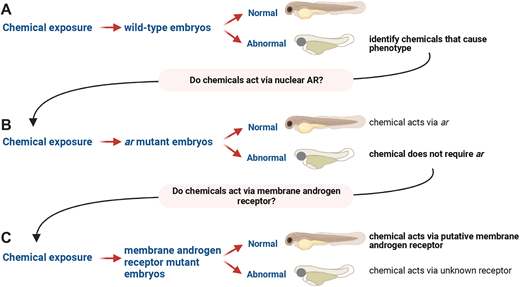
Fig. 1 Chemical-genetic screen to identify receptors that mediate androgen-dependent phenotypes. (A) We exposed wild-type embryos to multiple androgens at different concentrations beginning at 3 h post-fertilization. We assayed embryo morphology at 2 and 3 days post-fertilization. We identified chemicals that caused morphological abnormalities. (B) We tested whether the phenotype was rescued in zebrafish with mutations in the nuclear androgen receptor gene (ar). If the phenotype was rescued, then the steroid acts via AR. (C) If the phenotype persisted in the nuclear ar mutant, then we tested zebrafish with mutations in membrane steroid receptors. To efficiently generate membrane androgen receptor mutants, we injected embryos with Cas9 and guide RNAs, exposed injected embryos to chemicals, and screened for phenotypes. After phenotypic screening, embryos were genotyped to determine mutation burden.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development