- Title
-
Sema3a1 guides spinal motor axons in a cell- and stage-specific manner in zebrafish
- Authors
- Sato-Maeda, M., Tawarayama, H., Obinata, M., Kuwada, J.Y., and Shoji, W.
- Source
- Full text @ Development
|
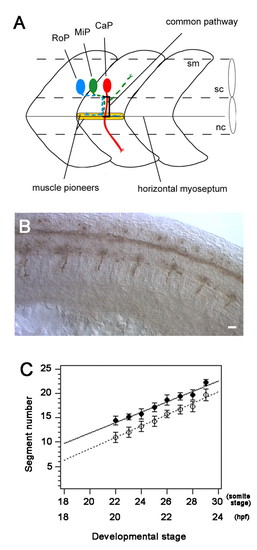
CaP axons extend sequentially starting with those from anterior segments. (A) Schematic representation of the three primary motoneurons (CaP, MiP and RoP) showing their axonal trajectories. CaP axons are projected first to establish the common pathway. The common pathway ends at the muscle pioneers located at the horizontal myoseptum that divides the myotome into dorsal and ventral halves. This point is a choice point where the three axons diverge and follow cell specific pathways to innervate the ventral (CaP), dorsal (MiP) and horizontal myoseptal (RoP) myotomes. sc, spinal cord; nc, notochord; sm, somite. (B) Side view of the trunk of a 28-somite stage (23 hpf) embryos showing that CaP axons labeled with mAb znp1 are more developed anteriorly. Scale bar: 20 Ám. (C) The compilation of the stage of initial CaP axon projection (black circle) and the stage when they arrive at the horizontal myoseptum (white circle) by CaPs located in specific segments. CaP axons were projected earlier in anterior segments, e.g. stage 22 for CaPs in segment 14 and stage 29 for those in segment 22. Most CaP axons reached the horizontal myoseptum 1.5 hours after time of initial projection. Each data point represents the mean of at least seven CaPs that were assayed from embryos at 22- to 29-somite stages (20-23.5 hpf). Bars in indicate standard deviations. |
|
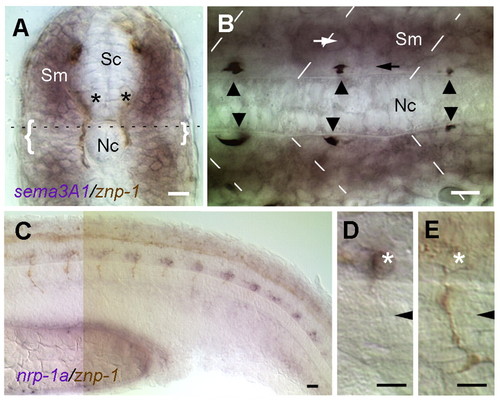
The expression patterns of sema3a1 and nrp1a correlate with extension of CaP axons along the common pathway. In situ hybridization (purple) for sema3a1 (A,B) or nrp1a (C-E) with immunostaining (brown) by mAb Znp1 that labels primary motor axons in 26-somite stage (22 hpf) embryos. Unless otherwise noted, embryos are oriented with rostral leftwards and dorsal upwards. (A) A transverse section of the trunk with dorsal upwards showing that sema3a1 is expressed in the dorsal and ventral regions of the myotome and less so in the horizontal myoseptal region (brackets). Asterisks indicate CaP motoneurons whose axons extend along the medial surface of the myotome. Sm, somite; Nc, notochord; Sc, spinal cord. Broken line indicates the level of the horizontal section shown in B. (B) A horizontal section with rostral leftwards, showing that the myotome cells immediately adjacent to the notochord, which CaP axons (arrowheads) extend upon, express little to no sema3a1 (black arrow). However, the more lateral cells express higher levels of sema3a1 (white arrow). Broken lines indicate somite borders. (C) Lateral view of the trunk showing that nrp1a is expressed segmentally in ventral spinal neurons that, based upon their axon trajectory, correspond to CaP neurons. Presumptive VaP (variable primary) neurons that arise in about half of the hemisegments as equivalent pair of CaP, but later die, may also express nrp1a. The expression of nrp1a declines in more anterior and developed CaPs. (D) nrp1a is expressed by CaP motoneurons (asterisk) while they are extending along the common pathway. (E) nrp1a expression is much reduced in CaP neurons (asterisk) with axons (mAb Znp1 immunostained in brown) extending onto the specific ventral pathway. Arrowheads in D,E indicates the position of the horizontal myoseptum. Scale bars: 20 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
