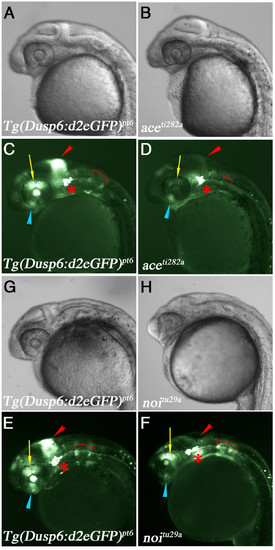
D2EGFP expression in fgf8/ace and pax2.1/noi mutants. (A-F) Lateral views of Tg(dusp6:d2EGFP)pt6 embryos at 28 hpf crossed into ace or noi mutants. Genotype is listed in bottom left corner. (A & B) Brightfield images of wildtype sibling and ace mutant embryo, respectively. (C & D) d2EGFP expression in WT sibling and ace mutant. Note loss of d2EGFP expression within the MHB, dorsal retina, and the smaller otic vesicle, while d2EGFP expression in the trigeminal ganglia is unaffected. (G & H) Brightfield images of wildtype sibling and noi mutant embryo. (E & F) d2EGFP expression is lost in the MHB and optic stalk. In contrast to the ace mutants, expression within the dorsal retina and otic vesicles are normal. PHENOTYPE:
|
|
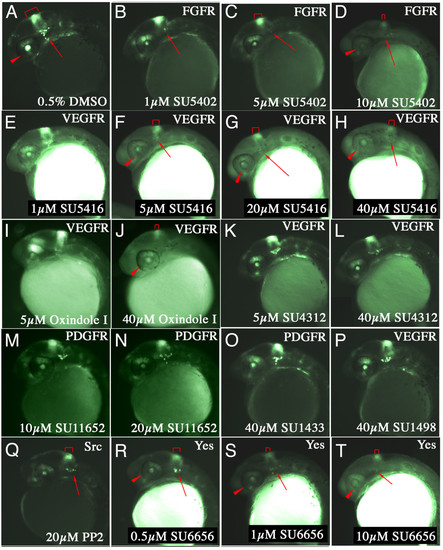
Validation of Tg(Dusp6:d2EGFP)pt6 line for chemical screening. (A-Y) Lateral views of 30 hpf embryos treated with the compound and dose are indicated on the bottom right. The protein targets for these compounds are listed in the top right hand corner. (A) Embryo incubated in 0.5% DMSO as control. (B-D) Increasing doses of SU5402 suppressed d2EGFP expression in the MHB (red bracket), trigeminal ganglia (red arrow) and dorsal retina (red arrowhead). (E-H) Increasing doses of SU5416, a non-specific inhibitor of VEGFRs, suppressed FGF signalling. (I & J) Oxindole I another related VEGFR inhibitor also suppressed d2EGFP fluorescence in transgenic embryos. (K-N) In contrast, two compounds with similar chemical structure SU4312 and SU11652, did not block FGF signalling. (O & P) Likewise, two unrelated inhibitors of PDGFR and VEGFR, SU1433 and SU1498 also failed to suppress d2EGFP expression. (Q-T) PP2 and SU6656, two Src Kinase inhibitors suppressed FGF signalling in transgenic embryos. |
|
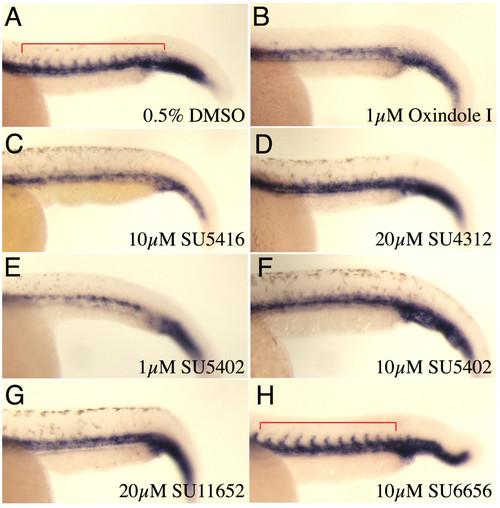
Expression of dusp6 in chemically treated embryos. (A-H) Lateral views of 24 hpf embryos treated with compounds indicated on bottom left and probed for the presence of dusp6 transcripts. (A) DMSO control, dusp6 is strongly expressed in the MHB (brackets), pharyngeal endoderm (arrow). (B) SU5402 at 10 μM greatly suppresses dusp6 transcription, while at a higher dose, 20 μM (C) dusp6 expression is almost eliminated. (D-F) SU6656, SU5416 and Oxindole I treated embryos exhibited weaker dusp6 expression. (G & H) SU4312 and SU11652 did not significantly alter dusp6 expression. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
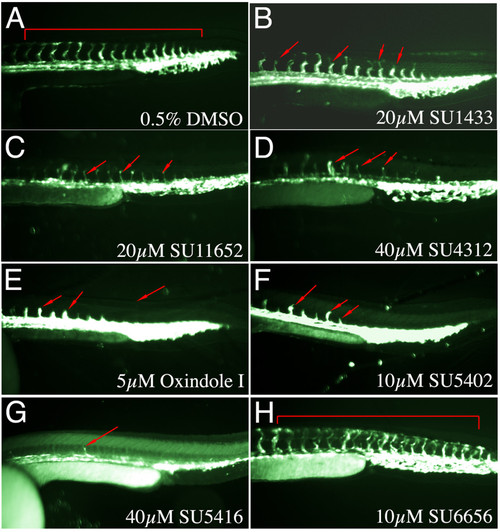
Specificity of Indolinones towards FGFR versus VEGFR signalling. (A-H) Lateral trunk views of 32 hpf Tg(Fli1:EGFP)y1 embryos treated with the chemicals shown on the bottom left. (A) DMSO control shows embryo with normal expression of EGFP within the intersegmental vessels. (B) 20 μM SU1433, (C) SU11652, (D) SU4312 (E) Oxindole I, (F) SU5402, and (G) SU5416 all suppressed ISV outgrowth as indicated by red arrows. (H) SU6656 in contrast did not alter ISV formation. |
|
Expression of fli1 in intersegmental vessels in indolinone treated embryos. (A-H) Lateral trunk views of fli mRNA expression within the ISV. (A) DMSO control shows vessel sprouts at 28 hpf. (B-G) Embryos treated with the compounds indicated show loss of ISV sprouts, while in (H) SU6656 did not affect these vessels. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|