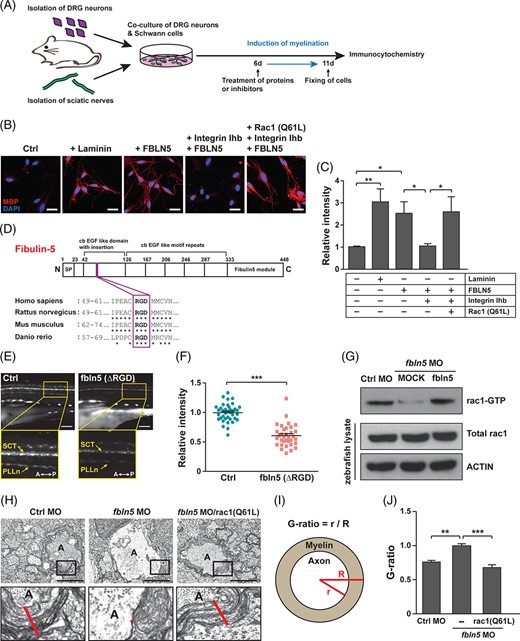
Fig. 5 FBLN5 regulates myelination through RAC1 activation in Schwann cells. A, A schematic diagram of the induction of axonal myelination by the co-culturing of mouse primary DRG neurons and Schwann cells isolated from sciatic nerves. The cells were treated with proteins or inhibitors at 6 days after co-cultivation and fixed for immunostaining 5 days after the treatment. B, Images of mouse primary Schwann cells immunostained with anti-MBP antibodies after co-cultivation with primary DRG neurons under the indicated conditions. Laminin-treated Schwann cells were a positive control of myelination-induced cells. Scale bars, 20 ?m. C, Quantification of the relative intensities of MBP staining in the images of (B). Statistical significance was determined using one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test (*P < .05, **P < .005). D, A schematic diagram of the human FBLN5 protein structure identifying the RGD motif conserved in rat, mouse, and zebrafish fbln5 protein. E, Lateral view images of the Tg(claudin K:gal4-vp16;uas:egfp) zebrafish injected with MOCK or fbln5 (?RGD) mRNAs at 5 dpf. The images within the rectangles are magnified in the bottom panels. SCT, spinal cord tracts; PLLn, posterior lateral line; A, anterior; P, posterior. Scale bars, 100 ?m. F, Quantification of the relative intensity of PLLn in equivalent fields of view in the images of (E). The data are shown as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments with ?20 embryos per condition. Statistical significance was determined using unpaired Student's t-test with Welch's correction (***P < .001). G, Results of pull-down assay for active rac1 in the indicated zebrafish tissues using PAK-PBP beads. Protein levels were normalized against ?-actin in the same blots. H, TEM images of cross-sectioned zebrafish of the indicated genotype at 5 dpf. The images within the rectangles are magnified in the bottom panels. The red lines indicate the thicknesses of the myelin sheaths in the Mauthner axons. A, axon. Scale bars, 2 ?m. I, A schematic diagram of how the G-ratio is obtained: the G-ratio is calculated by dividing the radius of the axon (r) by the total radius of the axon and myelin (R). J, Quantification of G-ratios calculated in the Mauthner axons of the indicated zebrafish. Statistical significance was determined using one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's post hoc test (**P < .005, ***P < .001). The data are shown as the mean ± SD (C, F, J)
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Stem Cells