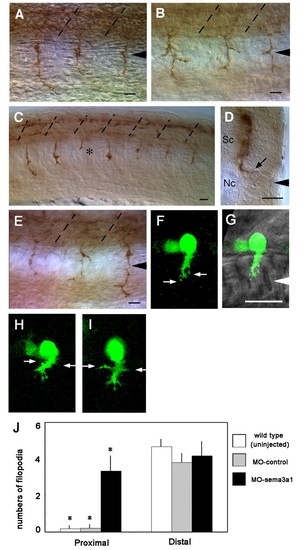
Extension by CaP axons is aberrant following knockdown of Sema3a1. (A) CaP axons extend normally in a control sema3a1 MO-injected embryo (24 hpf) seen in a lateral view. Arrowhead indicates the nascent horizontal myoseptum and broken lines indicate somitic segmental borders. (B) CaP axons often branch aberrantly in an antisense sema3a1 MO-injected embryo (24 hpf). (C) CaP axons can stall (asterisk) in an antisense sema3a1 MO-injected embryo (24 hpf). (D) Transverse section showing a CaP axon extending abnormally into the lateral myotome in the horizontal myoseptal region (arrow) in an antisense sema3a1 MO-injected embryo (24 hpf). Sc, spinal cord; Nc, notochord. (E) Aberrantly branched CaP axons in an antisense nrp1a MO-injected embryo (24 hpf). (F) GFP-labeled CaP neurons in a nrp1a:gfp transgenic embryo showing filopodia from the leading edge of the growth cone (arrows) but not the axon behind the growth cone. (G) Nomarski bright-field image is overlaid to show the location of the CaP growth cone. White arrowhead indicates the horizontal myoseptum. (H,I) Two independent examples showing the same feature. Filopodia extending from the growth cone and trailing axon (arrows) of CaP neurons in a nrp1a:gfp transgenic embryo following injection of antisense sema3a1 MO. (J) Histogram showing an increase in lateral filopodia in CaP axons in the proximal half of the axon in Sema3a1 morphant embryos compared with uninjected embryos and control morphants. Filopodia were quantified from 10 Ám CaP axons that were divided into proximal and distal halves. Bars indicate s.d. *P<0.002 for Student's t-test between CaP axons in antisense sema3a1 morphants (n=6) versus control morphants (n=5) and uninjected embryos (n=6). Scale bars: 20 Ám. |
|
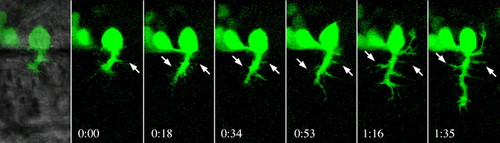
Some lateral filopodia extended from CaP axons develop into aberrant branches in antisense sema3a1 morphants. Sequential images of an extending CaP axon in a nrp1a:gfp embryo (starting at 22 hpf) showing that some of the lateral filopodia enlarge into branches (arrows). Time of each frame is shown below each micrograph. |
|
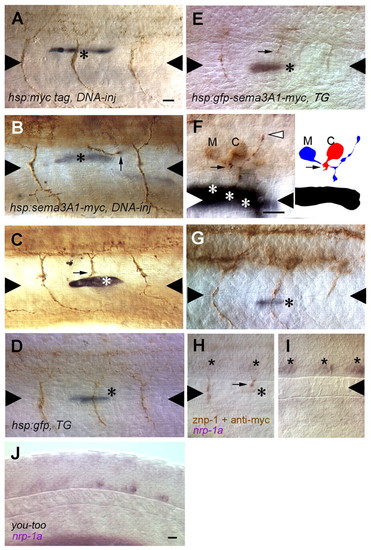
CaP axons are repulsed by myotome cells that express ectopic Sema3a1 along the common pathway but not by those along the CaP specific ventral pathway. (A) A CaP axon is not perturbed by a myotome cell (asterisk) along the common pathway that expresses the Myc epitope following heat induction of a hsp70:myc injected embryo. Triangles denote the horizontal myoseptum. (B) A CaP axon (arrow) appears to have turned away to avoid a myotome cell (asterisk) along the common pathway that expresses ectopic Sema3a1 following heat induction of a hsp70:sema3a1-myc-injected