Fig. 2
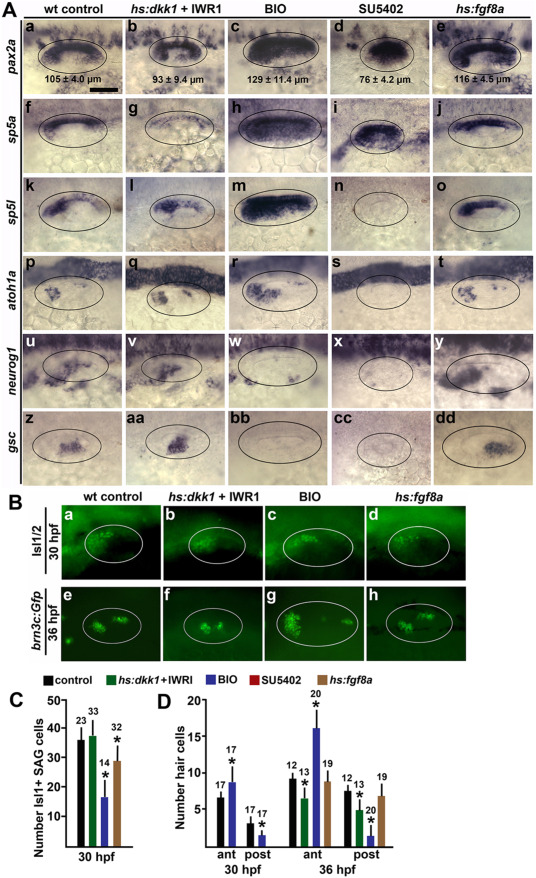
Fig. 2 Effects of altered Wnt and Fgf signaling on sensory-neural patterning in the otic vesicle. (A) Dorsolateral views (anterior to the left) showing expression of otic markers of the medial wall, sensory epithelia and neurogenic domains (indicated on the left) at 24 hpf following treatments to alter Wnt and Fgf signaling at 12 hpf. Oval marquees encircle the otic vesicle. Mean anteroposterior length of the otic vesicle (ąSD, n ?? ?8) is indicated in images of pax2a expression (Aa-e). Scale bar (Aa), 50 ??m. (B) Dorsolateral views of anti-Isl1/2 stained SAG neurons at 30 hpf (a?d) and brn3c:Gfp ?+ ?hair cells at 36 hpf (e?h) under the indicated conditions. (C, D) Quantification of the effects of signal modulation under conditions indicated by the key at the top. Mean values with errors (standard deviations) and sample sizes are indicated for each group. Asterisks indicate significant differences relative to controls. (C) Mean number of anti-Isl1/2 stained SAG neurons at 30 hpf. (D) Mean number of brn3c:gfp ?+ ?hair cells in the anterior and posterior sensory epithelia at 30 and 36 hpf.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 492, Tan, A.L., Mohanty, S., Guo, J., Lekven, A.C., Riley, B.B., Pax2a, Sp5a and Sp5l act downstream of Fgf and Wnt to coordinate sensory-neural patterning in the inner ear, 139-153, Copyright (2022) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.