- Title
-
Expression and regulation of the zinc finger transcription factor Churchill during zebrafish development
- Authors
- Londin, E.R., Mentzer, L., Gates, K.P., and Sirotkin, H.I.
- Source
- Full text @ Gene Expr. Patterns
|
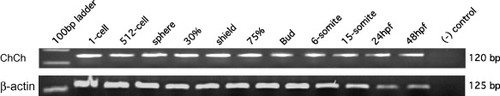
RT-PCR analysis of chch expression. RT-PCR of mRNA from staged wild-type embryos with chch specific primers reveals that chch transcripts are present during the first 48 h of development at all stages analyzed. β-Actin was run as a loading control. |
|
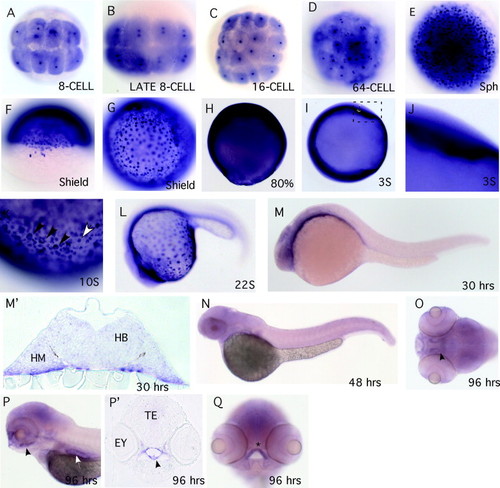
Whole mount RNA in situ hybridization analysis of chch expression in zebrafish. The chch expression pattern was examined in zebrafish by RNA in situ hybridization. In situ hybridization probes to the 52-UTR and coding region or just the 32-UTR were used; both gave similar results and only one is shown. During cleavage stages, chch transcripts are detected in the cytoplasm of all cells. Concentrated stain is also detected in the nucleus of each cell (A?D). At sphere and shield stages, chch is widely expressed and some cells express higher levels of transcript including a subset of forerunner cells (E?G). At 80% chch is ubiquitously expressed throughout the embryo but the punctate stain is less apparent (H). From the three-somite stage through the 22-somite stage chch transcripts are weakly detected throughout the embryo with highest levels in the ventral-most regions of the embryo close to the yolk (I?L) and in a punctate pattern on the surface of the yolk (focus on the surface of the yolk) (K). In panel (K), the black arrowheads mark presumptive mucous cells and the white arrowhead is a presumptive keratinocyte. At 30 hpf chch transcripts are enriched in anterior neural tissue and ventral cells adjacent to the yolk (M) and (M2). The section in (M2) is at the level of the hindbrain. At 48 hpf chch expression is weak and indistinct (N). At 96 hpf chch transcripts are detected in the pharynx (black arrowhead), gut (white arrowhead) and ethmoid plate (asterisk) (O?Q, section in P2). (A?E and G) Animal pole views; (F and O) dorsal views; (H?N and P) lateral views; and (Q) frontal view. Abbreviations used are: hindbrain (HB), head mesoderm (HM), eye (Ey) and tectum (TE). |
|
chch is zygotically expressed prior to the mid-blastula transition. To determine if the early nuclear stain observed represents new zygotic transcripts, embryos were microinjected with the transcription inhibitor Actinomycin D (B) or DMSO (A). Embryos were collected at the 64-cell stage and examined for chch expression by RNA in situ hybridization. Following Actinomycin D treatment, the nuclear stain is lost. As a further test to confirm early zygotic transcription of chch, real-time PCR was performed on 1-cell through 16-cell embryos to determine if the relative amount of chch gene expression is increased as development progresses. This analysis revealed an increase in chch expression over these stages (C). Together these results show that chch is zygotically transcribed prior to the mid-blastula transition. |
|
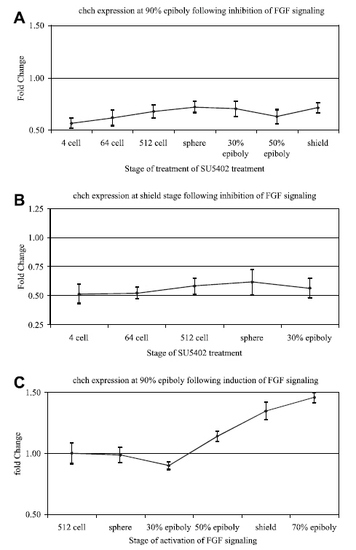
FGF signaling regulates zebrafish chch expression. To determine if FGF signaling regulates chch gene expression, chch expression was assayed by real-time PCR following inhibition (A–B) or activation (C) of FGF signaling. Wild-type embryos were placed in were treated for 2 h in SU5402 to block FGF signaling at the indicated stage (x-axis) and collected at 90% epiboly (A) or shield stage (B) for real-time PCR. FGF signaling was induced by the addition of AP20187 to iFGFR1 mRNA injected embryos. Embryos were placed in the AP20187 at the indicated stage (x-axis) for 15 min then washed and collected at 90% epiboly for real-time PCR (C). The fold change in chch transcript levels (y-axis) is graphed relative to untreated control embryos (which is set at 1). EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
Reprinted from Gene expression patterns : GEP, 7(6), Londin, E.R., Mentzer, L., Gates, K.P., and Sirotkin, H.I., Expression and regulation of the zinc finger transcription factor Churchill during zebrafish development, 645-650, Copyright (2007) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Gene Expr. Patterns