embryo. CaP axons in the segment anterior and posterior to the repulsed CaP follow a normal trajectory. The myotome cell expressing ectopic Sema3a1 in the posterior segment is out of the focal plane of the CaP axon and is located lateral to the medial myotome cells lining the common pathway. (C) A CaP axon (arrow) appears to have stalled when encountering a myotome cell (asterisk) along the common pathway that expresses ectopic Sema3a1 following heat induction of a hsp70: sema3a1-myc-injected embryo. (D) A CaP axon is not perturbed by a muscle pioneer cell (asterisk) laser induced to express GFP in a hsp70:gfp transgenic embryo. (E) A CaP axon (arrow) is stalled in the vicinity of a muscle pioneer (asterisk) laser induced to express ectopic Sema3a1 in a hsp70:gfp-sema3a1-myc transgenic embryo. (F) A CaP axon (arrow) is stalled in the vicinity of three myotome cells (asterisks) along the common pathway laser induced to express ectopic Sema3a1 in a hsp70:gfp-sema3a1-myc transgenic embryo, but a presumptive MiP axon (white arrowhead) is normal. Right panel shows a camera lucida drawing of the CaP and MiP motoneurons. C, the CaP cell body; M, the MiP cell body. (G) A CaP axon appears normal despite encountering a ventral muscle fiber beyond the horizontal myoseptum laser-induce to express ectopic Sema3a1 in a hsp70:gfp-sema3a1-myc transgenic embryo. The CaP axon immediately posterior to the experimental CaP axon maybe shorter because it is paused at the choice point. (H) nrp1a expression is downregulated in CaP neurons, despite not having reached the horizontal myoseptum because of stalling in the vicinity of a myotome cell (asterisk) laser induced to express ectopic Sema3a1 in a hsp70:gfp-sema3a1-myc transgenic embryo. Stars indicate CaP cell bodies. (I) CaPs (stars) in more caudal segments in the embryo shown in H have not yet projected axons but do express nrp1a. (J) nrp1a is downregulated in CaP neurons in you-too mutants (26 somite-stage; 22 hpf) in which CaP axons fail to extend properly along the common pathway. Scale bars: 20 μm. EXPRESSION / LABELING:
|
|
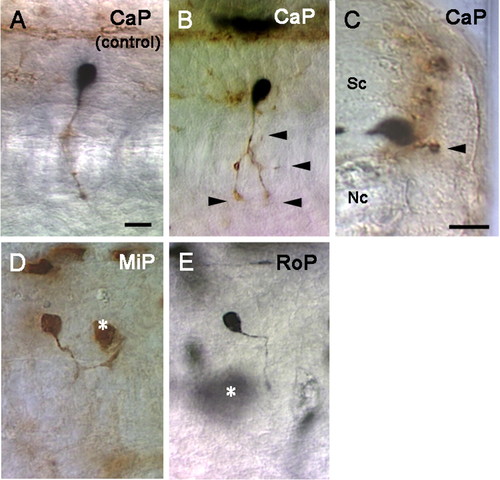
Ubiquitous expression of ectopic Sema3a1 induces abnormal outgrowth by CaP axons but not MiP or RoP axons. Wild-type biotin-labeled donor cells (black) were transplanted into unlabeled hsp70:gfp-sema3a1-myc transgenic hosts. Hosts were heat induced and donor motor axons assayed with mAb Znp1 (brown). (A) Wild-type donor CaP in a heat induced wild-type host extended normally. (B) Wild-type CaP neuron in a hsp70:gfp-sema3a1-myc transgenic host branched (arrowheads) aberrantly following heat induction of Sema3a1. (C) Transverse section showing a donor CaP axon extending aberrantly into lateral regions of the myotome (arrowhead) in a hsp70:gfp-sema3a1-myc transgenic host following heat induction of Sema3a1. (D) A donor MiP axon extended normally in a hsp70:gfp-sema3a1-myc transgenic host following heat induction of Sema3a1. Asterisk indicates a non-motoneuron donor cell. (E) A donor RoP axon extended normally in a hsp70:gfp-sema3a1-myc transgenic host following heat induction of Sema3a1. Scale bars: 20 μm. |